Consider the following scenario. There’s a ransomware attack, enhanced by AI, which paralyzes NHS systems—delaying medical care across the country.
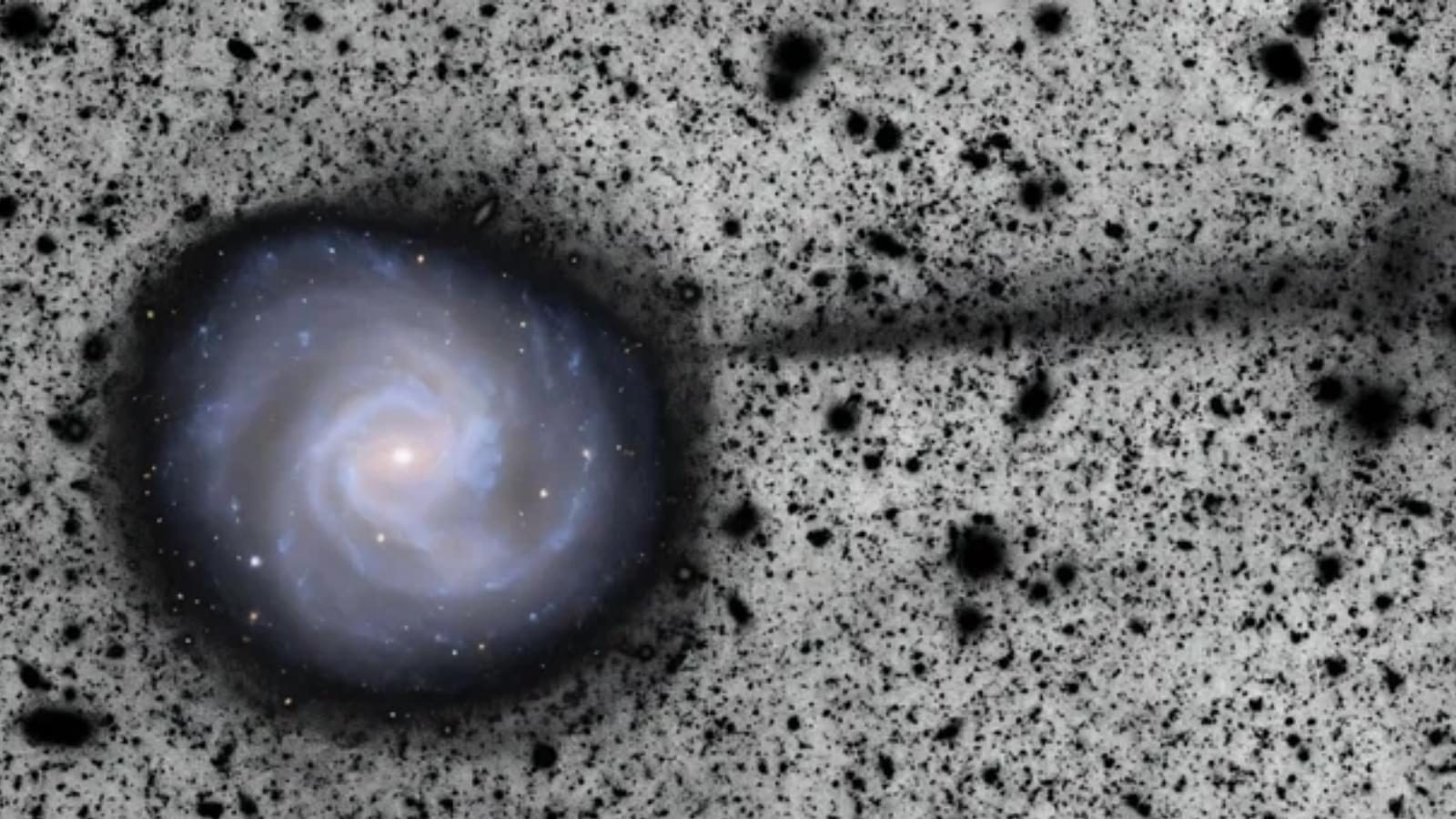




“We are expecting that when Rubin obtains very deep imaging of galaxies, we will see them surrounded by a faint network of stellar streams,” Romanowsky concluded. “The discovery of the stream shows the excellent characteristics of Rubin for making such observations, and points to a rich future of similar discoveries as vast areas of the sky are mapped out.”
