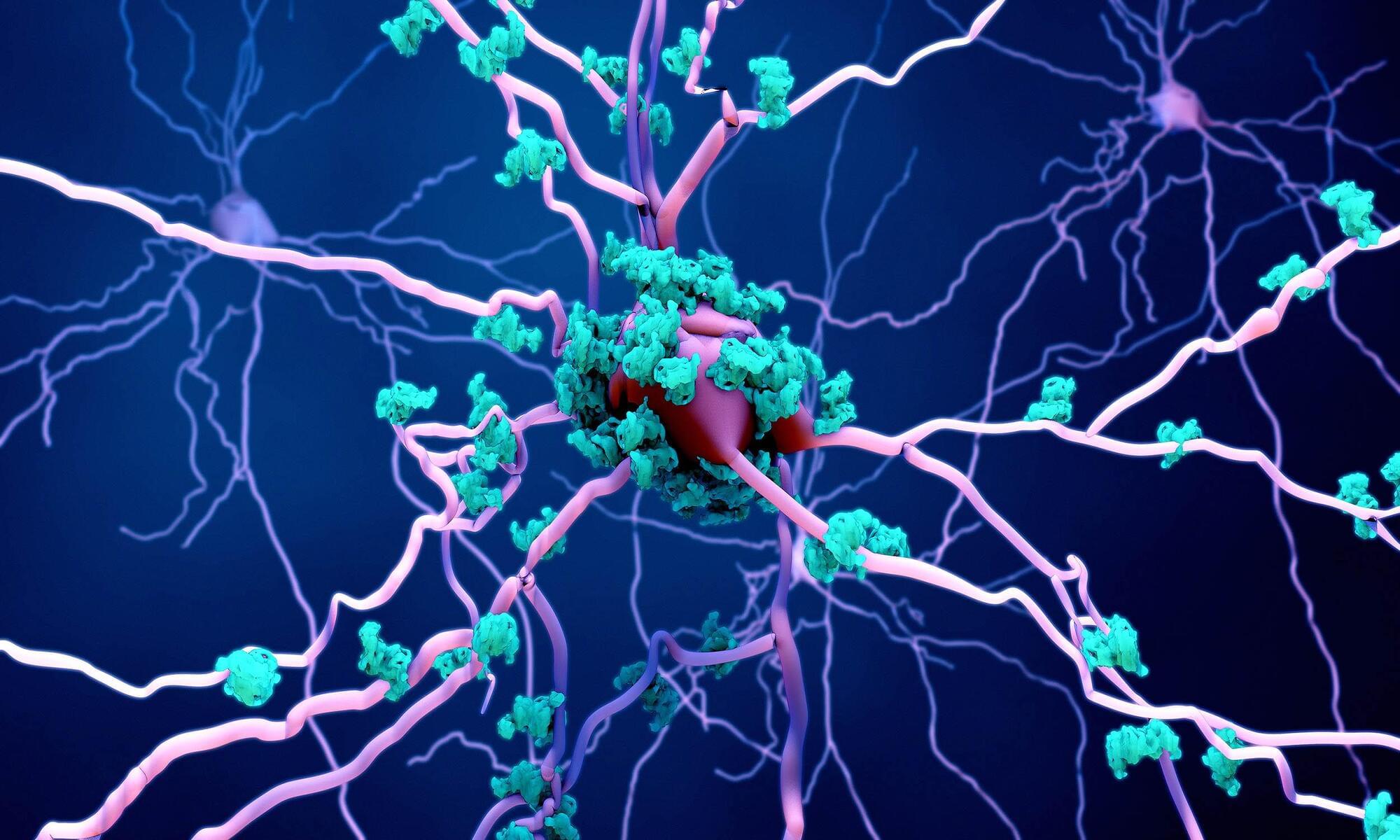
Researchers have created a 3D mouse organoid model to study how neurons in the nose regenerate, revealing that a type of stem cell once considered dormant may be crucial for repairing olfactory tissue.
What if accessing knowledge, which used to require hours of analyzing handwritten scrolls or books, could be done in mere moments?
Throughout history, the way humans acquire knowledge has experienced great revolutions. The birth of writing and books altered learning, allowing ideas to be preserved and shared across generations. Then came the Internet, connecting billions of people to vast information at their fingertips.
Today, we stand at another shift: the age of AI tools, where AI doesn’t just give us answers—it provides reliable, tailored responses in seconds. We no longer need to gather and evaluate the correct information for our problems. If knowledge is now a tool everyone can hold, the real revolution starts when we use this superpower to solve problems and improve the world.
It’s been thought that T cells would only move into the brain in the case of a serious problem. New work shows otherwise… | Cell And Molecular Biology
New YT video, featuring RAADFest creator, James Strole!
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Researchers think stopping necrosis, a harmful form of cell death, could prevent inflammation, protect aging organs, and reduce disease risk.
The cloud data company aims to attract customers who want to build their own artificial intelligence agents
By extending the scope of the key insight behind Fermat’s Last Theorem, four mathematicians have made great strides toward building a “grand unified theory” of math.
Researchers have generated Bose-Einstein condensates with a repetition rate exceeding 2 Hz, a feat that could increase the bandwidth of quantum sensors.
