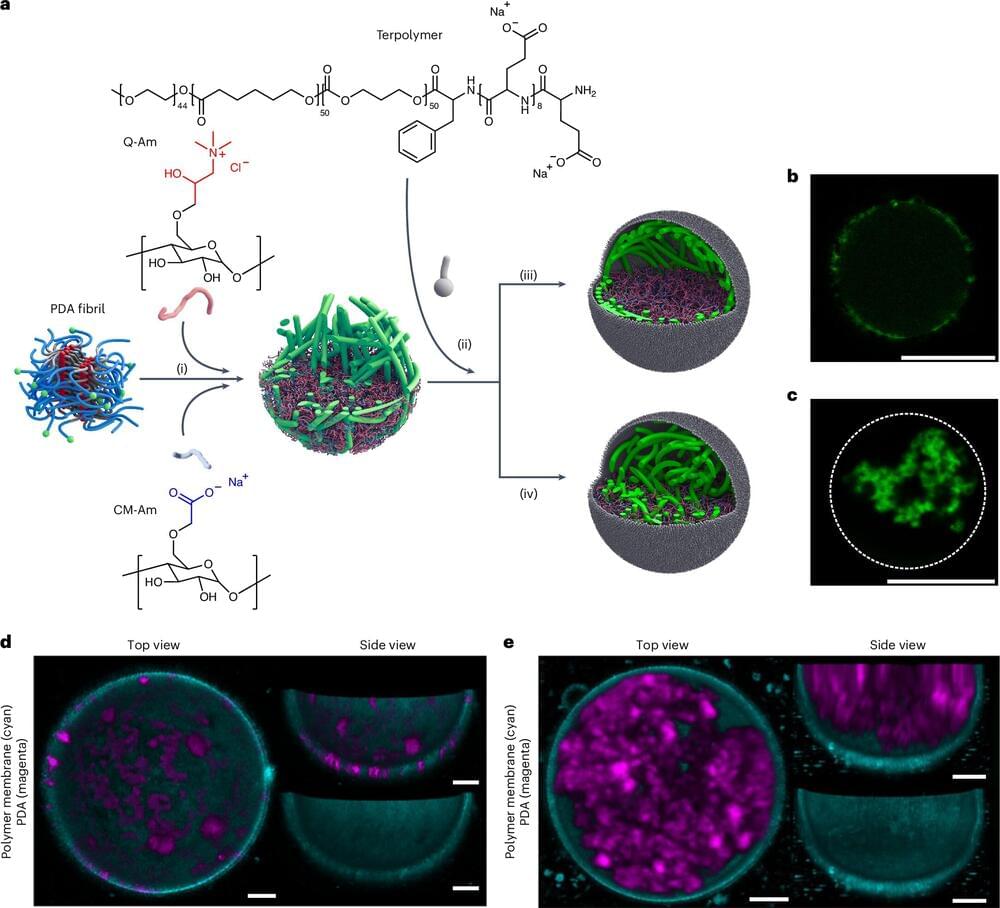
Just like your body has a skeleton, every cell in your body has a skeleton—a cytoskeleton to be precise. This provides cells with mechanical resilience, as well as assisting with cell division. To understand how real cells work, e.g. for drug and disease research, researchers create artificial cells in the laboratory.
However, many artificial cells to date cannot be used to study how cells respond to forces as they don’t have a cytoskeleton. TU/e researchers have designed a polymer-based network for artificial cells that mimics a real cytoskeleton, thus making it possible to study with greater accuracy in artificial cells how cells respond to forces.
The research is published in the journal Nature Chemistry.