The team’s research is available on the paper repository site arXiv.
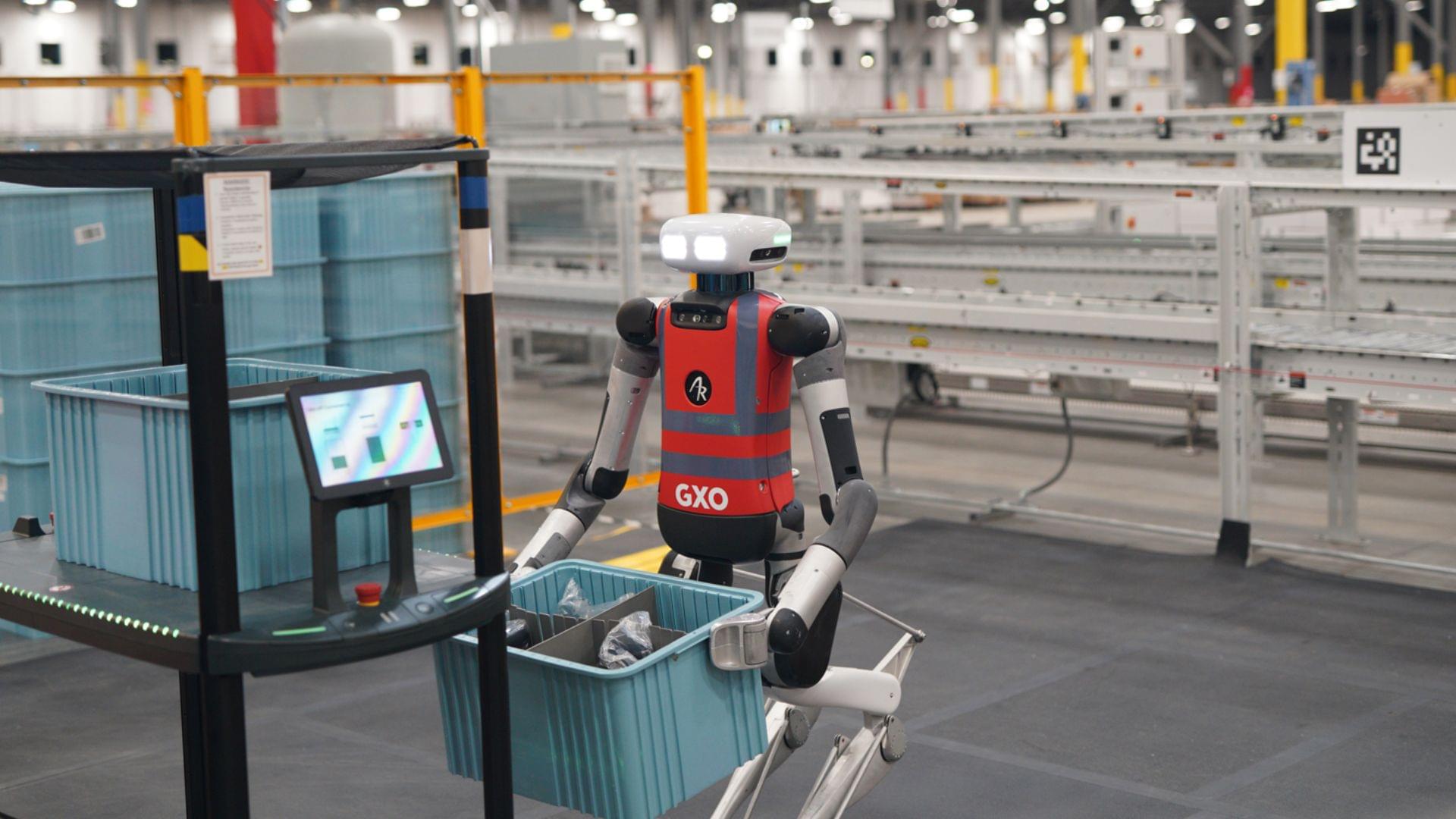



Oregon-based robotics company Agility Robotics announced Thursday that its humanoid robot Digit has moved more than 100,000 totes at a GXO Logistics facility in Flowery Branch, Georgia.