New physics may explain discrepant values for the ionization energy of a metastable state of helium.
In the search for new physics beyond the standard model of particle physics, a significant discrepancy between theory and experiment attracts attention, especially in a simple atomic system such as helium. Recently, evidence has appeared for a 9 discrepancy in the ionization energy of the metastable triplet state of helium-4 (4He) [1, 2]. This stands out like a sore thumb in a field where theory and experiment are both highly accurate and normally in agreement. However, in assessing the validity of the discrepancy, there is always the possibility that something has been overlooked or miscalculated. Now Gloria Clausen and Frédéric Merkt of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich have released the results of their latest research [3] in a series of high-precision experiments [1, 4]. Their results (Fig.
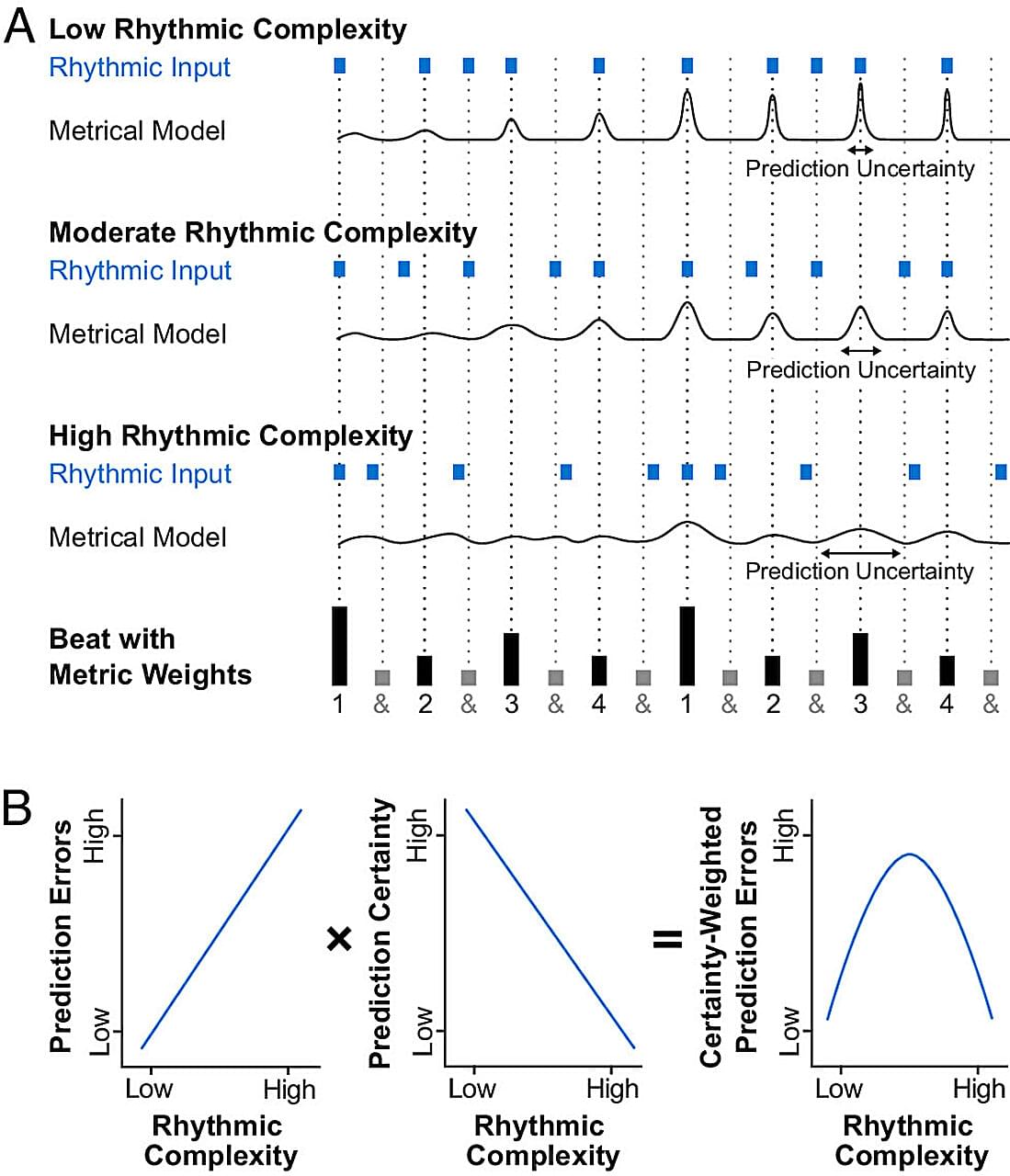
Research led by Aarhus University in Denmark reports that individuals with substance use disorders experience a heightened urge to move in response to music with complex rhythms and harmonies.
Long-term use of cocaine and heroin disrupts dopamine signaling in the brain, depleting receptors and diminishing the effects of non-drug stimuli, such as music, to trigger pleasure.
Prior research has shown that music can activate dopaminergic pathways involved in reward, anticipation, and movement. Groove, the pleasurable urge to move to music, follows an inverted-U pattern in healthy listeners, peaking when rhythms fall into a sweet spot of moderate rhythmic complexity. Most people feel the strongest compulsion to move their bodies to the beat when those beats are neither too simple nor too unpredictable.