Newly discovered altermagnetism at the Swiss Light Source SLS opens door to new physics & spintronics. Learn about this new addition to magnetic family!


Mapping the geometry of quantum worlds: measuring the quantum geometric tensor in solids.
Quantum states are like complex shapes in a hidden world, and understanding their geometry is key to unlocking the mysteries of modern physics. One of the most important tools for studying this geometry is the quantum geometric tensor (QGT). This mathematical object reveals how quantum states “curve” and interact, shaping phenomena ranging from exotic materials to groundbreaking technologies.
The QGT has two parts, each with distinct significance:
1. The Berry curvature (the imaginary part): This governs topological phenomena, such as unusual electrical and magnetic behaviors in advanced materials.
2. The quantum metric (the real part): Recently gaining attention, this influences surprising effects like flat-band superfluidity, quantum Landau levels, and even the nonlinear Hall effect.
While the QGT is crucial for understanding these phenomena, measuring it directly has been a challenge, previously limited to simple, artificial systems.
A breakthrough now allows scientists to measure the QGT in real crystalline solids. Using an advanced technique involving polarization-, spin-, and angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy, researchers have reconstructed the QGT in a material called CoSn, a “kagome metal” with unique quantum properties like topological flat bands. This metal forms patterns resembling a woven basket, hosting quantum effects that were previously only theorized.

The most common form – obstructive sleep apnoea – happens when the walls of the throat relax and narrow or close, with symptoms including choking noises, loud snoring and waking up a lot.
The three-hour procedure to fit Nyxoah’s Genio implant was carried out by medics at University College London Hospitals NHS foundation trust (UCLH) this month.
One of the two patients, Natalie Boller, 63, was feeling better within days and will return to the clinic to have the device activated in the coming weeks.

The Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope team at NASA has completed the integration of the telescope and its instruments onto the carrier, a significant milestone in the assembly process.
With the Coronagraph Instrument and the Optical Telescope Assembly in place, the Roman telescope is equipped to explore a vast array of astronomical phenomena, including exoplanets and cosmic mysteries like dark energy and dark matter. The Wide Field Instrument, a powerful 300-megapixel infrared camera, will enhance the telescope’s capability to survey the universe extensively. The project is on schedule for a 2026 completion and a 2027 launch.
Integration of roman space telescope components.
A NASA-led study reveals that the pattern of rainfall throughout the year—specifically the frequency and intensity of rain events—is nearly as significant to global vegetation health as the total amount of annual rainfall.
The research indicates that less frequent but heavier rainfalls can benefit plants in arid regions like the U.S. Southwest, while potentially harming those in wetter ecosystems such as the Central American rainforests due to longer intervals of dryness.
Impact of rainfall patterns on global vegetation.
Researchers at NASAs Armstrong Center are advancing an atmospheric probe for potential space missions.
Utilizing innovative designs based on past aircraft research, the team has successfully tested the probe, planning further improvements to increase its functionality and data-gathering capabilities.
NASA’s Innovative Atmospheric Probe

Researchers at the University of Virginia have made significant advancements in understanding how heat flows through thin metal films, critical for designing more efficient computer chips.
This study confirms Matthiessen’s rule at the nanoscale, enhancing heat management in ultra-thin copper films used in next-generation devices, thereby improving performance and sustainability.
Breakthrough in Chip Technology.
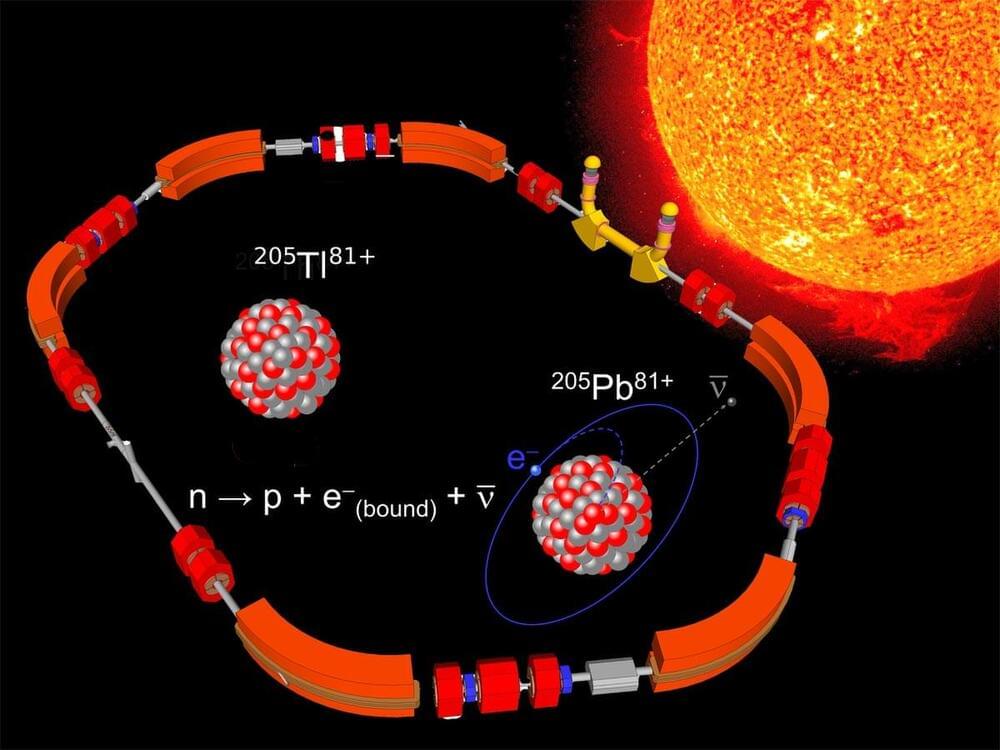
The LOREX experiment utilizes lorandite ore to gauge historical solar neutrino flux, revealing insights about the Sun’s development and climatic effects through advanced decay rate measurements.
The Sun, Earth’s life-sustaining powerhouse, generates immense energy through nuclear fusion while emitting a steady stream of neutrinos — subatomic particles that reveal its inner workings. While modern neutrino detectors shed light on the Sun’s current behavior, key questions remain about its stability over millions of years — a timeframe encompassing human evolution and major climate changes.
Addressing these questions is the mission of the LORandite EXperiment (LOREX), which depends on accurately determining the solar neutrino cross-section for thallium. An international team of scientists has now achieved this crucial measurement using the unique Experimental Storage Ring (ESR) at GSI/FAIR in Darmstadt. Their groundbreaking results, advancing our understanding of the Sun’s long-term stability, have been published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Research utilizing AI tool AlphaFold has revealed a new protein complex that initiates the fertilization process between sperm and egg, shedding light on the molecular interactions essential for successful fertilization.
Genetic research has uncovered many proteins involved in the initial contact between sperm and egg. However, direct proof of how these proteins bind or form complexes to enable fertilization remained unclear. Now, Andrea Pauli’s lab at the IMP, working with international collaborators, has combined AI-driven structural predictions with experimental evidence to reveal a key fertilization complex. Their findings, based on studies in zebrafish, mice, and human cells, were published in the journal Cell.
Fertilization is the first step in forming an embryo, starting with the sperm’s journey toward the egg, guided by chemical signals. When the sperm reaches the egg, it binds to the egg’s surface through specific protein interactions. This binding readies their membranes to merge, allowing their genetic material to combine and create a zygote—a single cell that will eventually develop into a new organism.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/