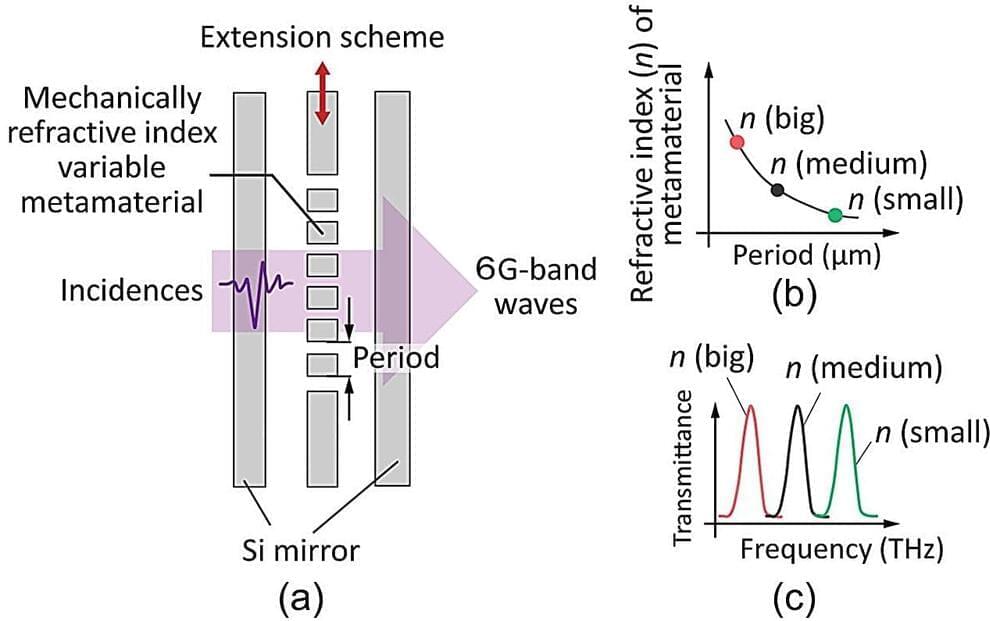
Electromagnetic waves in the terahertz frequency range offer many advantages for communications and advanced applications in scanning and imaging, but realizing their potential poses challenges. Researchers at Tohoku University have addressed one of the key challenges by developing a new type of tunable filter for signals in the terahertz wave band. They published their work in the journal Optics Letters.
Bitcoin has crushed its highest price ever, blasting past $72,000 for the first time in its history today.
The news comes after UK regulators announced they wouldn’t stand in the way of the creation of crypto-backed, exchange-traded notes (cETNs), CNBC reports. ETNs are a type of unsecured debt securities that trade on major exchanges, kind of like a stock.
The value of the mainstream cryptocurrency has risen considerably since the beginning of the year, spurred on by its growing acceptance by regulators around the globe and the fading shadow of the FTX collapse.
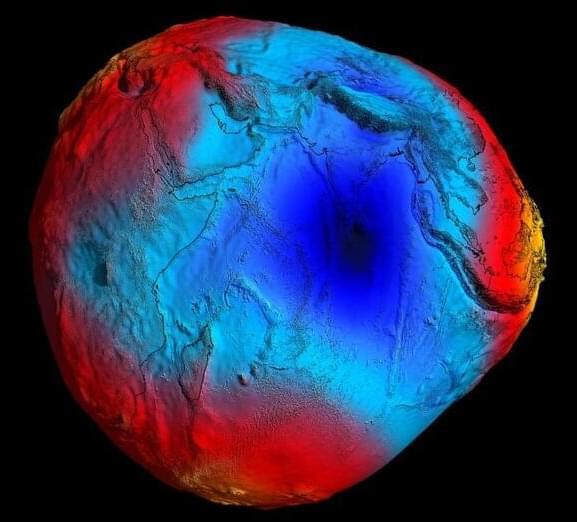
Due to the world’s largest gravity hole, the sea level in a large part of the Indian Ocean is up to 106 m (348 ft) lower than the rest of the world. We have just understood what causes this huge ‘black hole.’
If you look at a map of Earth’s gravity, you will see a huge blue spot south of India, indicating a region where gravity is weaker than average. This spot is called the Indian Ocean Geoid Low (IOGL), and it is the largest gravity anomaly on our planet.
A gravity anomaly is a difference between the actual gravity measured at a location and the theoretical gravity expected for a perfectly smooth and spherical Earth. But Earth’s gravity isn’t perfectly uniform and variations in mass distribution beneath the surface cause fluctuations in gravitational pull.
