Self replicating alien probes.
Found on Google from phys.org
Self replicating alien probes.
Found on Google from phys.org
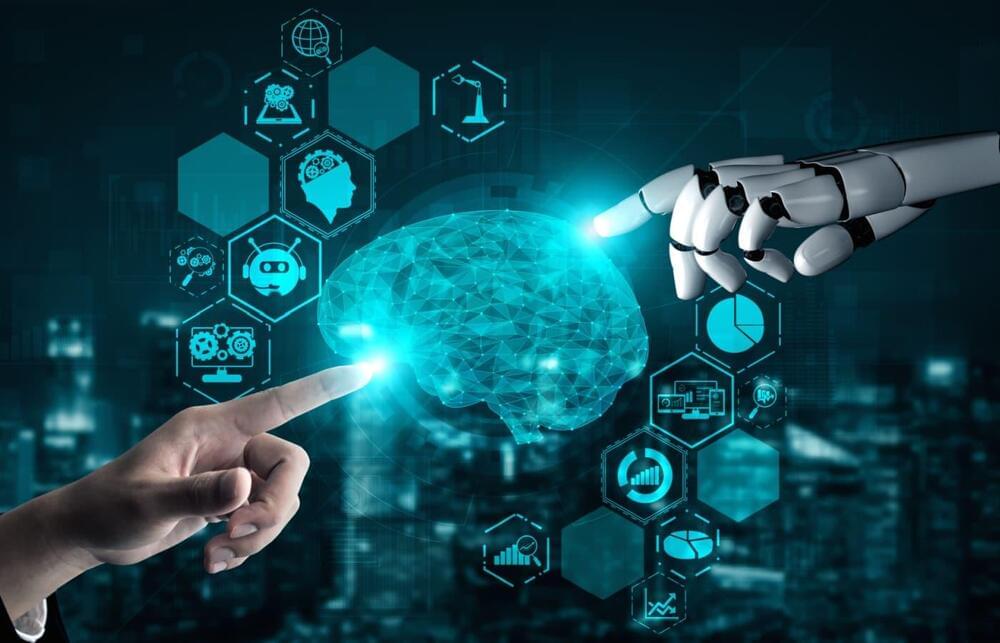

Google DeepMind has announced an impressive grab bag of new products and prototypes that may just let it seize back its lead in the race to turn generative artificial intelligence into a mass-market concern.
Top billing goes to Gemini 2.0—the latest iteration of Google DeepMind’s family of multimodal large language models, now redesigned around the ability to control agents—and a new version of Project Astra, the experimental everything app that the company teased at Google I/O in May.
MIT Technology Review got to try out Astra in a closed-door live demo last week. It was a stunning experience, but there’s a gulf between polished promo and live demo.
Google just launched a ton of new products—including Gemini 2.0, which could power a new world of agents. And we got a first look.

To predict your #longevity, you have two main options. You can rely on the routine tests and measurements your doctor likes to order for you, such as blood pressure, cholesterol levels, weight, and so on. Or you can go down a biohacking rabbit hole the way tech millionaire turned longevity guru Bryan Johnson did to live longer. Johnson’s obsessive self-measurement protocol involves tracking more than a hundred biomarkers, ranging from the telomere length in blood cells to the speed of his urine stream (which, at 25 milliliters per second, he reports, is in the 90th percentile of 40-year-olds).
Scientists crunched the numbers to come up with the single best predictor of how long you’ll live—and arrived at a surprisingly low-tech answer.
One year of treatment with the targeted drug olaparib improves long-term survival in women with high-risk, early-stage breast cancer with mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes, new results from a major clinical trial show.
Ten years since the first patient was recruited, new findings from the phase III OlympiA trial – presented at San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2024 – show that adding olaparib to standard treatment cuts the risk of cancer coming back by 35 per cent, and the risk of women dying by 28 per cent.
After six years, 87.5 per cent of patients who were treated with the drug were still alive compared with 83.2 per cent of those who were given the placebo pills.
Professor Andrew Tutt at The Institute of Cancer Research, London, and King’s College London is the global lead investigator and Chair of the Steering Committee for the OlympiA study, and was also involved in early laboratory research on PARP inhibitors such as olaparib, and their subsequent clinical development. The Breast International Group (BIG) coordinated the international OlympiA study, involving 671 study locations, globally across multiple partners. BIG coordinated the trial’s UK sites through the ICR Clinical Trials and Statistics Unit (ICR-CTSU).
