Scientists are experimenting with enzymes that turn sugar to fiber in the gut, microscopic sponges to soak up sugar, and more.


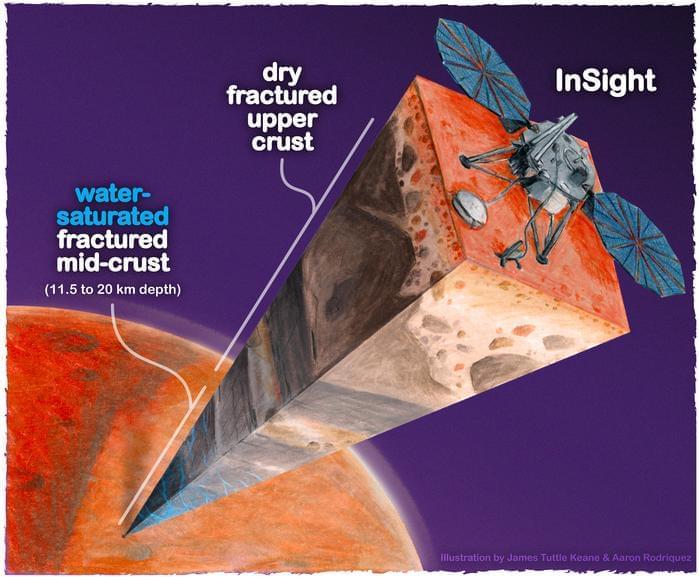
“Establishing that there is a big reservoir of liquid water provides some window into what the climate was like or could be like,” said Dr. Michael Manga.
While Mars is incapable of having liquid water on its surface, what about underground, and how much could there be? This is what a recent study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences hopes to address as a team of researchers investigated how liquid water might be present beneath the Martian surface. This study holds the potential to help researchers not only better understand the current conditions on the Red Planet, but also if these same conditions could have led to life existing on the surface in the past.
For the study, the researchers analyzed seismic data obtained by NASA’s now-retired InSight lander, which landed on Mars in 2018 and sent back valuable data regarding the interior of Mars until the mission ended in 2022. This was after mission planners determined the amount of dust that had collected on the lander’s solar panels did not allow for sufficient solar energy to keep it functioning. However, despite being expired for two years, scientists continued to pour over vast amounts of data regarding the interior of Mars.
Now, after combining this seismic data with models used on Earth to map underground oil fields and aquifers, the researchers determined that igneous rocks (cooled magma) are drenched in liquid water between 11.5 and 20 kilometers (7.15 and 12.4 miles) beneath the Martian surface. Additionally, they ascertained the volume of this liquid water could cover the entire surface of Mars up to approximately one-mile deep. The presence of liquid water beneath the surface could help scientists better understand the water cycle on Mars, but accessing this water for future astronauts or colonists is out of the question given its depth.
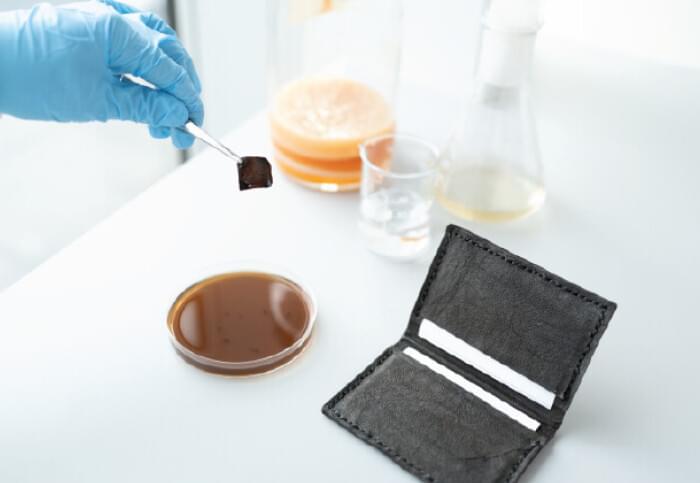

Inventing a new, faster way to produce sustainable, self-dyed leather alternatives is a major achievement for synthetic biology and sustainable fashion. Professor Tom Ellis
Synthetic chemical dyeing is one of the most environmentally toxic processes in fashion, and black dyes – especially those used in colouring leather – are particularly harmful. The researchers at Imperial set out to use biology to solve this.
Get a Wonderful Person Tee: https://teespring.com/stores/whatdamathMore cool designs are on Amazon: https://amzn.to/3QFIrFXAlternatively, PayPal donations ca…


We’ve detected that JavaScript is disabled in this browser. Please enable JavaScript or switch to a supported browser to continue using x.com. You can see a list of supported browsers in our Help Center.
Terms of Service Privacy Policy Cookie Policy Imprint Ads info © 2024 X Corp.

In a new study, a molecule identified and synthesized by UCLA Health researchers was shown to restore cognitive functions in mice with symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease by effectively jumpstarting the brain’s memory circuitry.
If proven to have similar effects in humans, the candidate compound would be novel among Alzheimer’s disease treatments in its ability to revitalize memory and cognition, study authors said.
There is really nothing like this on the market or experimentally that has been shown to do this.

How can older trees help combat climate change? This is what a recent study published in Nature Climate Change hopes to address as an international team of researchers investigated changes in woody biomass in older trees that have been while exposed to free-air CO2 enrichment (FACE) resulting from climate change. This study holds the potential to help researchers, climate scientists, and the public better understand the steps that can be taken to decrease CO2 emissions and combat climate change worldwide.
For the study, the researchers, led by the University of Birmingham’s Institute of Forest Research (BIFoR), conducted a FACE experiment through a combination of canopy laser scanning and tree-ring analysis to examine the 180-year-old Quercus robur L. woodland in central England between 2021and 2022. The goal was ascertaining the effectiveness of older trees compared to younger trees regarding their consumption of CO2, also known as CO2 storage. In the end, the researchers found increased levels of CO2 compared to ambient conditions in 2021 and 2022, respectively, equivalent to 1.7 tons of dry matter per hectare per year.
“Our findings refute the notion that older, mature forests cannot respond to rising levels of atmospheric CO2, but how they respond will likely depend on the supply of nutrients from the soil,” said Dr. Richard Norby from the University of Birmingham, who is lead author of the study. “Evidence from BIFoR FACE of a significant increase in woody biomass production supports the role of mature, long-established, forests as natural climate solutions in the coming decades while society strives to reduce its dependency on carbon.”
