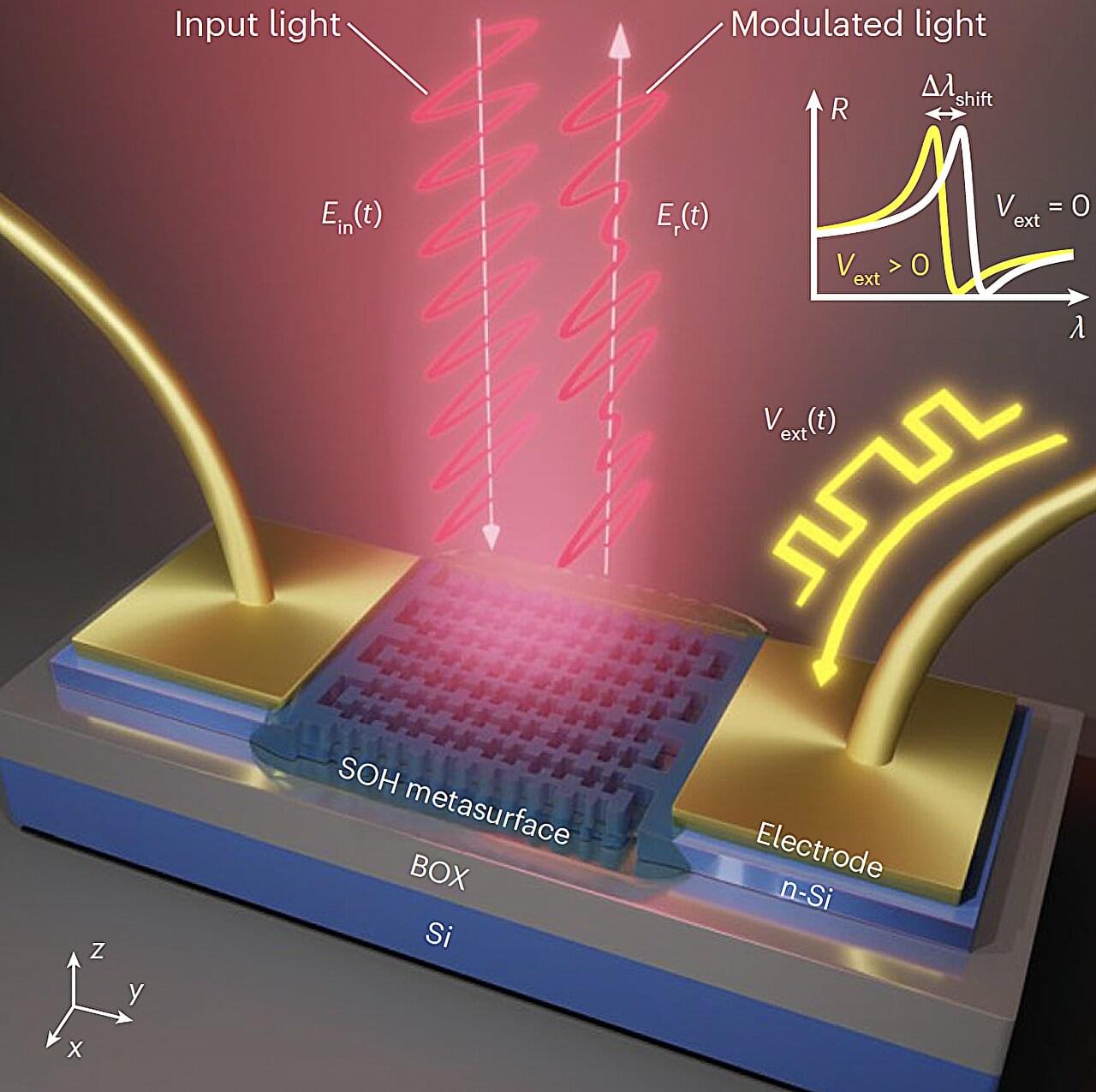
Metasurfaces are two-dimensional (2D), nanoengineered surfaces that interact strongly with electromagnetic waves and can control light with remarkable precision. These ultra-thin layers can be used to develop a wide range of advanced technologies, including optical photonic, sensing and communication systems.
Active metasurfaces, whose electromagnetic response can be dynamically tuned in real-time, are particularly promising for advanced real-world applications, particularly for the development of reconfigurable antennas, highly sensitive sensors and other adaptive systems. These metasurfaces can also serve as optical modulators, devices that adjust the intensity or phase of light and thus enable the encoding of information onto light beams.
While engineers have introduced various metasurface-based optical modulators over the past few years, most devices developed so far require high-voltage electrical signals to operate. This means that to noticeably change the optical response of the metasurfaces they are based on, users need to apply a strong electrical field to them.