Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

No teachers, no homework: School solely uses AI to teach students
A school in Texas is revolutionizing the way students learn by going all-in on artificial intelligence. Its leaders are using the technology to educate students without the help of a traditional teacher. NBC’s Gadi Schwartz reports for TODAY.
» Subscribe to TODAY: / @today.
About: TODAY brings you the latest headlines and expert tips on money, health and parenting. We wake up every morning to give you and your family all you need to start your day. If it matters to you, it matters to us. We are in the people business. Subscribe to our channel for exclusive TODAY archival footage \& our original web series.
Connect with TODAY Online!
Visit TODAY’s Website: https://www.today.com/
Find TODAY on Facebook: / today.
Follow TODAY on Twitter: / todayshow.
Follow TODAY on Instagram: / todayshow.
» Stream TODAY All Day: https://www.today.com/allday.
About: TODAY All Day is a 24/7 streaming channel bringing you the top stories in news and pop culture, celebrity interviews, cooking, and more. All in one place.
#ai #parenting #school

Intelligence at the Edge of Chaos
Abstract: We explore the emergence of intelligent behavior in artificial systems by investigating how the complexity of rule-based systems influences the capabilities of models trained to predict these rules. Our study focuses on elementary cellular automata (ECA), simple yet powerful one-dimensional systems that generate behaviors ranging from trivial to highly complex. By training distinct Large Language Models (LLMs) on different ECAs, we evaluated the relationship between the complexity of the rules’ behavior and the intelligence exhibited by the LLMs, as reflected in their performance on downstream tasks. Our findings reveal that rules with higher complexity lead to models exhibiting greater intelligence, as demonstrated by their performance on reasoning and chess move prediction tasks. Both uniform and periodic systems, and often also highly chaotic systems, resulted in poorer downstream performance, highlighting a sweet spot of complexity conducive to intelligence. We conjecture that intelligence arises from the ability to predict complexity and that creating intelligence may require only exposure to complexity.
From: Shiyang Zhang [view email].


Rutgers Professor Cracks Two of Mathematics’ Greatest Mysteries
A distinguished mathematics professor at Rutgers, has resolved two critical problems in mathematics that have puzzled experts for decades.
He tackled the 1955 Height Zero Conjecture and made significant advancements in the Deligne-Lusztig theory, enhancing theoretical applications in several sciences.
A Rutgers University-New Brunswick professor, dedicated to unraveling the mysteries of higher mathematics, has resolved two separate, fundamental problems that have baffled mathematicians for decades.
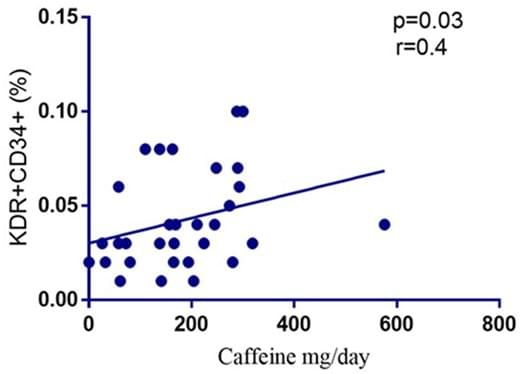
Caffeine improves systemic lupus erythematosus endothelial dysfunction by promoting endothelial progenitor cells survival
Researchers from the Sapienza University of Rome found that caffeine has a positive effect on endothelial cells, a group of cells responsible for vascular regeneration.
We studied the role of caffeine intake on endothelial function in SLE by assessing its effect on circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) both ex vivo in SLE patients and in vitro in healthy donors (HD) treated with SLE sera.
Methods.
We enrolled SLE patients without traditional cardiovascular risks factors. Caffeine intake was evaluated with a 7-day food frequency questionnaire. EPCs percentage was assessed by flow cytometry analysis and, subsequently, EPCs pooled from six HD were co-cultured with caffeine with and without SLE sera. After 7 days, we evaluated cells’ morphology and ability to form colonies, the percentage of apoptotic cells by flow cytometry analysis and the levels of autophagy and apoptotic markers by western blot. Finally, we performed a western blot analysis to assess the A2AR/SIRT3/AMPK pathway.
Newly Discovered Protein Complex Shapes Synapses and Mental Health
Summary: Researchers have identified a protein complex, TrkC-PTPσ, that plays a key role in the structural organization of synapses in the brain, impacting cognitive behaviors. By studying this complex, scientists uncovered how it regulates synaptic protein phosphorylation, essential for healthy brain function. Disruptions in this protein complex led to anxiety-like behaviors in mice, providing insights into mental health conditions like anxiety and autism.
The study sheds light on synaptic mechanisms that could help develop new therapeutic strategies. These findings advance our understanding of synapse function and its role in cognitive disorders, bringing hope for targeted treatment options in the future.