Good morning 🌅
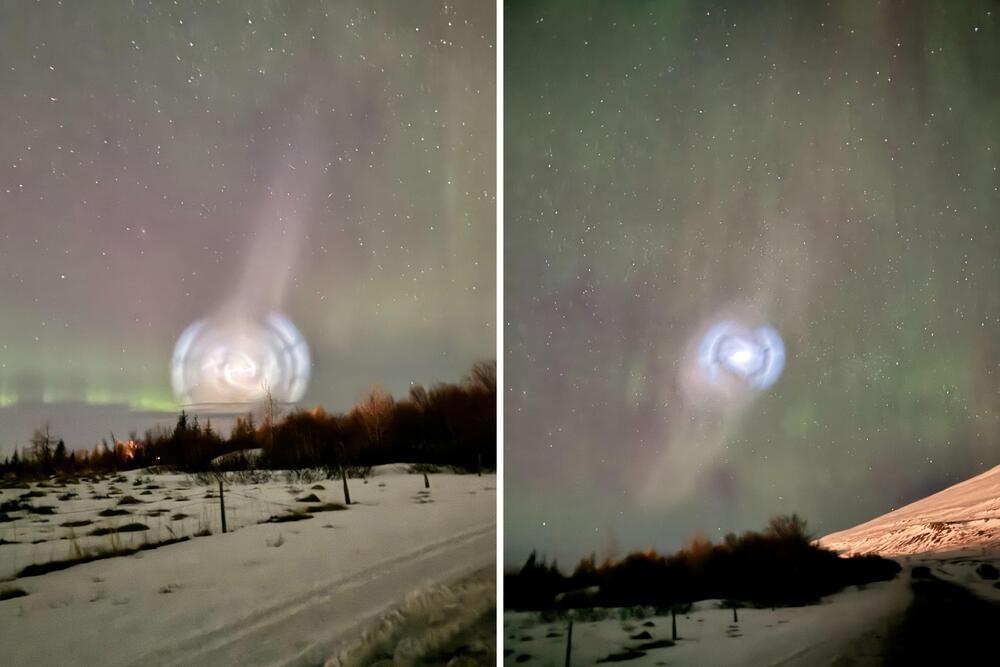
The view was “awe-inspiring and a little scary,” Shang Yang told Newsweek, noting “it was definitely not part of normal aurora activity.”
The company, which filed for bankruptcy in September, had been negotiating a deal for its founders to provide fresh capital and buy it out of Chapter 11.
The new nonprofit Fairly Trained certifies that artificial intelligence models license copyrighted data—which often isn’t the case.
By Ben Guarino
Pixart-σ weak-to-strong training of diffusion transformer for 4K text-to-image generation.
PixArt-Σ
Weak-to-strong training of diffusion transformer for 4K text-to-image generation.
In this paper, we introduce PixArt-Sigma, a Diffusion Transformer model~(DiT) capable of directly generating images at 4K resolution.
Join the discussion on this paper page.
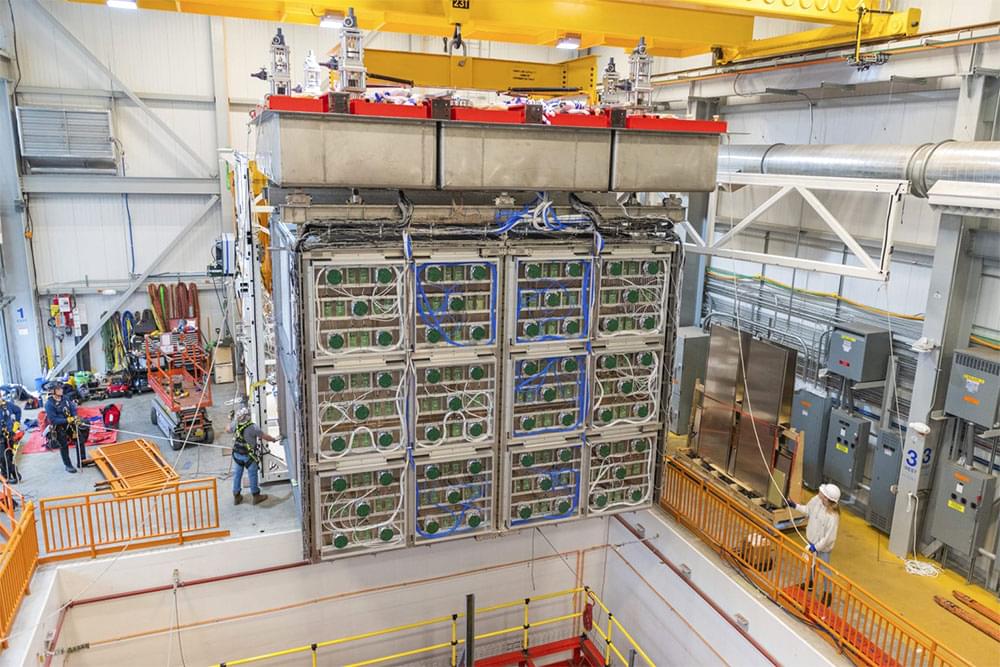
The Short-Baseline Near Detector collaboration is preparing for an exciting year at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. After nearly a decade of planning, prototyping and construction, the team is in the final stretch of commissioning of their detector.
In January, engineers began introducing gaseous argon into SBND to push air out of the cryostat. Now that the detector is mostly free of impurities, the team has begun filling it with liquid argon.
“We’re all excited to get to this point. It’s one of the last steps before we see our first particle tracks,” said Roberto Acciarri, the detector assembly and installation co-coordinator for SBND.
A new computer model mimics Moon dust so well that it could lead to smoother and safer Lunar robot teleoperations. The tool, developed by researchers at the University of Bristol and based at the Bristol Robotics Laboratory, could be used to train astronauts ahead of Lunar missions. Working with their industry partner, Thales Alenia Space in the UK, who has specific interest in creating working robotic systems for space applications, the team investigated a virtual version of regolith, another name for Moon dust.
Lunar regolith is of particular interest for the upcoming Lunar exploration missions planned over the next decade. From it, scientists can potentially extract valuable resources such as oxygen, rocket fuel or construction materials, to support a long-term presence on the Moon. To collect regolith, remotely operated robots emerge as a practical choice due to their lower risks and costs compared to human spaceflight.
However, operating robots over these large distances introduces large delays into the system, which make them more difficult to control. Now that the team know this simulation behaves similarly to reality, they can use it to mirror operating a robot on the Moon. This approach allows operators to control the robot without delays, providing a smoother and more efficient experience.