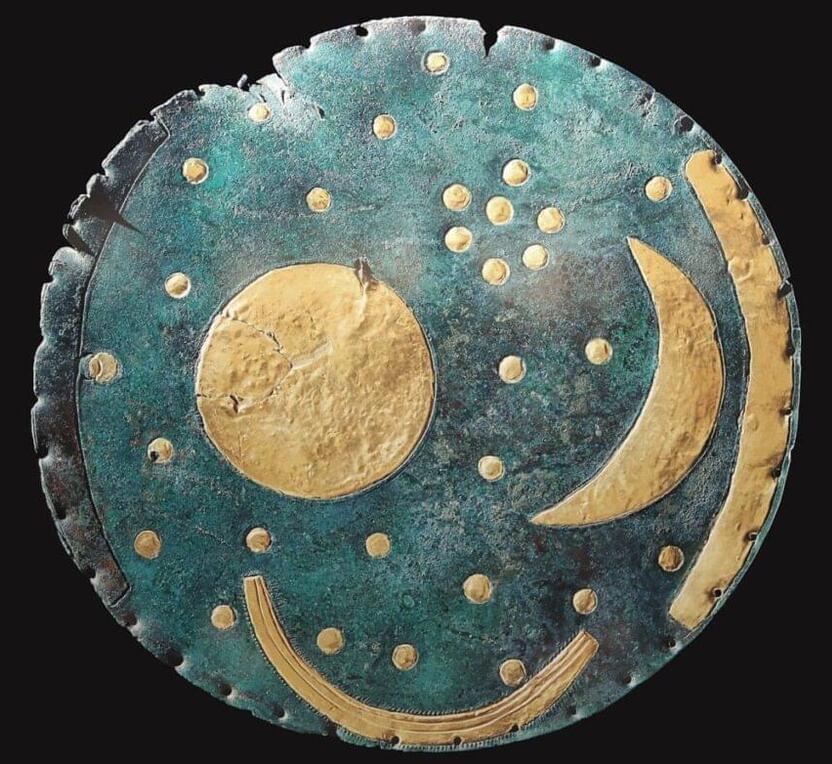
Discovered in 1999 in Germany, the Nebra Sky Disc is the oldest known depiction of the cosmos. A recent examination of the Bronze Age artifact revealed the intricate methods used in its creation, which UNESCO described as “one of the most important archaeological finds of the twentieth century.”
The Nebra Sky Disc is a product of the Únětice culture, which originated in the Bronze Age of Central Europe. It reflects a sophisticated ancient understanding of both metalworking and astronomy and was created sometime between 1800 and 1,600 BCE. Clusters of stars, a sun, and a crescent moon are among the celestial bodies depicted by golden inlays covering the blue-green patina of the Nebra Sky Disc. The angle between the solstices is thought to be indicated by two golden arcs that run along the sides of the disc, one of which is now absent. It is thought that a boat is represented by another arc at the composition’s base. Only a few millimeters thick, the disc has a diameter of around 12 inches.
The Nebra Sky Disc is one of the best-investigated archaeological objects. The origin of the raw materials it is made of is well known The disc is made from copper, tin, and gold—materials whose origins have been traced to Cornwall, England. The rich blue-green patina of the disc’s bronze today results from chemical changes over time. Originally, it would have been a deep bronze hue.