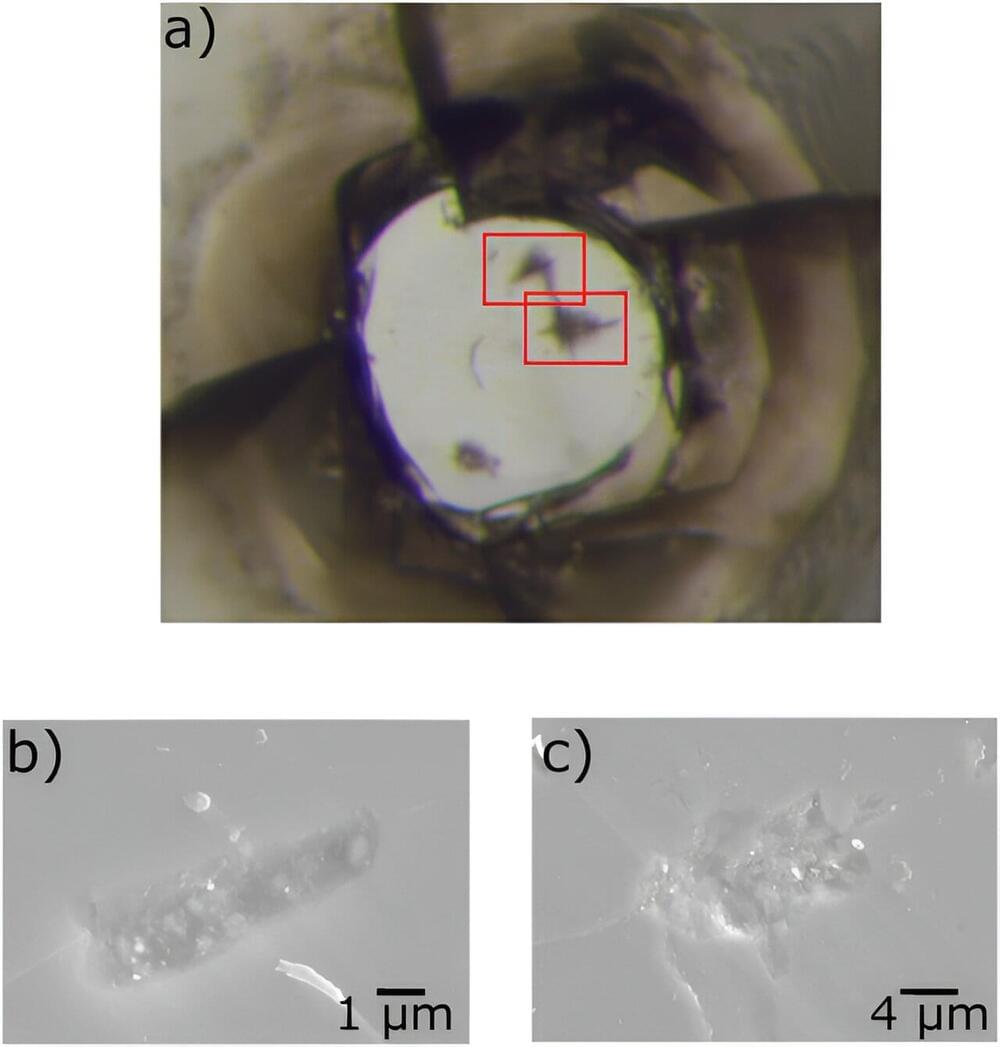
A stroke happens when blood flow is lost to part of the brain. Your brain cells cannot get the oxygen and nutrients they need from blood, and they start to die in a few minutes. This can cause lasting brain damage, long-term disability, or even death.
A stroke can occur when an obstruction such as a blood clot travels from another part of the body and lodges inside an artery in the brain.
When an arterial wall becomes damaged, various types of emboli, or obstructions, can form. Emboli can be made up of various substances such as platelets, elements in the blood that help it clot, blood clots that form elsewhere and pass to the damaged area, cholesterol, or a combination of things.
For example, an embolism is formed in the carotid artery and breaks loose, traveling towards the brain where it will eventually lodge, blocking the blood the brain needs. The blocked artery deprives the brain of oxygen, which cause damage to the surrounding tissue. The result is a stroke.