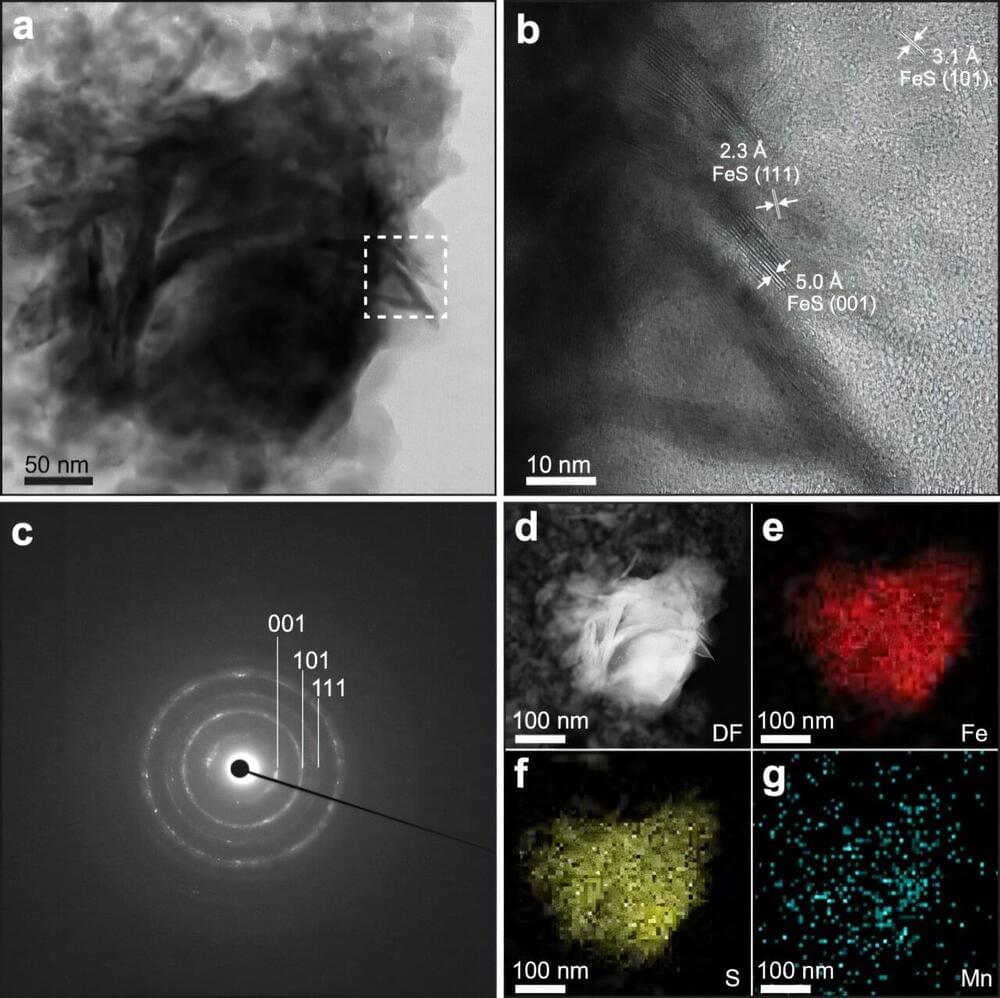
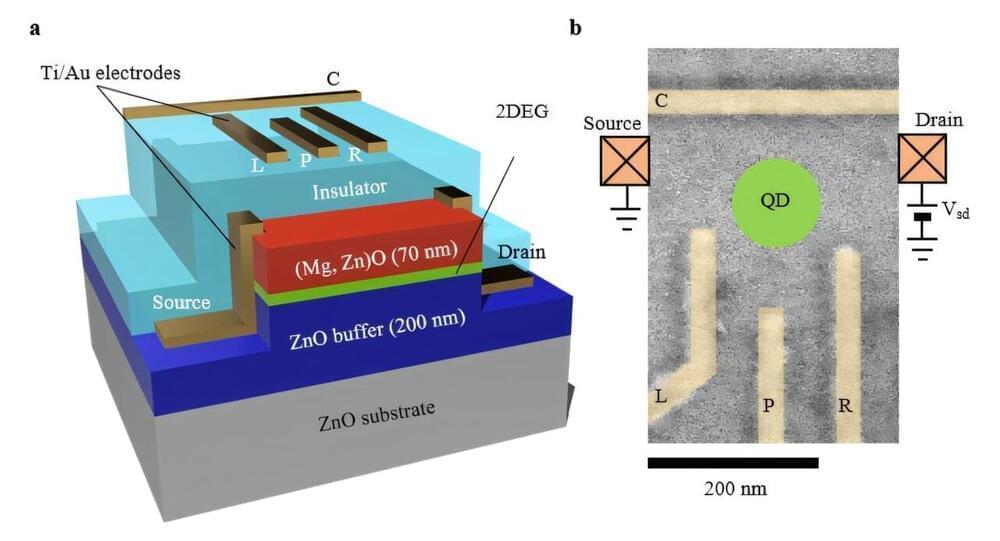
A quiet revolution is brewing in labs around the world, where scientists’ use of AI is growing exponentially. One in three postdocs now use large language models to help carry out literature reviews, coding, and editing. In October, the creators of our AlphaFold 2 system, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper became Nobel Laureates in Chemistry for using AI to predict the structure of proteins, alongside the scientist David Baker, for his work to design new proteins. Society will soon start to feel these benefits more direct ly, with drugs and materials designed with the help of AI currently making their way through development.
In this essay, we take a tour of how AI is transforming scientific disciplines from genomics to computer science to weather forecasting. Some scientists are training their own AI models, while others are fine-tuning existing AI models, or using these models’ predictions to accelerate their research. Scientists are using AI as a scientific instrument to help tackle important problems, such as designing proteins that bind more tightly to disease targets, but are also gradually transforming how science itself is practised.
There is a growing imperative behind scientists’ embrace of AI. In recent decades, scientists have continued to deliver consequential advances, from Covid-19 vaccines to renewable energy. But it takes an ever larger number of researchers to make these breakthroughs, and to transform them into downstream applications. As a result, even though the scientific workforce has grown significantly over the past half-century, rising more than seven fold in the US alone, the societal progress that we would expect to follow, has slowed. For instance, much of the world has witnessed a sustained slowdown in productivity growth that is undermining the quality of public services. Progress towards the 2030 Sustainable Development Goals, which capture the biggest challenges in health, the environment, and beyond, is stalling.