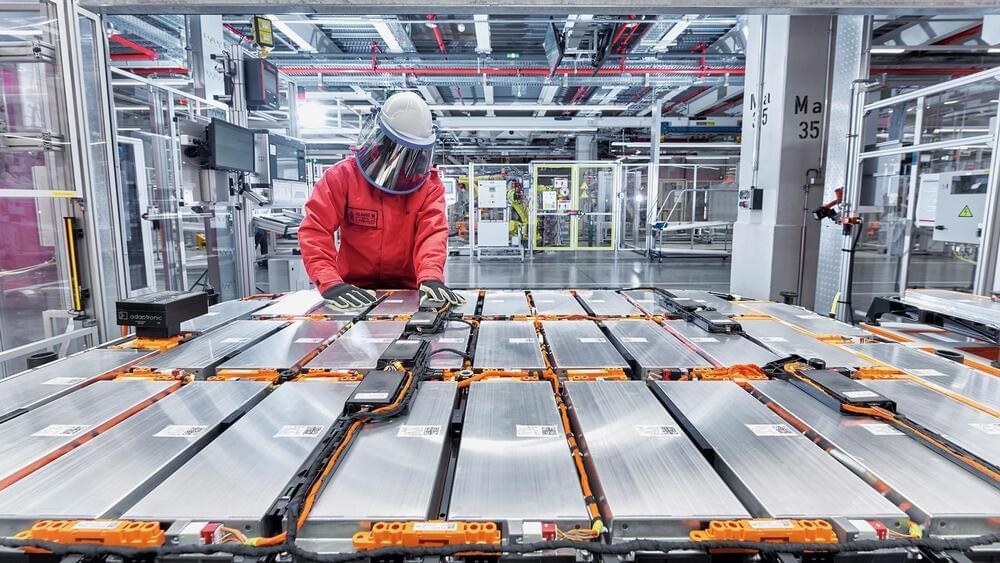
That will get battery costs below the point needed to achieve EV price parity with gasoline vehicles.



Coming out of stealth, cybersecurity startup Twine announced today $12 million in seed funding, co-led by Ten Eleven Ventures and Dell Technologies Capital, with participation from angel investors including the founders of Wiz. Twine plans to address cybersecurity’s critical talent shortage by developing AI agents or “digital employees” to augment companies’ security teams. Alex, Twine’s first digital employee, is an expert in identity and access management or IAM.
Alex is deployed as a SaaS platform, connecting to different systems within the customer’s environment. “The user interacts with the Alex interface in order to ask him questions or assign tasks,” explains Benny Porat, Twine’s co-founder and CEO. “For any task assigned, Alex creates a plan, seeks approval, provides full visibility, and proceeds with an A-to-Z execution of the plan.”
In a report published a few months ago, the World Economic Forum warned that the “cybersecurity industry faces a critical global shortage of nearly 4 million professionals.” This at a time when the rapid adoption of cloud computing, remote work and new AI solutions has significantly increased the number of cyber attacks.


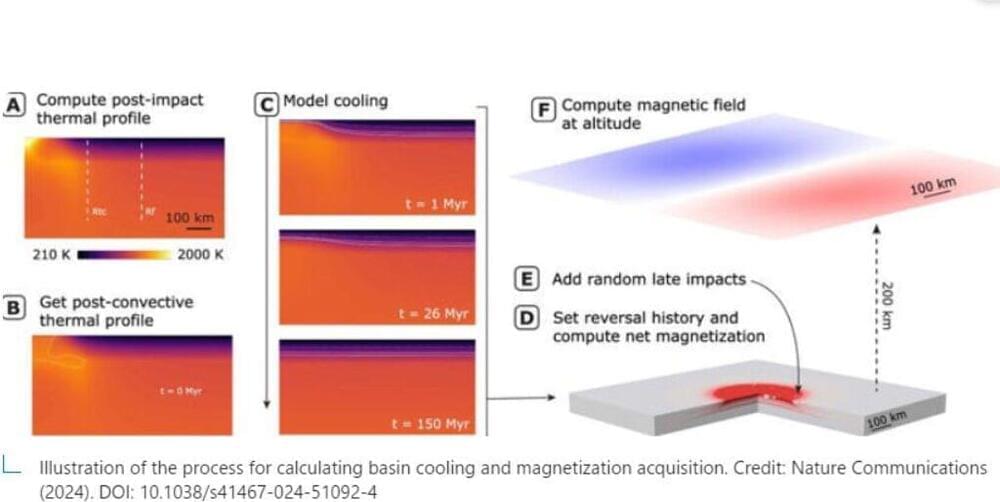
Evidence suggests Mars could very well have been teeming with life billions of years ago. Now cold, dry, and stripped of what was once a potentially protective magnetic field, the red planet is a kind of forensic scene for scientists investigating whether Mars was indeed once habitable, and if so, when.