This milestone marks a significant step for the company in proving the practical value of humanoid robots in real-world logistics. Instead of polished demo clips, this result proves the robot can handle real warehouse tasks every day.
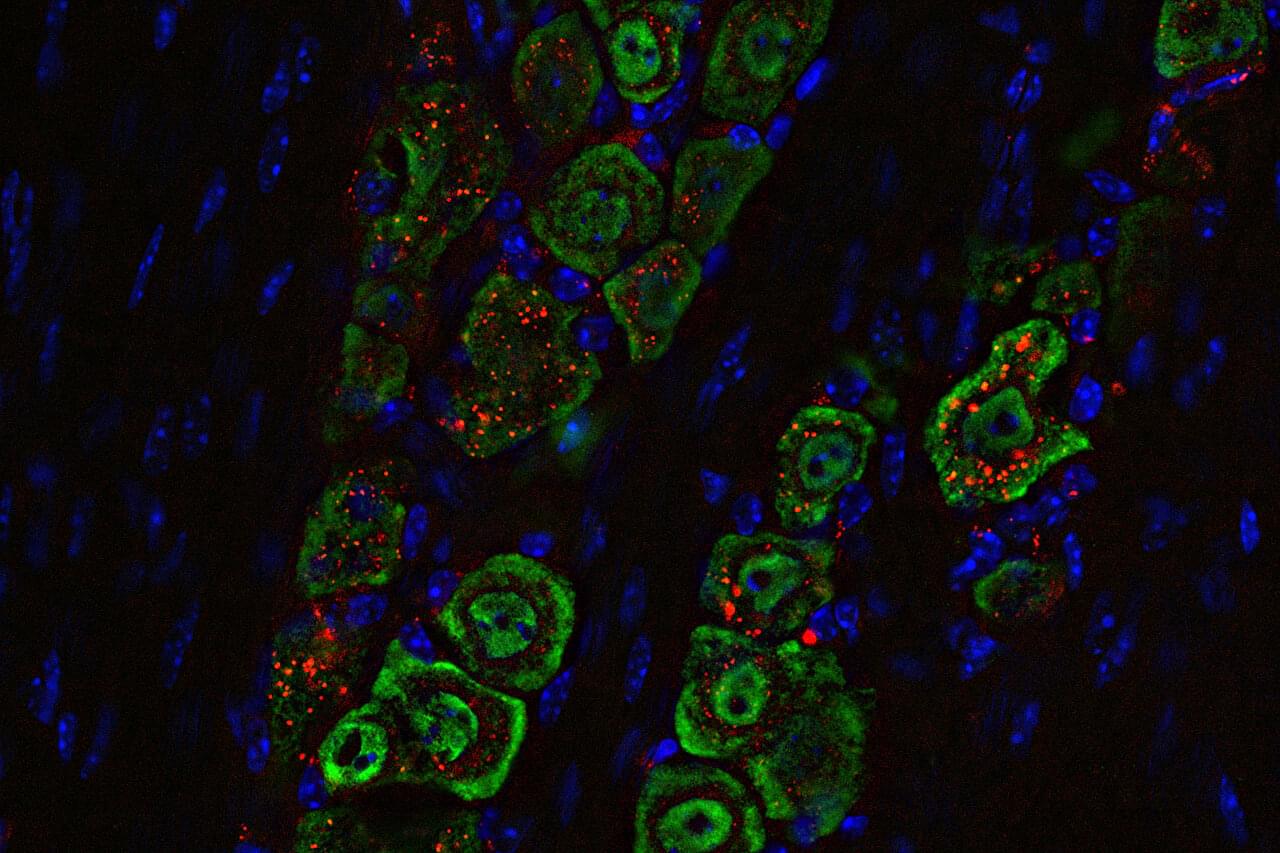
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, along with collaborators at Northwestern University, have developed a noninvasive approach to treat one of the most aggressive and deadly brain cancers. Their technology uses precisely engineered structures assembled from nano-size materials to deliver potent tumor-fighting medicine to the brain through nasal drops. The novel delivery method is less invasive than similar treatments in development and was shown in mice to effectively treat glioblastoma by boosting the brain’s immune response.
