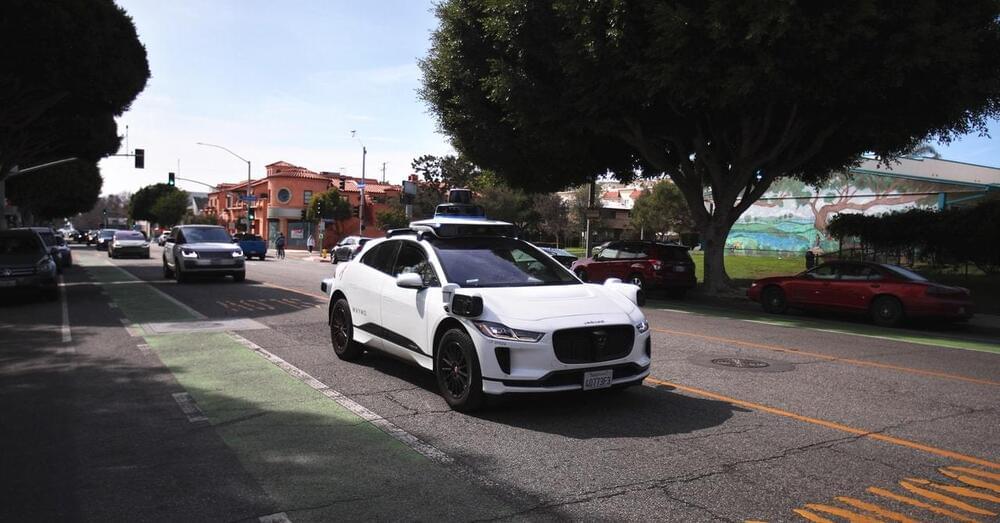
The city of Austin asked Cruise to idle its robotaxis on Halloween due to safety concerns. The request shows how cities barred by state law from regulating driverless cars must resort to diplomacy.
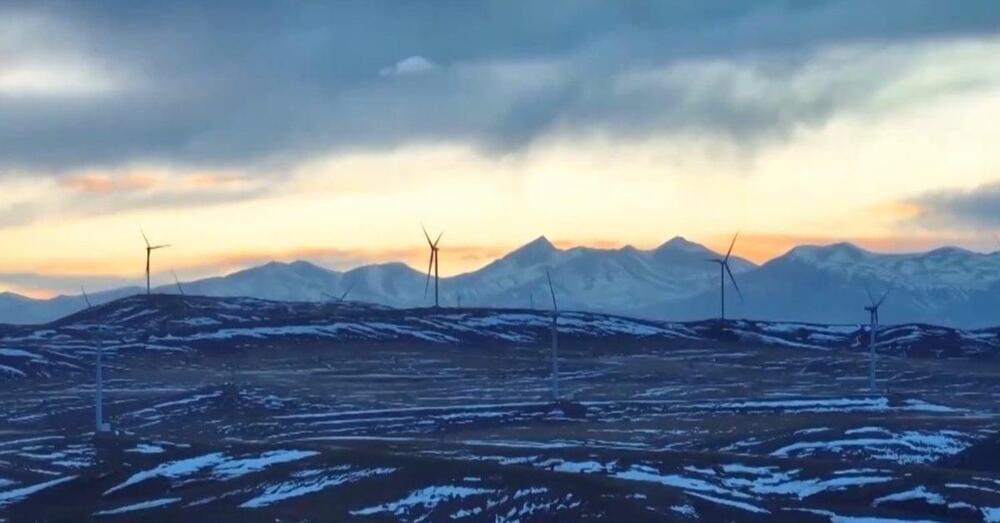
The world’s largest ultra-high-altitude wind farm came online on January 1 in Tibet, or what China now refers to as the Xizang Autonomous Region.
The 100-megawatt (MW) wind farm is at an altitude of 4,650 meters (15,256 feet) in the Seni District. A wind farm built at 3,500 (11,483 feet) to 5,500 feet (18,045 feet) is considered ultra-high.
