Year 2021 face_with_colon_three
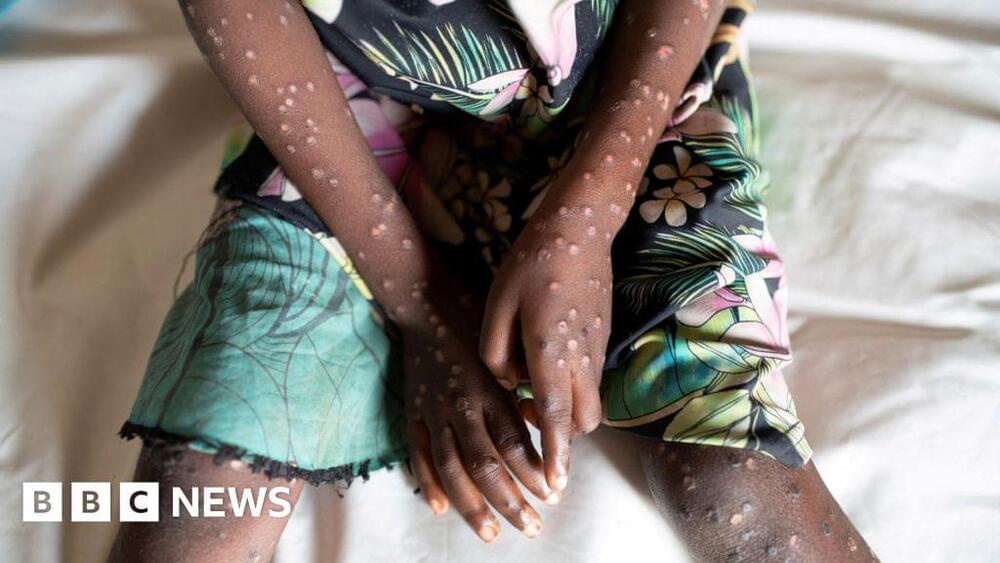
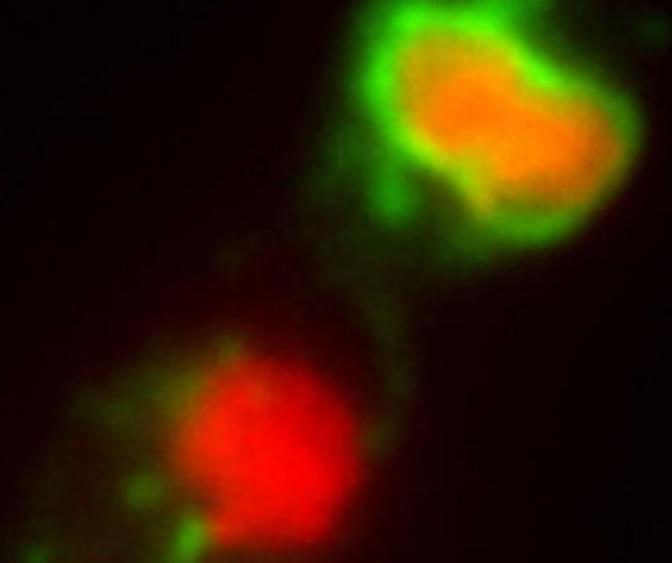
The quasi-local notion of an isolated horizon is employed to study the entropy of black holes without any particular symmetry in loop quantum gravity. The idea of characterizing the shape of a horizon by a sequence of local areas is successfully applied in the scheme to calculate the entropy by the S O(1, 1) BF boundary theory matching loop quantum gravity in the bulk. The generating function for calculating the microscopical degrees of freedom of a given isolated horizon is obtained. Numerical computations of small black holes indicate a new entropy formula containing the quantum correction related to the partition of the horizon. Further evidence shows that, for a given horizon area, the entropy decreases as a black hole deviates from the spherically symmetric one, and the entropy formula is also well suitable for big black holes.