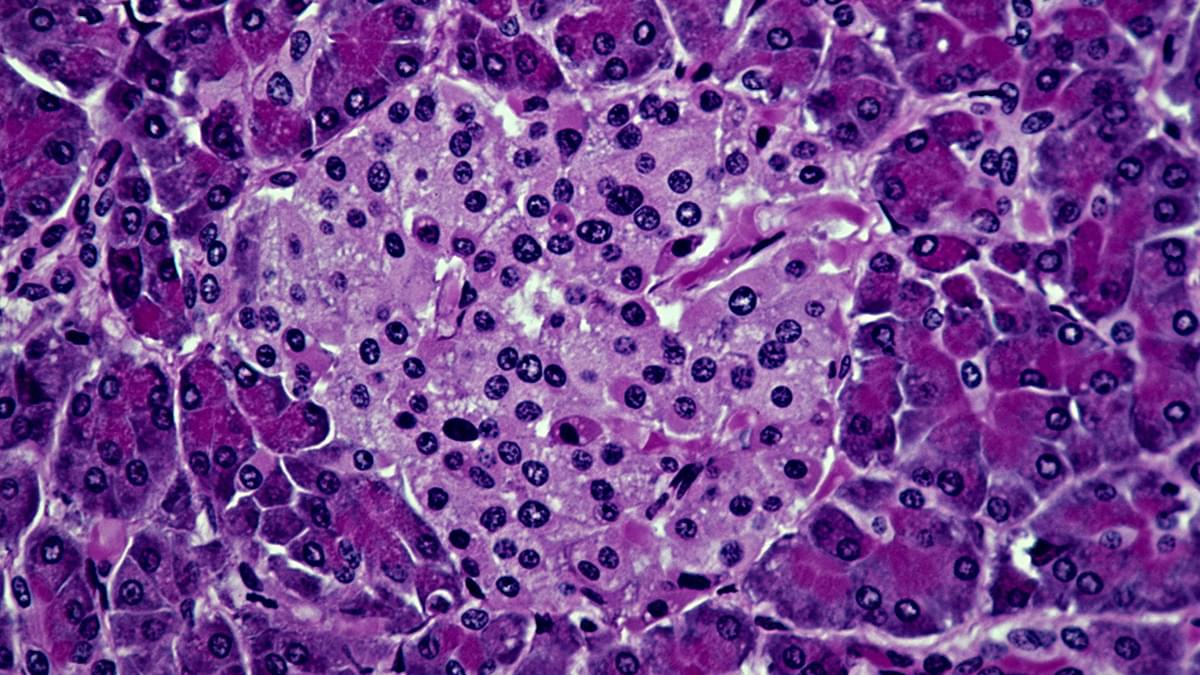
A specially devised hybrid treatment has shown tremendous potential for treating type 1 diabetes in mice, scoring full marks at preventing the condition in prediabetic animals and at reversing the condition in animals with fully developed diabetes.
What makes the new approach stand out is that it successfully combines immune system cells from both the patient mouse and a donor mouse, encouraging them to live in harmony without a need for immunosuppressive drugs for at least four months.
The researchers behind the work, led by a team from the Stanford School of Medicine, are hopeful the same approach could be successful in humans too. The treatment might also have potential for other procedures where transplants are required.
