A lot of information to see your brains complexity.
Mind-boggling mind research.
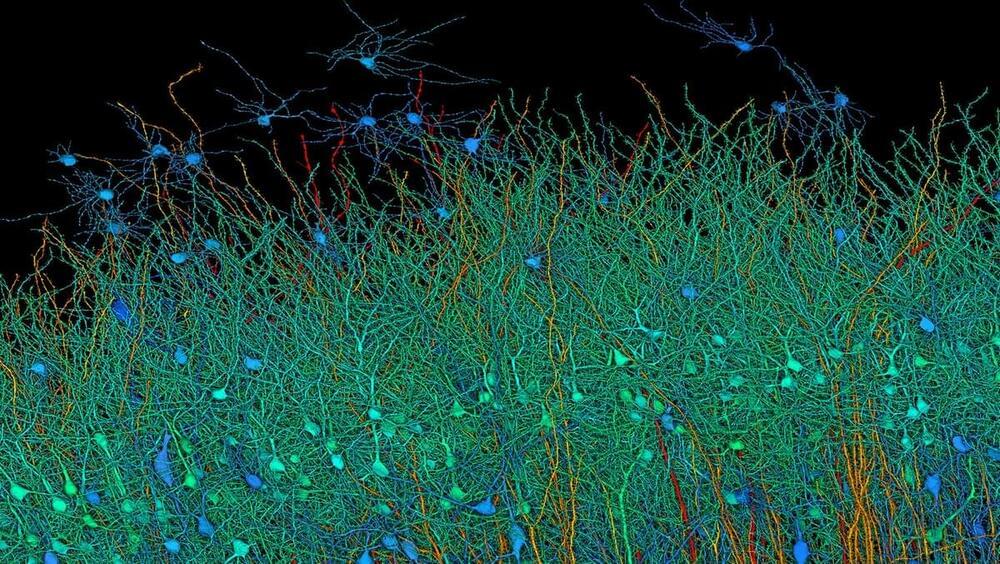


ALGORITHMS THAT DECODE IMAGES A PERSON SEES OR IMAGINES will enable visual representations of dreams a sleeper is having, and give deeper insights into emotionally disturbed or mentally ill patients.
Go to a href= https://brilliant.org/coldfusion
The rapid development and deployment of humanoid robots in the global labor market is inevitable and offers significant advantages over human labor, leading to a race to adopt this technology as quickly as possible Questions to inspire discussion What are the advantages of humanoid robots over human labor? —Humanoid ro.
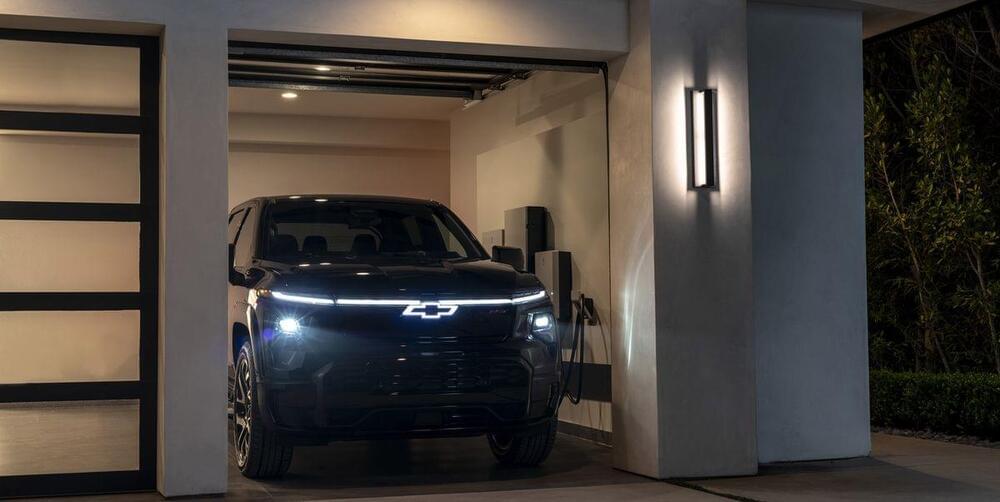

