Some say OpenAI’s o1 models are close to artificial general intelligence.


To get started planning a career that works on one of the world’s most pressing problems, sign up now at https://80000hours.org/isaacarthur.
Gravity is a fascinating force, it’s what holds everything on our planet together, and it might one day help us travel to other planets.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
Gravitic Spaceship Propulsion.
Episode 477a; December 15, 2024
Produced, Narrated \& Written: Isaac Arthur.
Graphics: Jeremy Jozwik, Sergio Botero.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music Courtesy of Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Stellardrone, \
Win a meteorite💥! Join my email list: http://briankeating.com/yt.
What is time? Is it just a ticking clock, or is it something more profound?
In this thought-provoking episode of Into the Impossible, Stephen Wolfram challenges everything we know about time, offering a revolutionary computational perspective that could forever change how we understand the universe.
Stephen Wolfram is a computer scientist, physicist, and businessman. He is the founder and CEO of Wolfram Research and the creator of Mathematica, Wolfram Alpha, and Wolfram Language. Over the course of 4 decades, he has pioneered the development & application of computational thinking. He has been responsible for many discoveries, inventions & innovations in science, technology, and business.
He argues that time is the inevitable progress of computation in the universe, where simple rules can lead to complex behaviors. This concept, termed computational irreducibility, implies that time has a rigid structure and that our perception of it is limited by our computational capabilities. Wolfram also explores the relationship between time, space, and gravity, suggesting that dark matter might be a feature of the structure of space.
Tune in to discover the true nature of time.
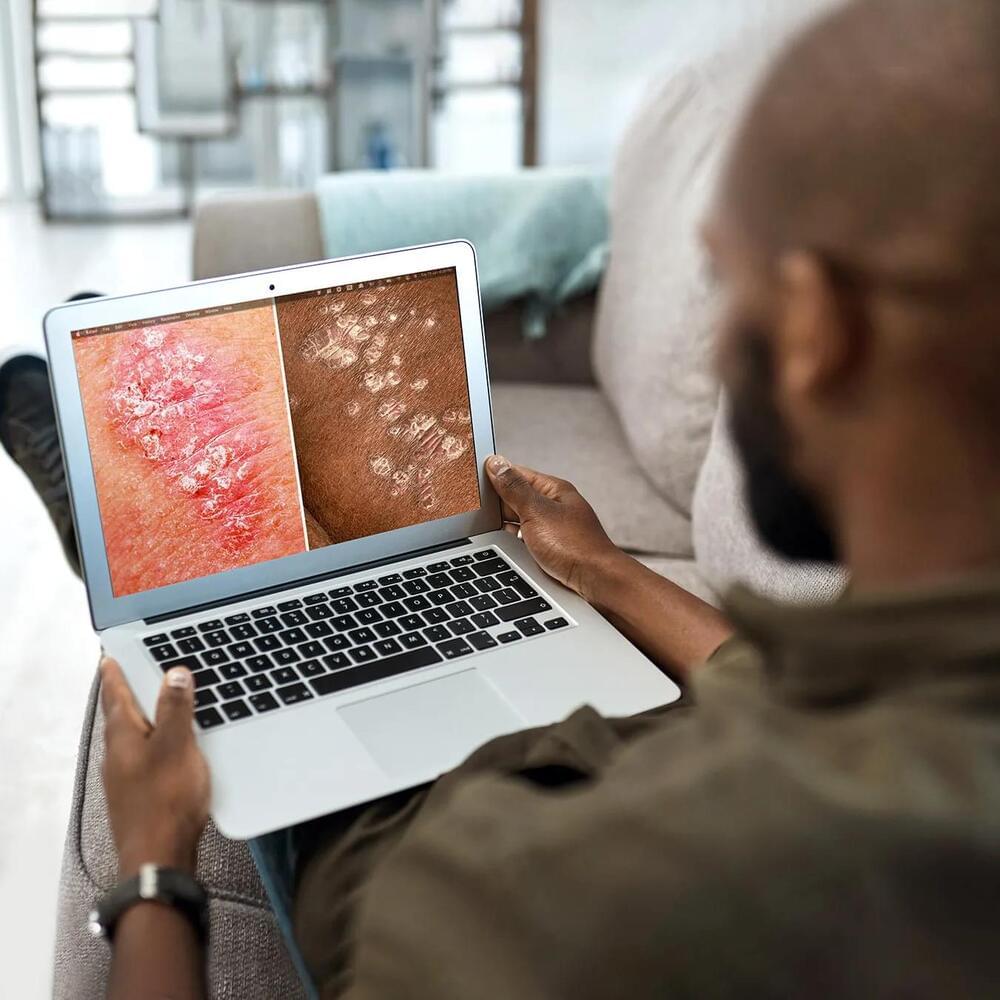

A Sweden-based firm has launched a plasma confinement project to achieve commercially viable fusion energy.
The TauEB project by Novatron Fusion Group aims to revolutionize plasma confinement and energy containment in fusion reactors.
Novatron’s project will introduce a first-of-its-kind integration of three physical confinement techniques, which will include Magnetic Confinement, Ambipolar Plugging, and Ponderomotive Confinement.