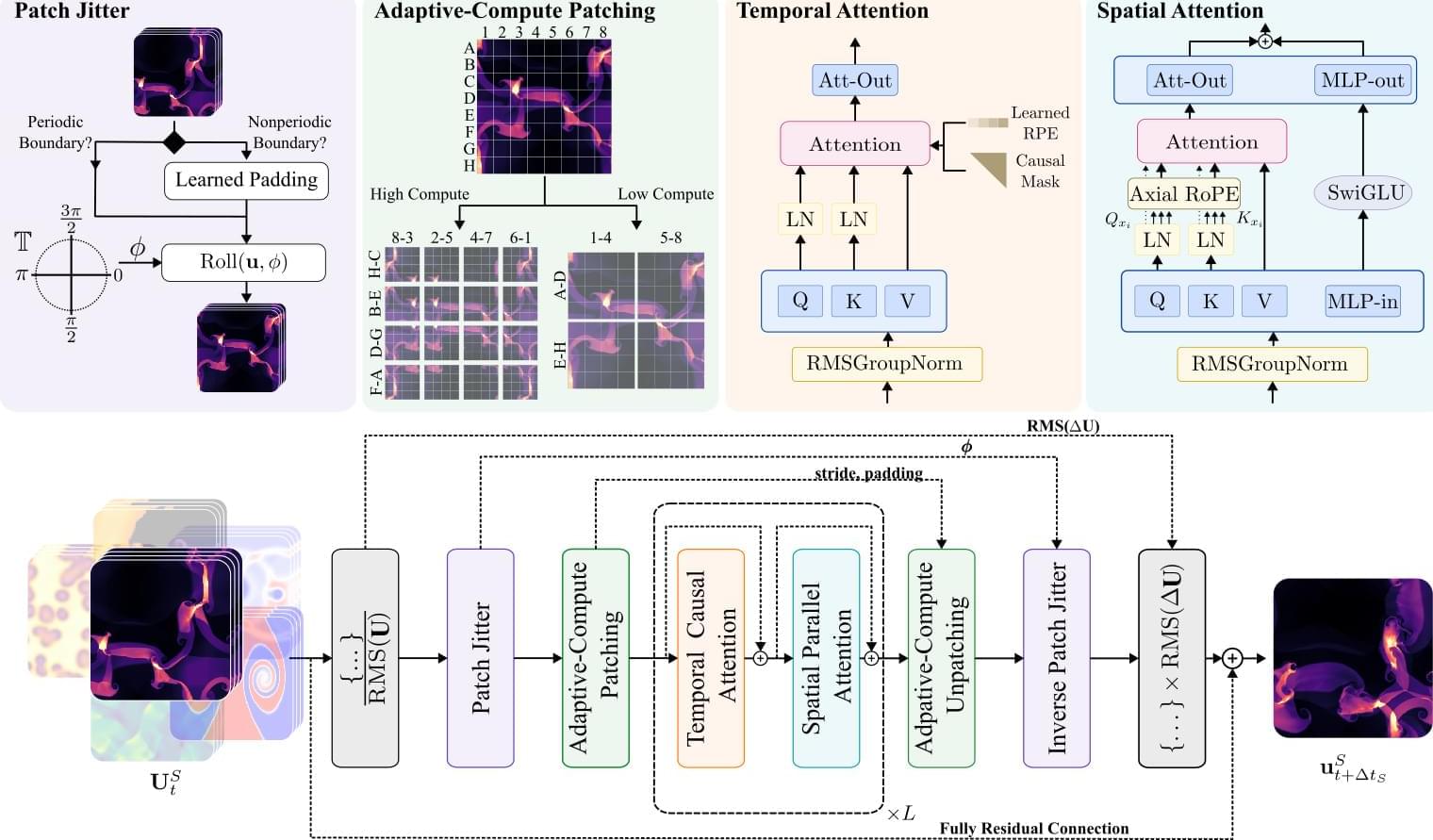
Using simulation-based techniques, scientists can ask how their ideas, actions, and designs will interact with the physical world. Yet this power is not without costs. Cutting edge simulations can often take months of supercomputer time. Surrogate models and machine learning are promising alternatives for accelerating these workflows, but the data hunger of machine learning has limited their impact to data-rich domains. Over the last few years, researchers have sought to side-step this data dependence through the use of foundation models— large models pretrained on large amounts of data which can accelerate the learning process by transferring knowledge from similar inputs, but this is not without its own challenges.
