An undersea volcano off the southeastern coast of the Big Island of Hawaii has been rocked by a swarm of more than 70 earthquakes since the weekend, according to the U.S. Geological Survey.
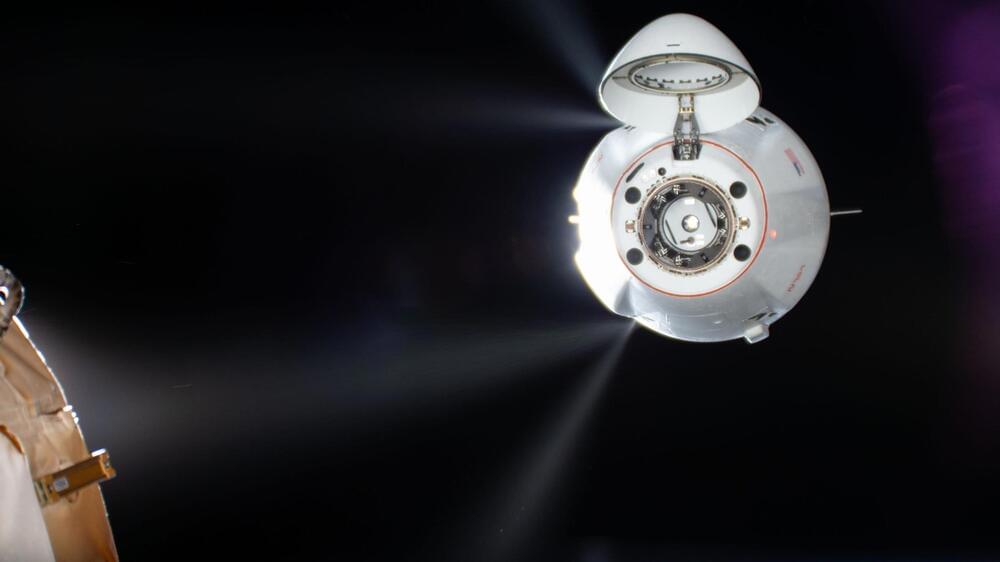





At 9:52 a.m. EST, the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft successfully docked to the forward port of the International Space Stations Harmony module.
This mission, SpaceX’s 31st commercial resupply service for NASA, delivered over 6,000 pounds of scientific equipment and cargo to the space station. The journey began at 9:29 a.m. on November 4, when a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launched from Launch Complex 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

When considering the potential for life on exoplanets, scientists often focus on the habitable zone, the region around a star where conditions might allow liquid water to exist. However, new research suggests that this concept alone oversimplifies the dangers these planets face. It’s not just about being in the right place; it’s also about avoiding interstellar chaos.
While identifying exoplanets in the habitable zone is a crucial step in the search for extraterrestrial life, their environments can be treacherous. In a study soon to be published in The Astronomical Journal, researchers led by Tisyagupta Pyne from Visva-Bharati University highlight the threats lurking in dense stellar neighborhoods. Stellar flybys and catastrophic supernovae explosions have the power to disrupt entire planetary systems, stripping atmospheres or ejecting planets into interstellar space.
Advancements in nuclear physics may soon enable the creation of stable, superheavy nuclei, paving the way for new materials and insights into atomic stability.
A team of scientists has made significant advancements in the quest to create new, long-lasting superheavy nuclei. These double magic nuclei, which have a precise number of protons and neutrons that form a highly stable configuration, are exceptionally resistant to decay. Their research could deepen our understanding of the forces that bind atoms and pave the way for the development of new materials with unique properties. This work brings us a step closer to the so-called “Island of Stability,” a theoretical region in the nuclei chart where it’s believed some nuclei could exist far longer than those created so far.
The study, led by Professor Feng-Shou Zhang, has predicted promising reactions between different elements that could be used in experiments to create double magic nuclei. One key discovery involves a reaction between a special type of radioactive calcium isotope and a plutonium target, which could produce the predicted double magic nuclei 298 Fl. Another potential double magic nuclei, 304 120, could be created by combining vanadium and berkelium, although this reaction is currently less likely to succeed.
This development comes from…
Researchers have designed a high-speed 3D bioprinter to accurately print human tissues.
Interestingly, this advanced bioprinter is capable of fabricating a diverse array of tissues, including both soft brain tissue and harder materials such as cartilage and bone.
This development comes from biomedical engineers from the University of Melbourne.
Remember to watch part 1: https://youtu.be/tANAl15CCLE
Welcome to the year 2,324, where humanity has transcended its Earthly origins to build civilizations across the solar system. Mars, Titan, and even the clouds of Venus are now home to more than 2.5 billion people, thanks to anti-aging technologies and AI-driven advancements. But how did we get here? And what does life look like in this brave new world? In this continuation of my speculative future series, I explore the political structures, societal shifts, and technological innovations that define our interplanetary existence. Get ready for a journey through a transformed solar system!
Like, comment, and subscribe to join me in imagining our cosmic future!
Credit to ‘StolenMadWolf’ for creating the collection that several of the solar system flags in this video are based on: https://www.deviantart.com/stolenmadwolf/gallery/82886572/sol-flag-collection
The discovery of pyrene in this far-off cloud, which is similar to the collection of dust…
A team led by researchers at MIT has discovered that a distant interstellar cloud contains an abundance of pyrene, a type of large, carbon-containing molecule known as a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH).
The discovery of pyrene in this far-off cloud, which is similar to the collection of dust and gas that eventually became our own solar system, suggests that pyrene may have been the source of much of the carbon in our solar system. That hypothesis is also supported by a recent finding that samples returned from the near-Earth asteroid Ryugu contain large quantities of pyrene.
“One of the big questions in star and planet formation is: How much of the chemical inventory from that early molecular cloud is inherited and forms the base components of the solar system? What we’re looking at is the start and the end, and they’re showing the same thing. That’s pretty strong evidence that this material from the early molecular cloud finds its way into the ice, dust, and rocky bodies that make up our solar system,” says Brett McGuire, an assistant professor of chemistry at MIT.