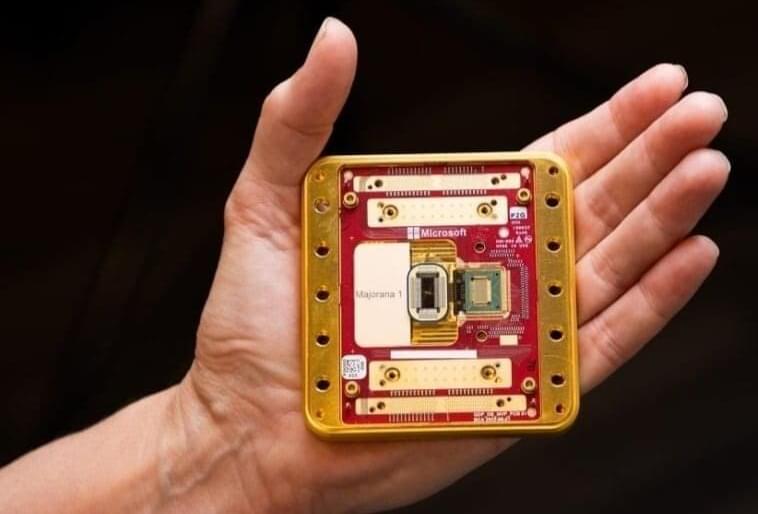
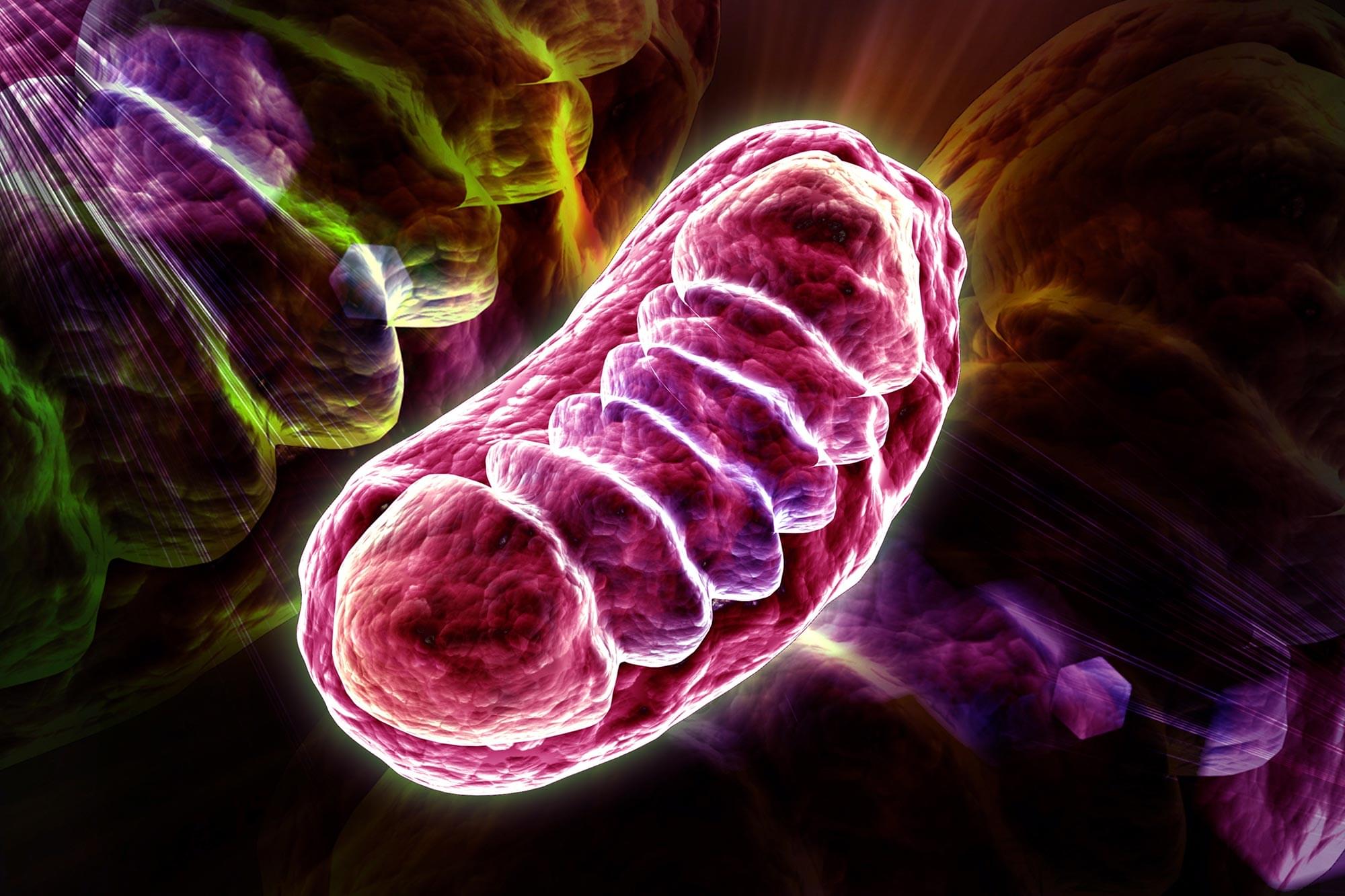
A study conducted by researchers from the University of São Paulo sheds light on new discoveries about the mechanisms of oxidative phosphorylation in ATP production. Recent findings highlight the involvement of sodium in mitochondrial respiration.
In an article published in Trends in Biochemical Sciences, Alicia Kowaltowski, a full professor at the University of São Paulo’s Institute of Chemistry (IQ-USP) in Brazil, calls for a “rewriting” of textbooks regarding the location of the electron transport chain in mitochondria and the role of sodium in mitochondrial respiration.
Kowaltowski is also a member of the Research Center for Redox Processes in Biomedicine (Redoxoma), a Research, Innovation, and Dissemination Center (RIDC) funded by FAPESP and based at IQ-USP.