Andrew Cassy had spent his working life in a telecommunications research department until a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease in 2010 pushed him into early retirement. Curious about his illness, which he came to think of as an engineering problem, he decided to volunteer for clinical trials.
“I had time, something of value that I could give to the process of understanding the disease and finding good treatments,” he says.
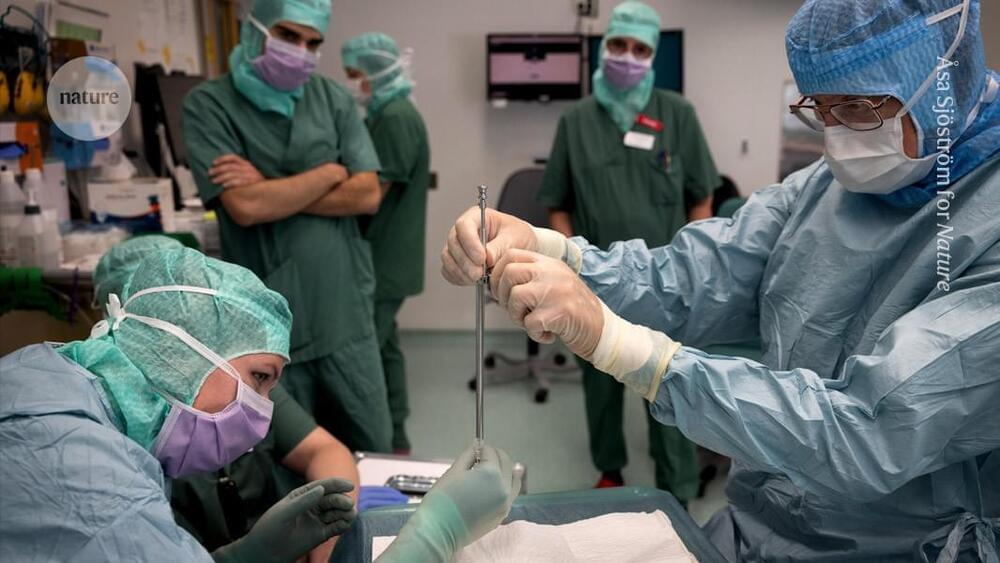
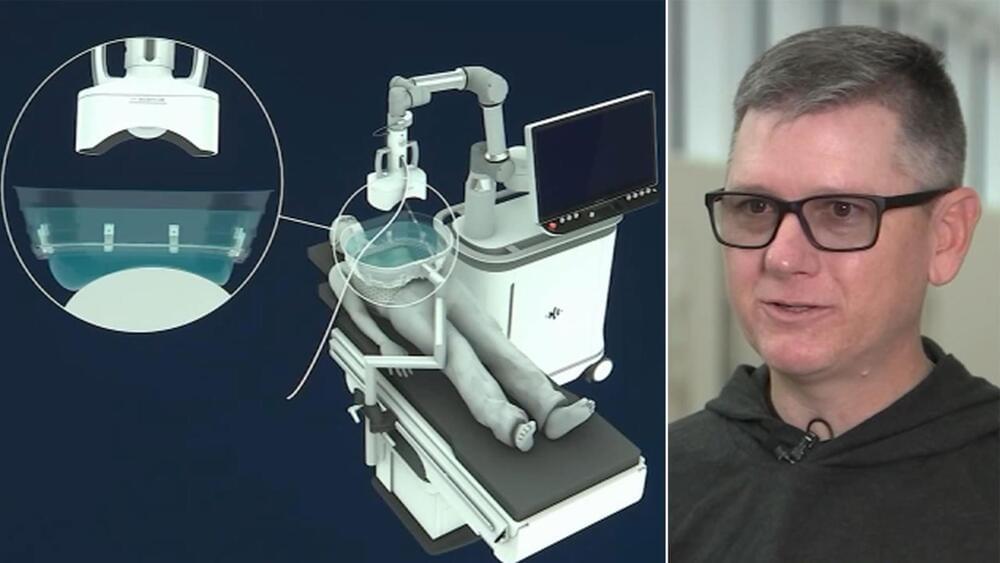
In 2024, he was accepted into a radical trial. That October, surgeons in Lund, Sweden, placed neurons that were derived from human embryonic stem (ES) cells into his brain. The hope is that they will eventually replace some of his damaged tissue.
The study is one of more than 100 clinical trials exploring the potential of stem cells to replace or supplement tissues in debilitating or life-threatening diseases, including cancer, diabetes, epilepsy, heart failure and some eye diseases. It’s a different approach from the unapproved therapies peddled by many shady clinics, which use types of stem cell that do not turn into new tissue.
More than 100 clinical trials put stem cells for regenerative medicine to the test. It’s a turning point for a field beset with ethical and political controversy.