Link :
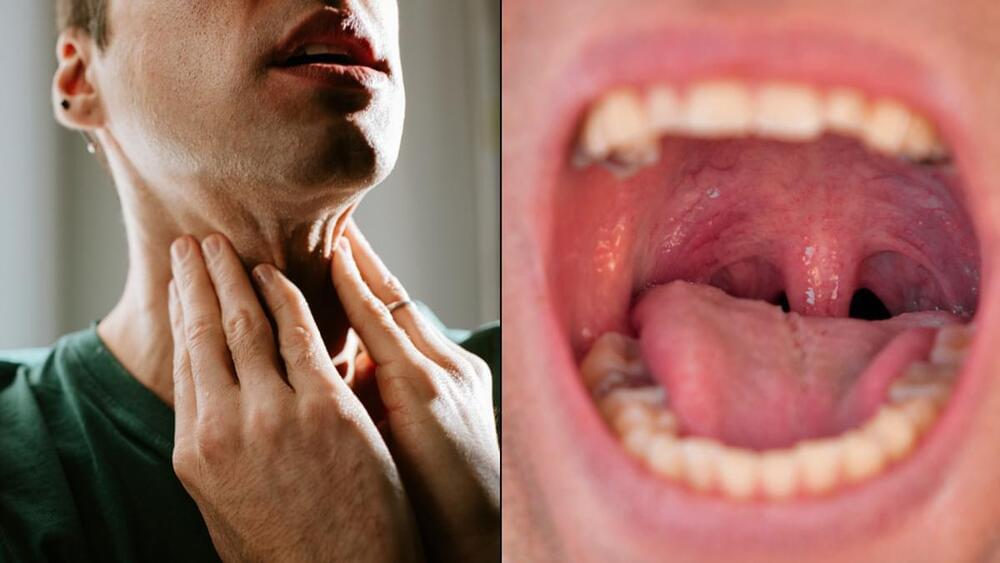
That was quite the scare for one US woman who was told she needed to have hers removed, despite having had them removed 40 years earlier.
Katy Golden told CNN: “I knew that there was some sort of little flap or something that’s been there for years, but I didn’t realize what it was. I just thought, ‘I’m not a doctor myself. I don’t know much about mouth structure. That’s just how it is’.”