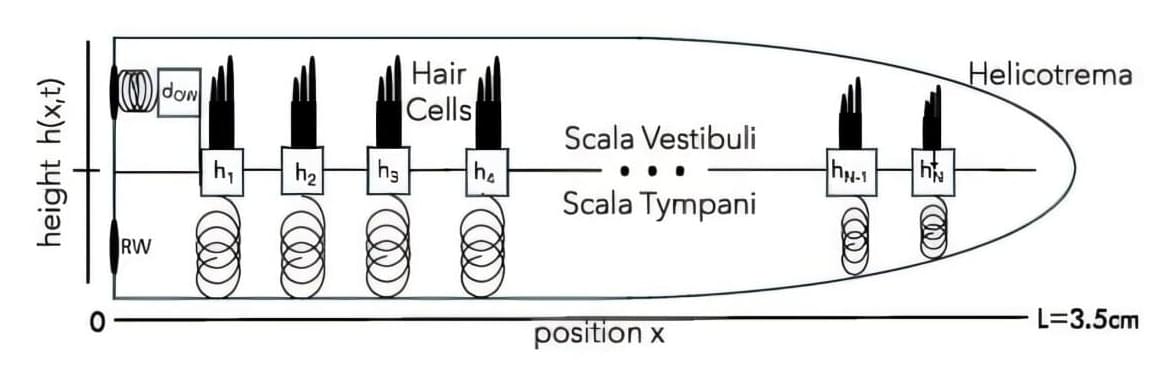
Yale physicists have discovered a sophisticated, previously unknown set of “modes” within the human ear that put important constraints on how the ear amplifies faint sounds, tolerates noisy blasts, and discerns a stunning range of sound frequencies in between.
By applying existing mathematical models to a generic mock-up of a cochlea—a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear—the researchers have revealed a new layer of cochlear complexity. The findings, which appear in PRX Life, offer fresh insight into the remarkable capacity and accuracy of human hearing.
“We set out to understand how the ear can tune itself to detect faint sounds without becoming unstable and responding even in the absence of external sounds,” said Benjamin Machta, an assistant professor of physics in Yale’s Faculty of Arts and Science and co-senior author of the new study. “But in getting to the bottom of this we stumbled onto a new set of low frequency mechanical modes that the cochlea likely supports.”