You can run your house for a week on a high-capacity EV battery. To prove it, GM Energy deliberately cut power to an event showing off its bi-directional V2H.
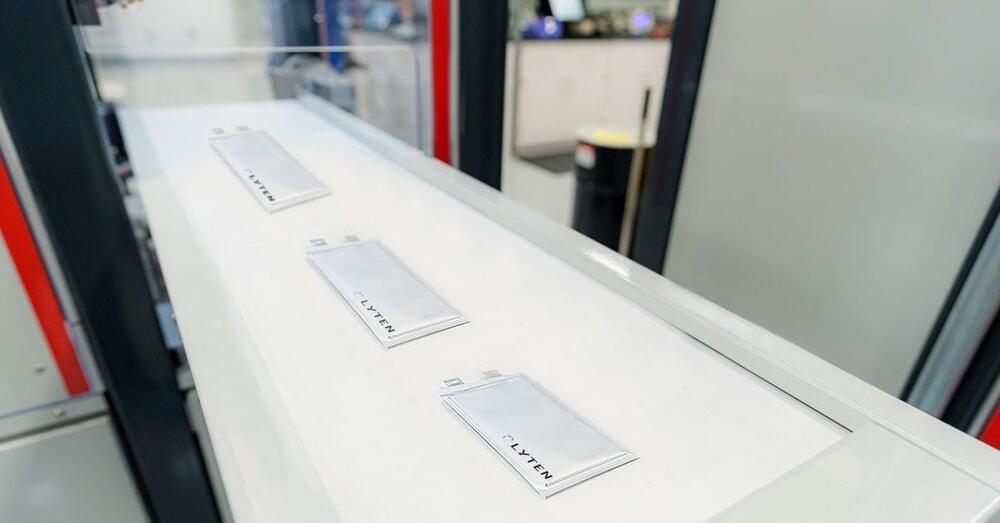

In a milestone, supermaterials trailblazer Lyten has shipped lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries to Stellantis and other US and EU OEMs for testing.
Lyten’s shipment of A samples of its 6.5 Ah Li-S pouch cells is the first major step in the commercial evaluation of lithium-sulfur batteries by leading US and European automakers. Stellantis announced that it had invested in Lyten’s lithium-sulfur battery development in May 2023.
“This milestone is the result of years of dedicated work and innovation from the Lyten team, and we are just at the start of further expanding the capabilities of our lithium-sulfur battery cells,” said Lyten CEO and cofounder Dan Cook.

Tesla is planning to remove the steering wheel nag, which alerts drivers to apply torque on the steering wheel, with a new Supervised Full Self-Driving (FSD) update coming next week.
Yesterday, we reported on CEO Elon Musk giving an outline of the upcoming FSD software updates.
The CEO says that Tesla is preparing to launch fully retrained models in FSD v12.4 as soon as next week.

ChatGPT sparked a generative AI frenzy in the corporate workplace. Efforts to implement that technology responsibly, however, haven’t kept up.
Researchers have developed a revolutionary material that can help eliminate microplastics, one of the most pervasive artificial contaminants in nature, from our waterways.
Scientists at the Indian Institute of Science have created a sustainable hydrogel — a polymer-based material that can adapt its structure to its environment even after absorbing water — with a “unique intertwined polymer network” that binds the microplastics and breaks them down using UV light, the institute summarized on its website.
Hydrogels have chainlike molecules called polymers that are tightly joined like glue and can easily stick to water molecules. When particles adhere to it, the structure remains intact despite holding a lot of water.

The lab’s latest AI news is something different, though. Instead of designing a model to master a single game, DeepMind has teamed up with researchers from the University of British Columbia to develop an AI agent capable of playing a whole bunch of totally different games.
Called SIMA (scalable i nstructable m ulti-world a gent), the project also marks a shift from competitive to cooperative play as the AI operates by following human instructions.
But SIMA wasn’t created simply to help sleepy players grind out levels or farm up resources. The researchers instead hope that by better understanding how SIMA learns in these virtual playgrounds, we can make AI agents more cooperative and helpful in the real world.