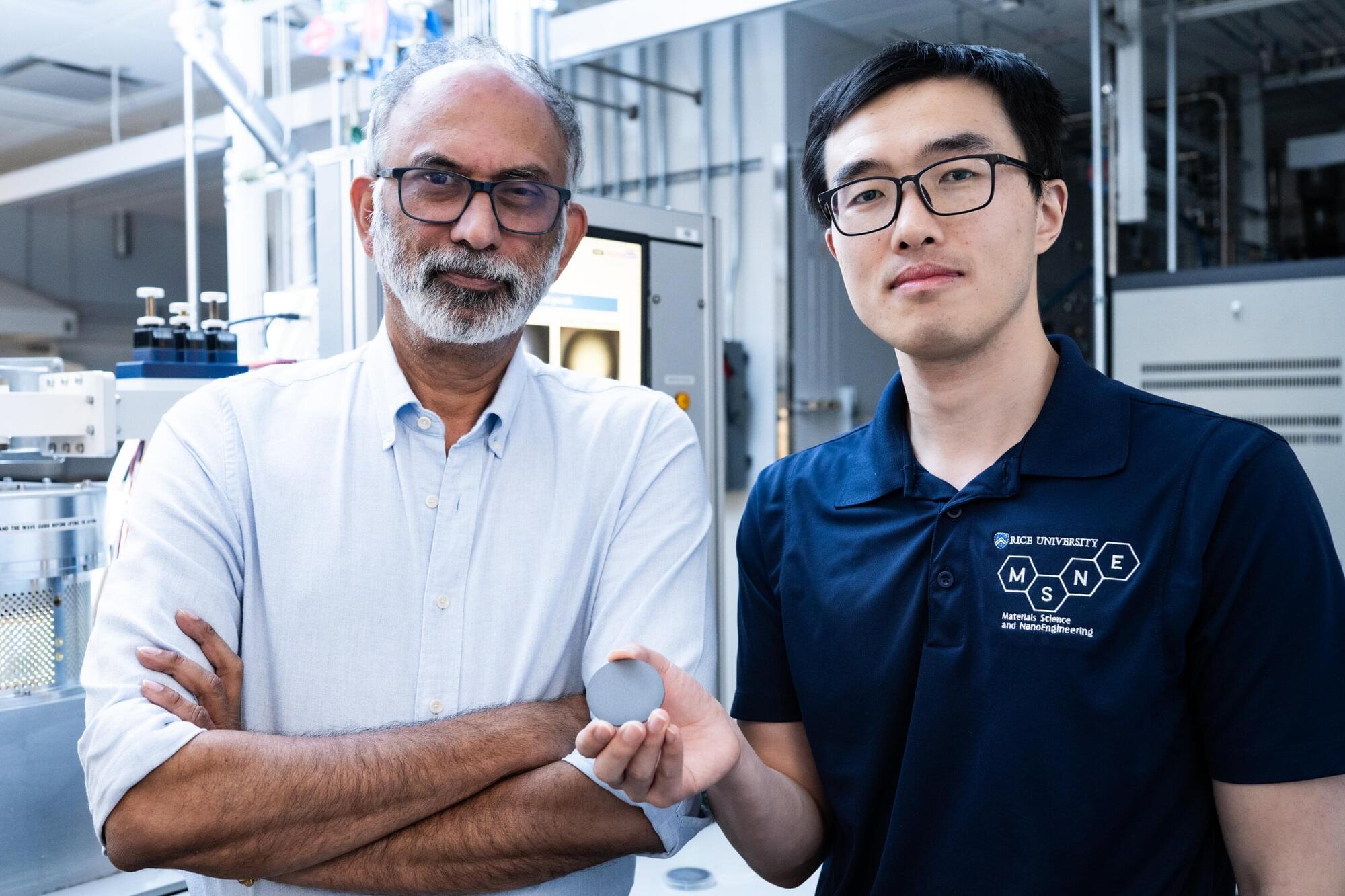
In industrial pipes, mineral deposits build up the way limescale collects inside a kettle ⎯ only on a far larger and more expensive scale. Mineral scaling is a major issue in water and energy systems, where it slows flow, strains equipment and drives up costs.
A new study by Rice University engineers shows that lab-grown diamond coatings could resolve the issue, providing an alternative to chemical additives and mechanical cleaning, both of which offer only temporary relief and carry environmental or operational downsides.
“Because of these limitations, there is growing interest in materials that can naturally resist scale formation without constant intervention,” said Xiang Zhang, assistant research professor of materials science and nanoengineering and a first author on the study alongside Rice postdoctoral researcher Yifan Zhu. “Our work addresses this urgent need by identifying a coating material that can ‘stay clean’ on its own.”