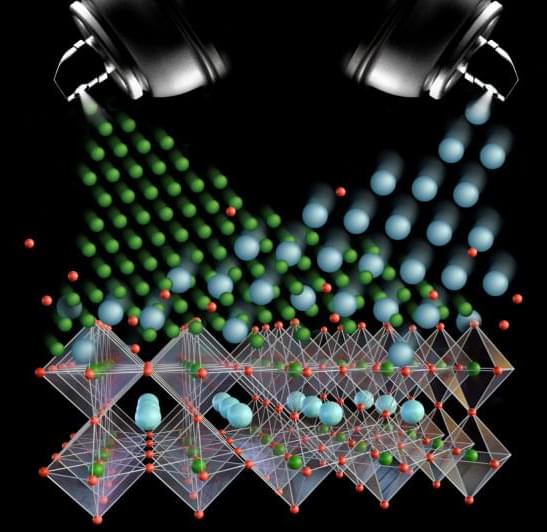
What’s the best way to precisely manipulate a material’s properties to the desired state? It may be straining the material’s atomic arrangement, according to a team led by researchers at Penn State. The team discovered that “atomic spray painting” of potassium niobate, a material used in advanced electronics, could tune the resulting thin films with exquisite control.
The finding, published in Advanced Materials (“Colossal Strain Tuning of Ferroelectric Transitions in KNbO 3 Thin Films”), could drive environmentally friendly advancements in consumer electronics, medical devices and quantum computing, the researchers said.
The process, called strain tuning, alters a material’s properties by stretching or compressing its atomic unit cell, which is the repeating motif of atoms that builds up its crystal structure. The researchers use molecular beam epitaxy (MBE), a technique that involves depositing a layer of atoms on a substrate to form a thin film. In this case, they produced a thin film of strain-tuned potassium niobate.