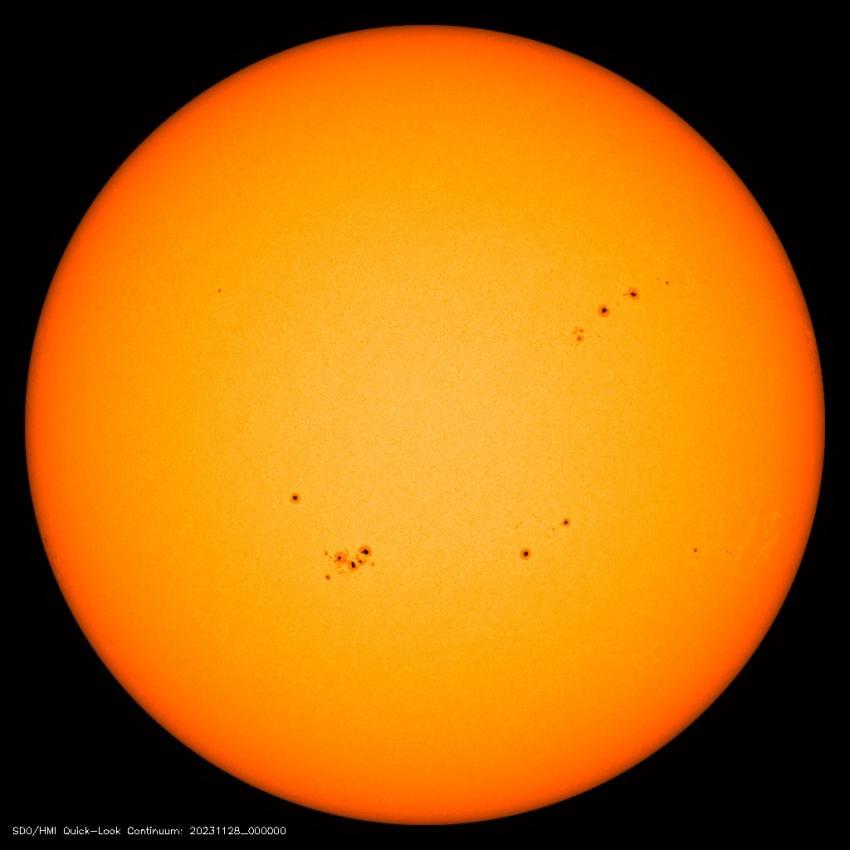
Researchers at the Center of Excellence in Space Sciences India at IISER Kolkata have discovered a new relationship between the Sun’s magnetic field and its sunspot cycle, that can help predict when the peak in solar activity will occur. Their work indicates that the maximum intensity of solar cycle 25, the ongoing sunspot cycle, is imminent and likely to occur within a year. The new research appears in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: Letters.
Our star, the Sun, is made up of hot ionized gas known as plasma.
Huge plasma flows and convection conspire together to form magnetic fields inside the Sun which manifest on the surface as dark spots.