DeepSeek-R1 performs reasoning tasks at the same level as OpenAI’s o1 — and is open for researchers to examine.



Researchers at the Large Hadron Collider tested whether top quarks, the most massive known elementary particles, comply with Einstein’s theory of relativity.
Despite theories suggesting potential deviations at high energies, the experiments confirmed that Lorentz symmetry remains intact, offering no evidence of variation in particle behavior due to the experiment’s orientation or the time of day.
Lorentz Symmetry and Relativity.

However, until now, “measuring this qubit’s spin was like trying to pick up a very, very weak light signal, like trying to squint at some dim light to determine whether the qubit was spin-up or spin-down,” Eric Rosenthal, a postdoctoral scholar at Stanford University, said.
This is where a new study from Rosenthal and his team can make a big difference. They have figured out a way to measure the spin of tin-based qubits with 87 percent accuracy, enhancing the strength of signals from these qubits to a great extent.
A tin vacancy qubit is formed when two carbon atoms in a diamond are replaced by a single tin atom. This tin center has exceptional optical properties as it emits photons in the telecom wavelength range, which is highly suitable for quantum communication applications.
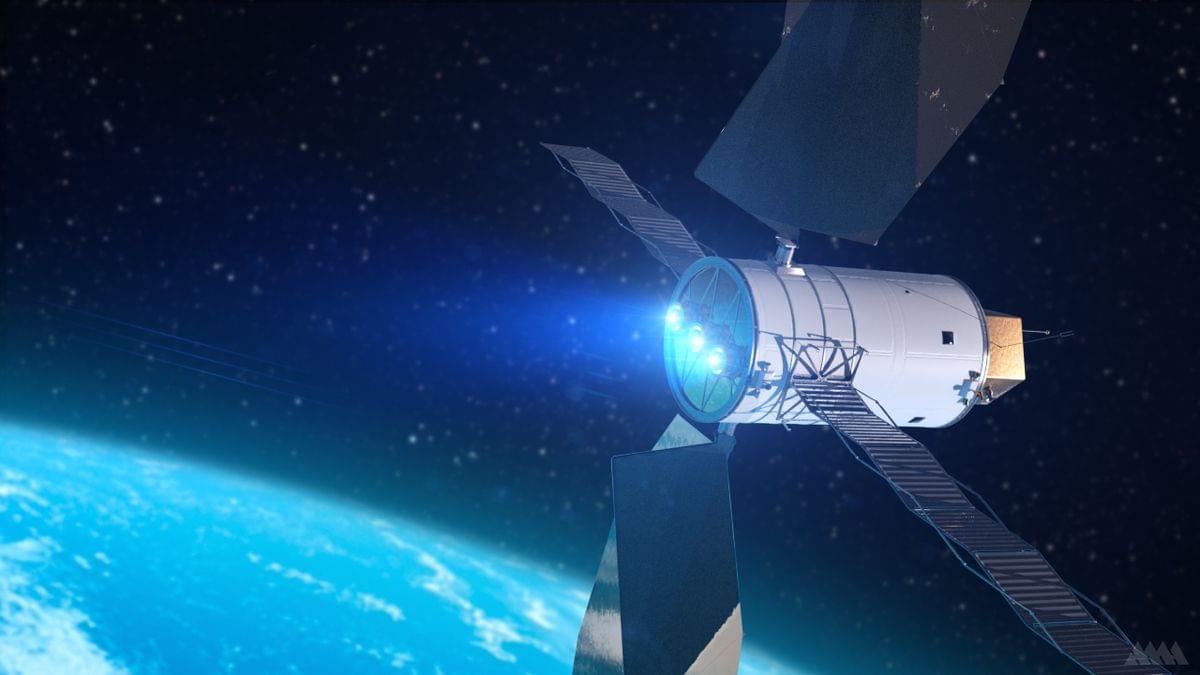
Spacecraft powered by electric propulsion could soon be better protected against their own exhaust, thanks to new supercomputer simulations.
Electric propulsion is a more efficient alternative to traditional chemical rockets, and it’s being increasingly used on space missions, starting off with prototypes on NASA’s Deep Space 1 and the European Space Agency’s SMART-1 in 1998 and 2003, respectively, and subsequently finding use on flagship science missions such as NASA’s Dawn and Psyche missions to the asteroid belt. There are even plans to use electric propulsion on NASA’s Lunar Gateway space station.
For the first time, researchers have measured the shape of an electron as it moves through a solid. This achievement could open a new way of looking at how electrons behave inside different materials.
Their discovery highlights many effects that could be relevant to everything from quantum information science to electronics manufacturing.
Those findings come from a team led by physicist Riccardo Comin, MIT’s Class of 1947 Career Development Associate Professor of Physics and leader of the work, in collaboration with other institutions.
As science wrestles with the thorny job of proving, defining and understanding human consciousness, one pioneering startup aims to apply cutting-edge theories of consciousness to AI models – and create the first sentient AI. This is wild stuff.



El Capitan can reach a peak performance of 2.746 exaFLOPS, making it the National Nuclear Security Administration’s first exascale supercomputer. It’s the world’s third exascale machine after the Frontier supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee and the Aurora supercomputer at the Argonne Leadership Computing Facility, also in Illinois.
The world’s fastest supercomputer is powered by more than 11 million CPU and GPU cores integrated into 43,000+ AMD Instinct MI300A accelerators. Each MI300A APU comprises an EPYC Genoa 24-core CPU clocked at 1.8GHz and a CDNA3 GPU integrated onto a single organic package, along with 128GB of HBM3 memory.

LEV is upon us.
OpenAI chief executive Sam Altman, who provided the initial $180mn to seed the start-up, will put in more money in the series A. The company is in talks with family offices, venture capitalists and sovereign wealth funds, as well as a US “hyperscaler” data centre to provide computing power to run the AI models it uses to create and test its treatments.
In partnership with OpenAI, the start-up has built a bespoke AI model that designs proteins to temporarily turn regular cells into stem cells, which it says can reverse their ageing process.
The San Francisco-based biotech will use the money to fund clinical trials for three drugs, including a potential treatment for Alzheimer’s disease, which will be tested in an early stage study in Australia this year. It is also working on drugs for rejuvenating blood and brain cells.