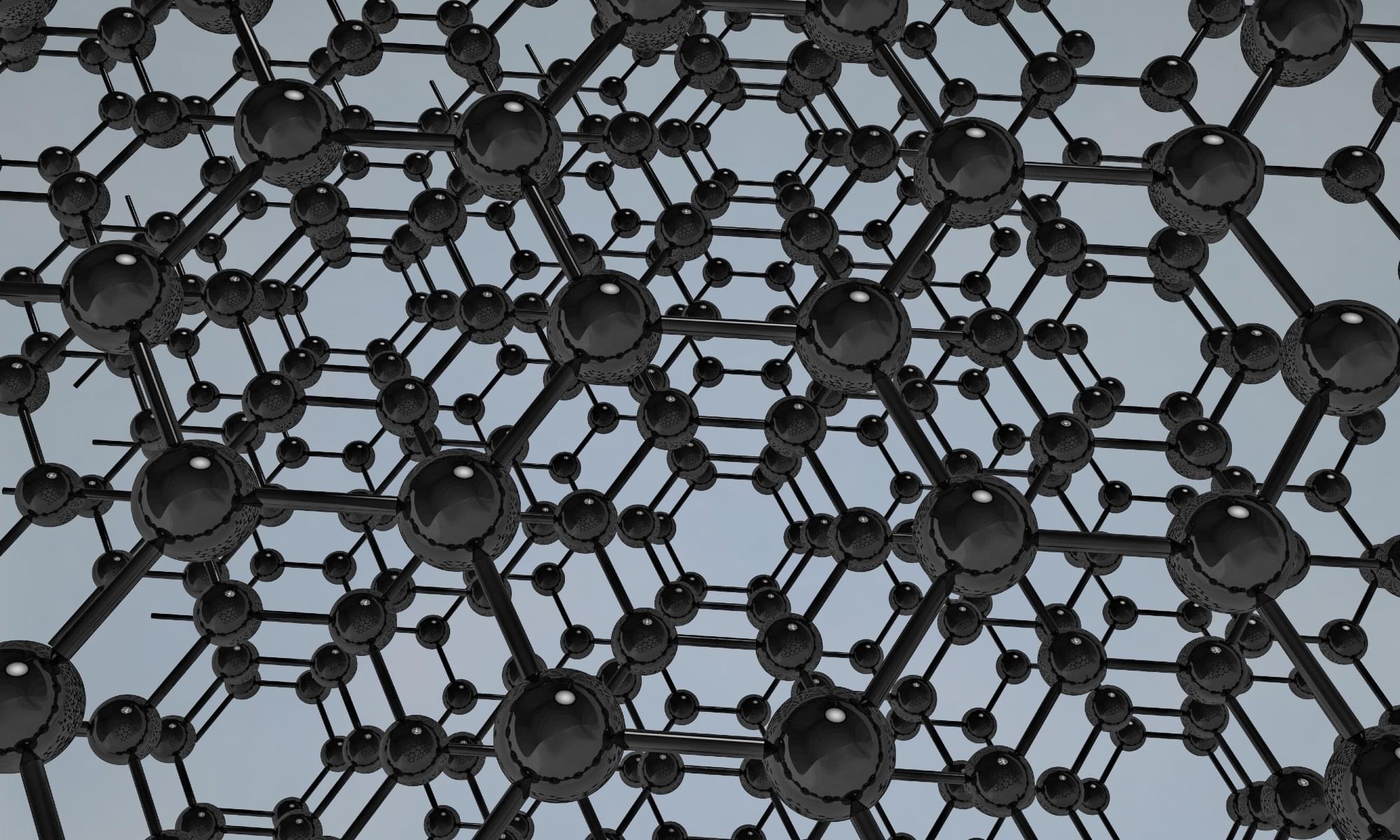
Graphene is a two-dimensional material composed of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Its first discovery was so astonishing because, despite its atomic-scale thickness, graphene exhibits exceptional mechanical strength, approximately 200 times greater than steel.
It also has high electrical and thermal conductivity and a very high theoretical surface area of approximately 2,630 m2/g, which means it can easily be functionalized, broadening its scope.
These properties make graphene suitable for applications in quantum electronics, biomedicine, sustainable construction, and energy storage.
Graphene’s role in technology is expanding, offering solutions for energy storage, cancer therapy, and sustainable construction through innovative research.