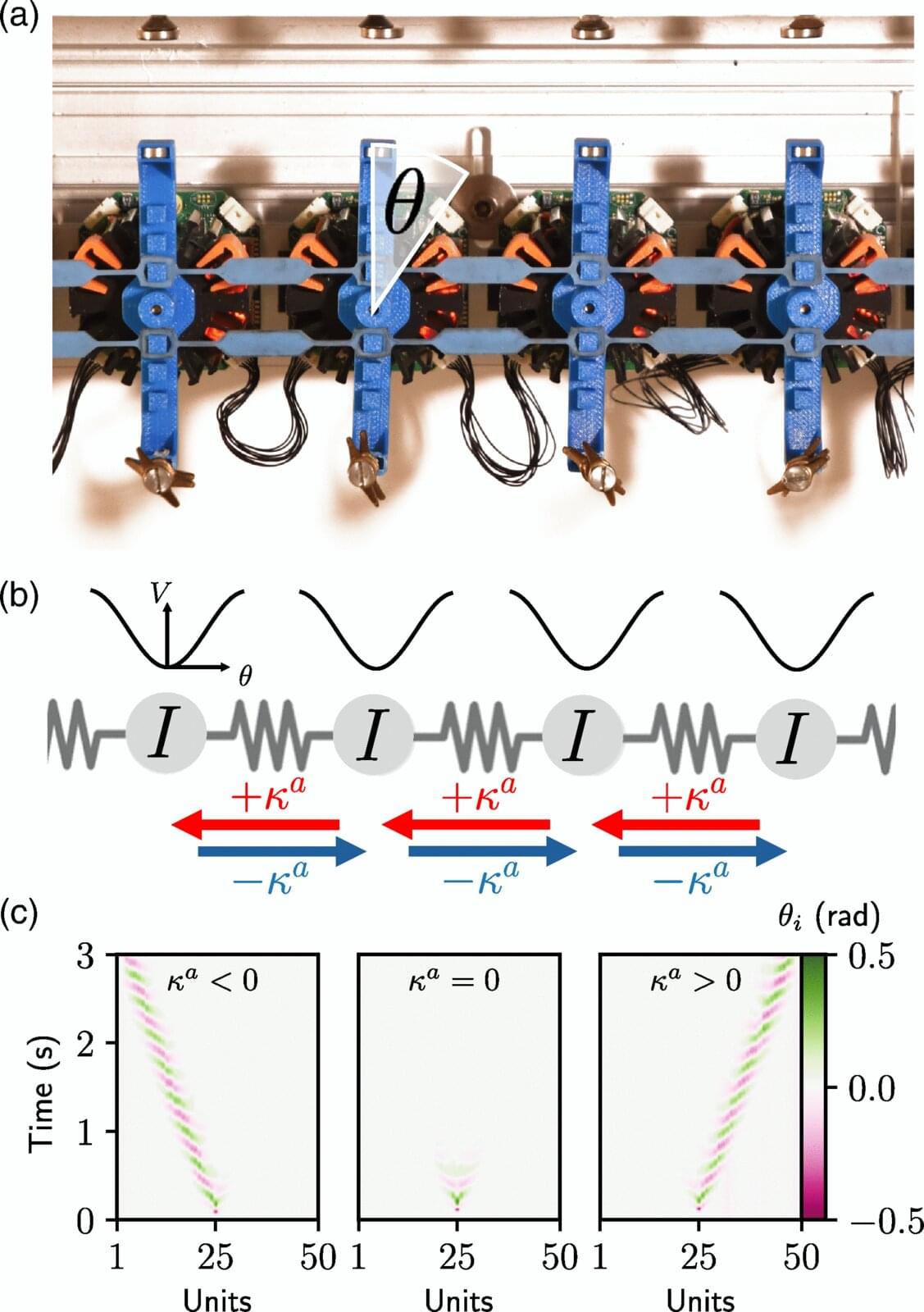
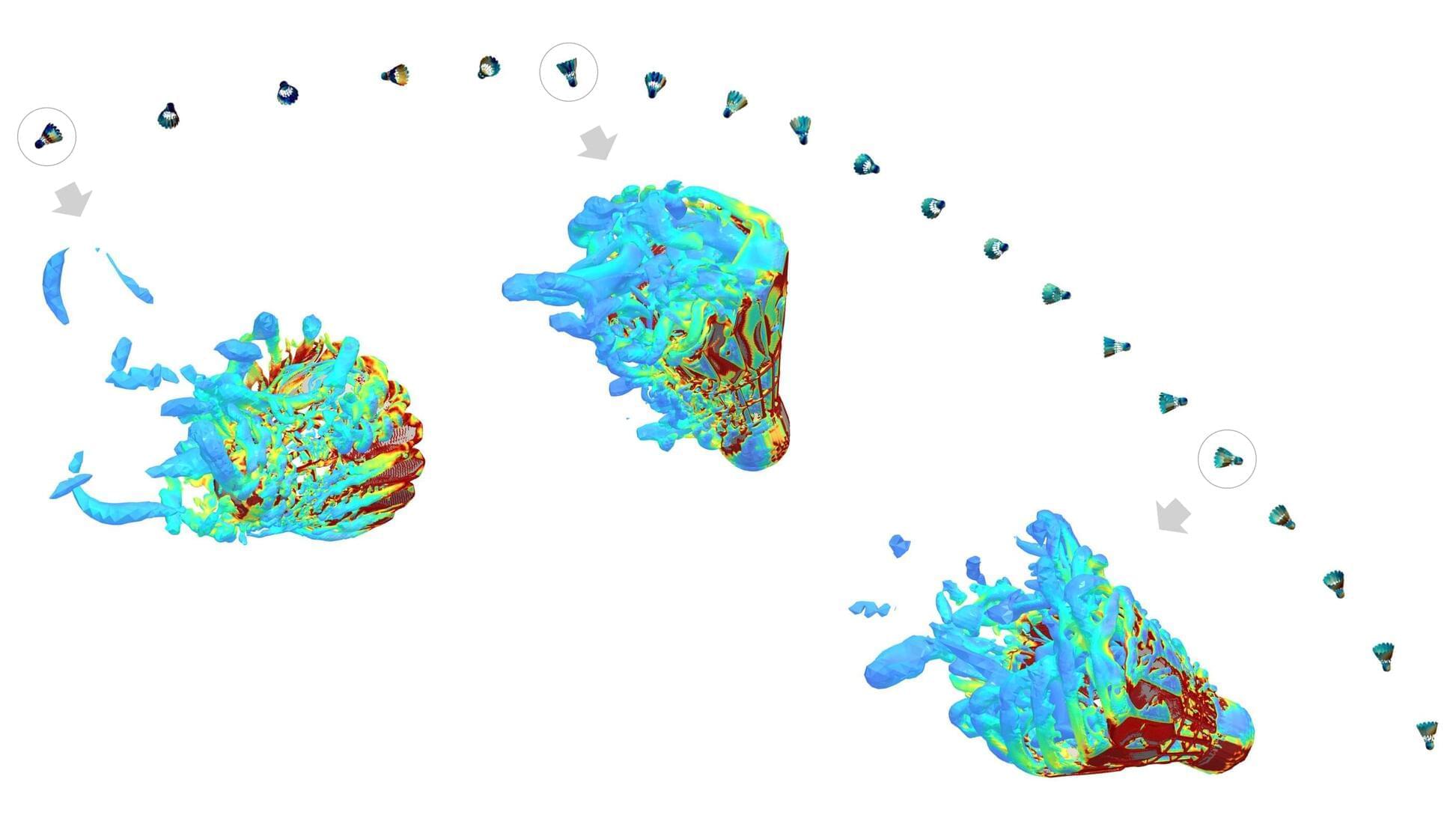
Solitonic waves—waves that keep their shape and direction of motion for a long time—have intrigued physicists for almost two centuries. In real-world circumstances, these waves eventually die out due to energy loss. A team of UvA physicists have now discovered how a particular type of interaction can be used to create very stable solitons, even in circumstances where energy is not conserved.
In 1834, John Scott Russell observed an unusual phenomenon in the Union Canal in Scotland. After a moving boat had come to a halt, the water wave that the boat had caused continued moving through the canal, keeping virtually the same speed and the same shape.
It took more than half a century, until the work of Dutch mathematicians Diederik Korteweg and Gustav de Vries in 1895, before the phenomenon that Russell observed had been explained in all its mathematical detail. What Russell had seen was a “solitary wave,” a phenomenon now better known as a soliton.