The “when” question in particular has driven researchers in Harvard’s Paleomagnetics Lab in the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences. A new paper in Nature Communications makes their most compelling case to date that Mars’ life-enabling magnetic field could have survived until about 3.9 billion years ago, compared with previous estimates of 4.1 billion years—so hundreds of millions of years more recently.
The study was led by Griffin Graduate School of Arts and Sciences student Sarah Steele, who has used simulation and computer modeling to estimate the age of the Martian “dynamo,” or global magnetic field produced by convection in the planet’s iron core, like on Earth. Together with senior author Roger Fu, the John L. Loeb Associate Professor of the Natural Sciences, the team has doubled down on a theory they first argued last year that the Martian dynamo, capable of deflecting harmful cosmic rays, was around longer than prevailing estimates claim.
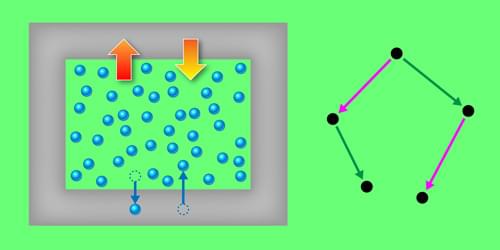
The identification of a new type of symmetry in statistical mechanics could help scientists derive and interpret fundamental relationships in this branch of physics.
Symmetry is a foundational concept in physics, describing properties that remain unchanged under transformations such as rotation and translation. Recognizing these invariances, whether intuitively or through complex mathematics, has been pivotal in developing classical mechanics, the theory of relativity, and quantum mechanics. For example, the celebrated standard model of particle physics is built on such symmetry principles. Now Matthias Schmidt and colleagues at the University of Bayreuth, Germany, have identified a new type of invariance in statistical mechanics (the theoretical framework that connects the collective behavior of particles to their microscopic interactions) [1]. With this discovery, the researchers offer a unifying perspective on subtle relationships between observable properties and provide a general approach for deriving new relations.
The concept of conserved, or time-invariant, properties has roots in ancient philosophy and was crucial to the rise of modern science in the 17th century. Energy conservation became a cornerstone of thermodynamics in the 19th century, when engineers uncovered the link between heat and work. Another important type of invariance is Galilean invariance, which states that the laws of physics are identical in all reference frames moving at a constant velocity relative to each other, resulting in specific relations between positions and velocities in different frames. Its extension, Lorentz invariance, posits that the speed of light is independent of the reference frame. Einstein’s special relativity is based on Lorentz invariance, while his general relativity broadens the idea to all coordinate transformations. These final examples illustrate that invariance not only provides relations between physical observables but can shape our understanding of space, time, and other basic concepts.
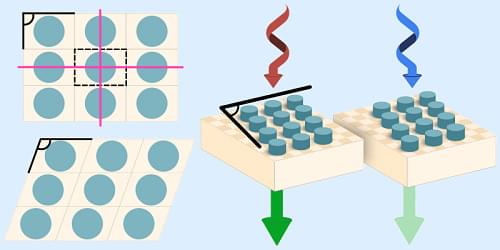
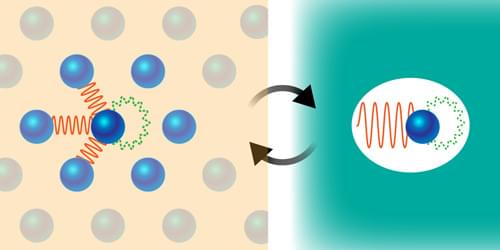
A new framework that embeds electrons in a surrounding bath captures nonlocal correlation effects that are relevant to metals, semiconductors, and correlated insulators.
Searching for new types of superconductors, magnets, and other useful materials is a bit like weaving a tapestry with threads of many different colors. The weaver selects a short-range (local) pattern for how the individual threads intertwine and at the same time chooses colors that will give an overall (nonlocal) mood. A materials scientist works in a similar way, mixing atoms instead of threads, trying to match the motion of their electrons—their correlations—on both local and nonlocal scales. Doing so by trial-and-error synthesis is time intensive and costly, and therefore numerical simulations can be of huge help. To contribute to bridging computations to material discovery, Jiachen Li and Tianyu Zhu from Yale University have developed a new approach that treats local and nonlocal electronic correlations on an equal footing [1] (Fig. 1). They demonstrated their method by accurately predicting the photoemission spectra of several representative materials.