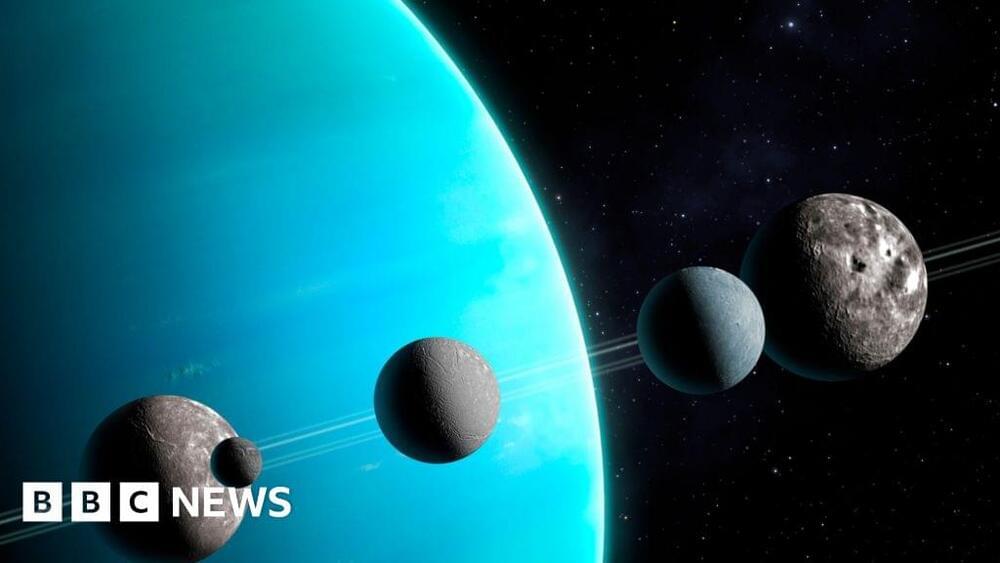

When people say moons and Uranus it is phonetically a bit nasty, but, even but sounds a bit strange.
Instead, they may have oceans, and the moons may even be capable of supporting life, scientists say. Much of what we know about them was gathered by NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft which visited nearly 40 years ago.
S visit coincided with a powerful solar storm, which led to a misleading idea of what the Uranian system is really like. +Uranus is a beautiful, icy ringed world in the outer reaches of our solar system. It is among the coldest of all the planets. It is also tilted on its side compared to all the other worlds – as if it had been knocked over – making it arguably the weirdest.
The planet Uranus and its five biggest moons may not be the dead sterile worlds that scientists have long thought.
Instead, they may have oceans, and the moons may even be capable of supporting life, scientists say.
Much of what we know about them was gathered by NASA’s Voyager 2 spacecraft which visited nearly 40 years ago.