Author(s): Yuki Shizuya Originally published on Towards AI. Photo by gilber franco on UnsplashRecently, I needed to research image similarity search. I wonder if there are any differences among embeddings based on the architecture training methods. However, few blogs compare embeddings among several models. So, in this blog, I will compare the vision embeddings of EfficientNet [1], ViT [2], DINO-v2 [3], CLIP [4], and BLIP-2 [5] for image similarity search using the Flickr dataset [6]. I will mainly use Huggingface and Faiss libraries for implementation. First, I will briefly introduce each deep learning model. Next, I will show you the code implementation and the comparison results.
With the approach of a new year, and the prospect of accelerating technological advancement, all eyes are on AI. The new best-selling book \.
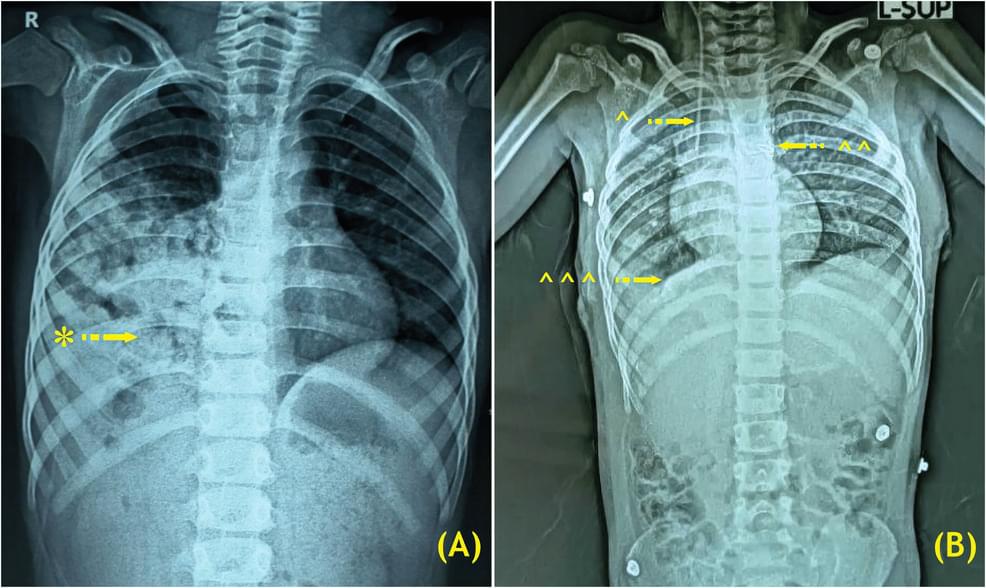
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) is a diaphragmatic defect that is usually situated on the left side in the posterolateral region, named a Bochdalek hernia (BH), which allows abdominal organs to herniate into the thoracic cavity. BH is a prevalently observed birth anomaly in infants but is rare in adults. Right-sided BH that involves the colon is exceptionally rare, and no prior cases have described ileocecal appendix involvement. Here, we present a case of a preschooler with a right-sided BH and patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), requiring distinct surgical approaches: left open thoracotomy for PDA ligation and right open thoracotomy for CDH repair. Surgical intervention is associated with reduced morbidity and mortality, favorable long-term outcomes, and a low recurrence rate, irrespective of the selected approach.
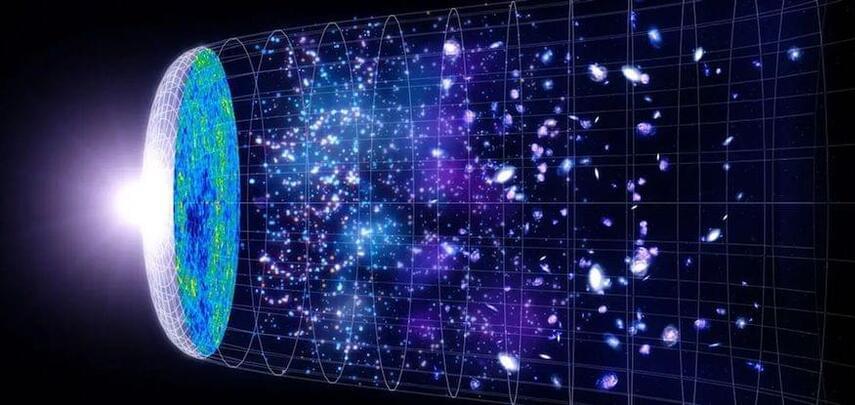
In case dark matter didn’t seem mysterious enough, a new study proposes that it could have arisen before the Big Bang.
Conventional thinking goes that the Big Bang was the beginning of everything – matter, dark matter, space, energy, all of it. After the event itself, the Universe went through a period of cosmic inflation, which saw its size swell by a factor of 10 septillion within an unfathomable fraction of a second.
But some theories suggest that this inflation period actually occurred before what we call the Big Bang. And now, physicists at the University of Texas (UT) at Austin have proposed that dark matter was formed during this brief window.