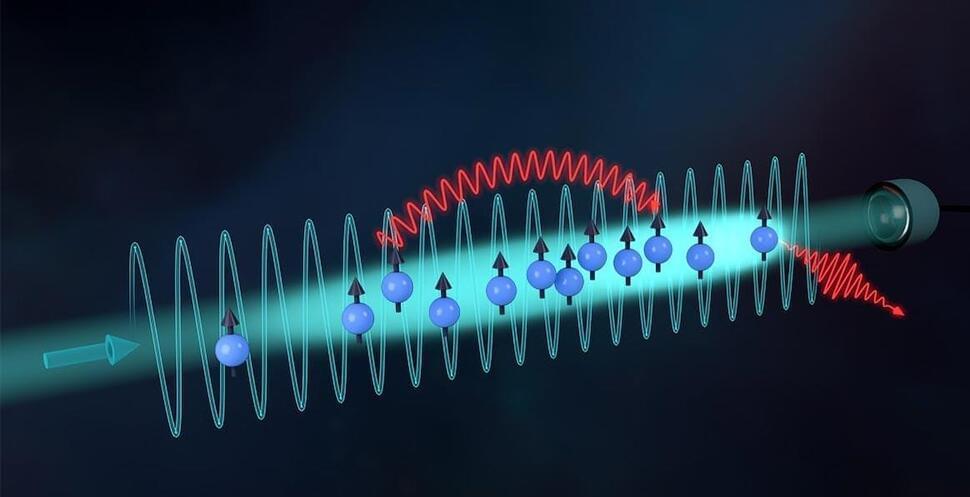
Superradiance in optical cavities involves atoms emitting light collectively when interacting with cavity photons, a phenomenon not yet observed in free space due to synchronization challenges.
Researchers have used theoretical simulations to probe these effects under various conditions, revealing significant differences in behavior between cavity and free-space systems.
Superradiance in Optical Cavities.