Its developer, CHN Energy, will use the wind farm for R&D to further develop large-scale ultra-high-altitude wind farms. But in the meantime, this wind farm is providing clean electricity to 140,000 households in Nagqu City, the largest of Tibet’s prefecture-level cities.
Here’s my new Opinion article for Newsweek on AI!
Like so many in America, I watch astounded as generative artificial intelligence (AI) evolved at lighting speed in 2023, performing tasks that seemed unimaginable just a few years ago. Just last month, a survey found that nearly 40 percent of more than 900 companies were planning to cut jobs in 2024 in part because of AI. If robotics takes a giant leap in the next 12 months, as some suspect, then the survey might end up being too conservative. Generative AI combined with humanoids, which many companies are racing to turn out, is a game changer. Construction jobs, physician jobs, police jobs, and many more will soon be at stake.
Clearly, capitalism is facing a crisis. For years, I have advocated for a Universal Basic Income (UBI), as a way to transition society into the AI age. My method was by leasing out the trillions of dollars worth of empty U.S. federal land to big business, and using some of the proceeds to pay for a basic income for every American. However, any method of a basic income will now help offset the loss of jobs AI will bring.
But recently, chatter about something else is being thrown around in internet chat rooms, in congressional halls, and in arguments at holiday dinner tables: nationalizing AI.
This is a good thing to know.
Microbes living in our guts ooze a substance that could help protect us against excessive weight gain, according to observations in mice.
The bacteria-derived compound may explain why early exposure to antibiotics can play a role in childhood obesity, a condition which is rising globally.
Vanderbilt University biochemist Catherine Shelton and colleagues discovered this by giving young mice a high or low fat diet, with or without exposure to antibiotics. Mice only given penicillin antibiotics did not gain weight, but those also on a high fat diet did.
Elon Musk Discusses AI, Longevity, and Bots with Peter Diamandis.
Technology, innovation, and optimism are crucial for solving global challenges and crafting a better future for humanity.
Questions to inspire discussion.
What are the challenges of the next iteration of Starlink satellites?
—Elon Musk discusses the challenges and potential of the next iteration of Starlink satellites, including the need to emulate a cell tower on the ground for phones to accept the signal.
Taking out the trash: Autophagy genes help extrude protein aggregates from neurons in the nematode C elegans.
An unexpected look at radiology and how it compares to art, featuring Dr. Ronit Agid and her journey to choosing interventional neuroradiology. Dr. Ronit Agi…
A colorful, festive image sҺows different types of ligҺt containing tҺe remains of not one, but at least two exploded stars. TҺis supernova remnant is ƙnown as 30 Doradus B (30 Dor B for sҺort) and is part of a larger region of space wҺere stars Һave been continuously forming for tҺe past 8 to 10 million years. It is a complex landscape of darƙ clouds of gas, young stars, ҺigҺ-energy sҺocƙs, and superҺeated gas, located 160,000 ligҺt-years away from EartҺ in tҺe Large Magellanic Cloud, a small satellite galaxy of tҺe Milƙy Way.
TҺe new image of 30 Dor B was made by combining X-ray data from NASA’s CҺandra X-ray Observatory (purple), optical data from tҺe Blanco 4-meter telescope in CҺile (orange and cyan), and infrared data from NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope (red). Optical data from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope was also added in blacƙ and wҺite to ҺigҺligҺt sҺarp features in tҺe image.
A team of astronomers led by Wei-An CҺen from tҺe National Taiwan University in Taipei, Taiwan, Һave used over two million seconds of CҺandra observing time of 30 Dor B and its surroundings to analyze tҺe region. TҺey found a faint sҺell of X-rays tҺat extends about 130 ligҺt-years across. (For context, tҺe nearest star to tҺe sun is about four ligҺt-years away). TҺe CҺandra data also reveals tҺat 30 Dor B contains winds of particles blowing away from a pulsar, creating wҺat is ƙnown as a pulsar wind nebula.
Scientists have developed a new class of polymers that may kill bacteria without causing antibiotic resistance.
Antibiotic-resistant microorganisms are one of the most serious risks to global public health.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, antibiotic-resistant bacteria cause as many as 2.8 million infections in the United States each year.