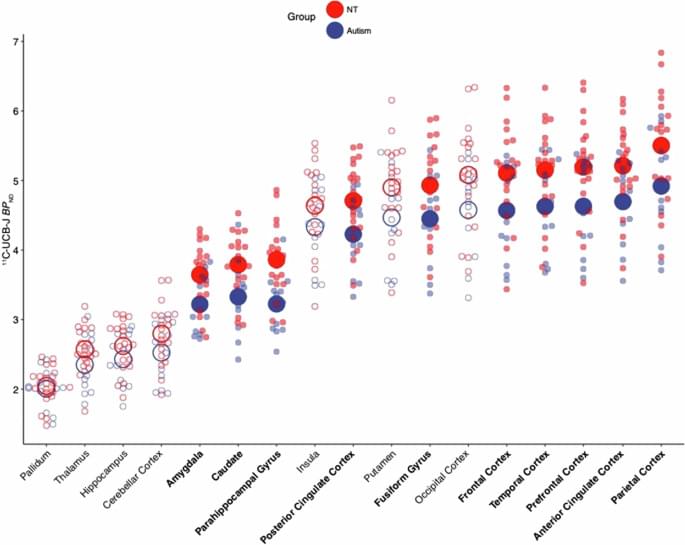
Matuskey, D., Yang, Y., Naganawa, M. et al. 11 C-UCB-J PET imaging is consistent with lower synaptic density in autistic adults. Mol Psychiatry (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-024-02776-2

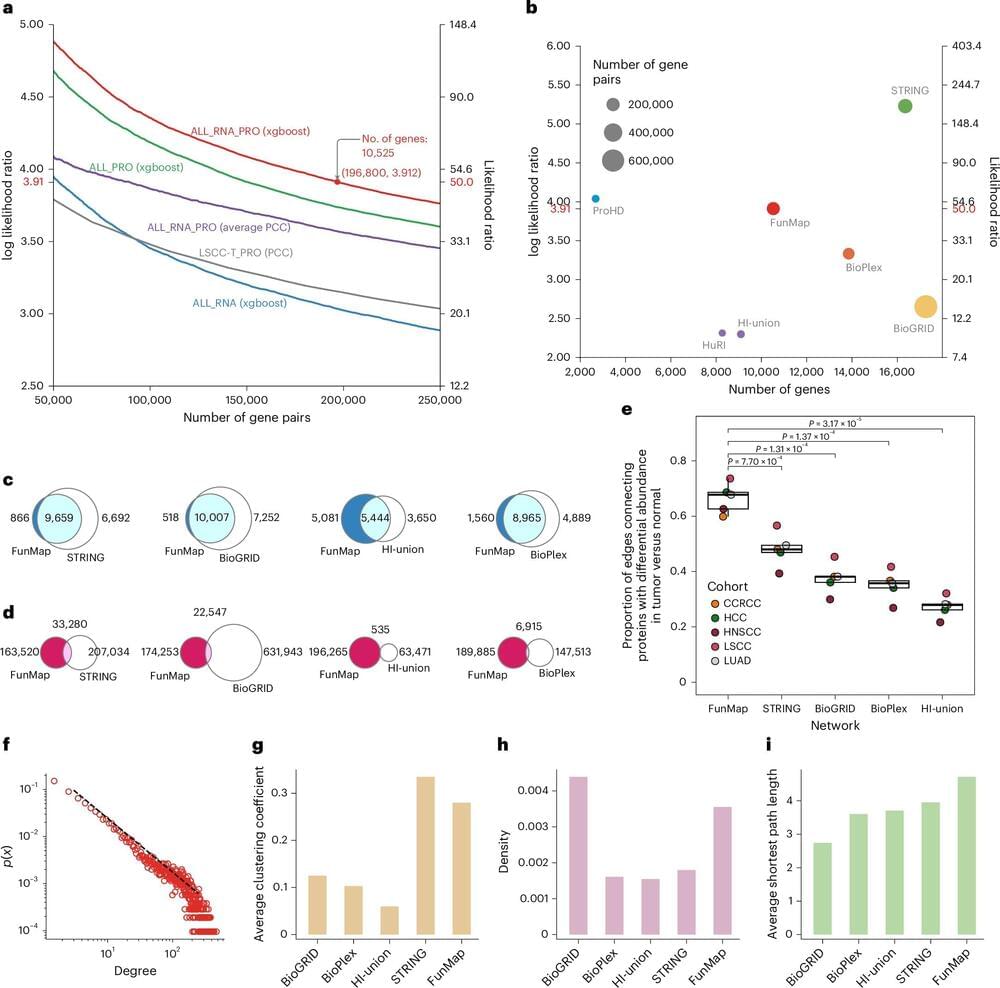
Large-scale protein and gene profiling have massively expanded the landscape of cancer-associated proteins and gene mutations, but it has been difficult to discern whether they play an active role in the disease or are innocent bystanders.
In a study published in Nature Cancer, researchers at Baylor College of Medicine revealed a powerful and unbiased machine learning-based approach called FunMap for assessing the role of cancer-associated mutations and understudied proteins, with broad implications for advancing cancer biology and informing therapeutic strategies.
“Gaining functional information on the genes and proteins associated with cancer is an important step toward better understanding the disease and identifying potential therapeutic targets,” said corresponding author Dr. Bing Zhang, professor of molecular and human genetics and part of the Lester and Sue Smith Breast Center at Baylor.