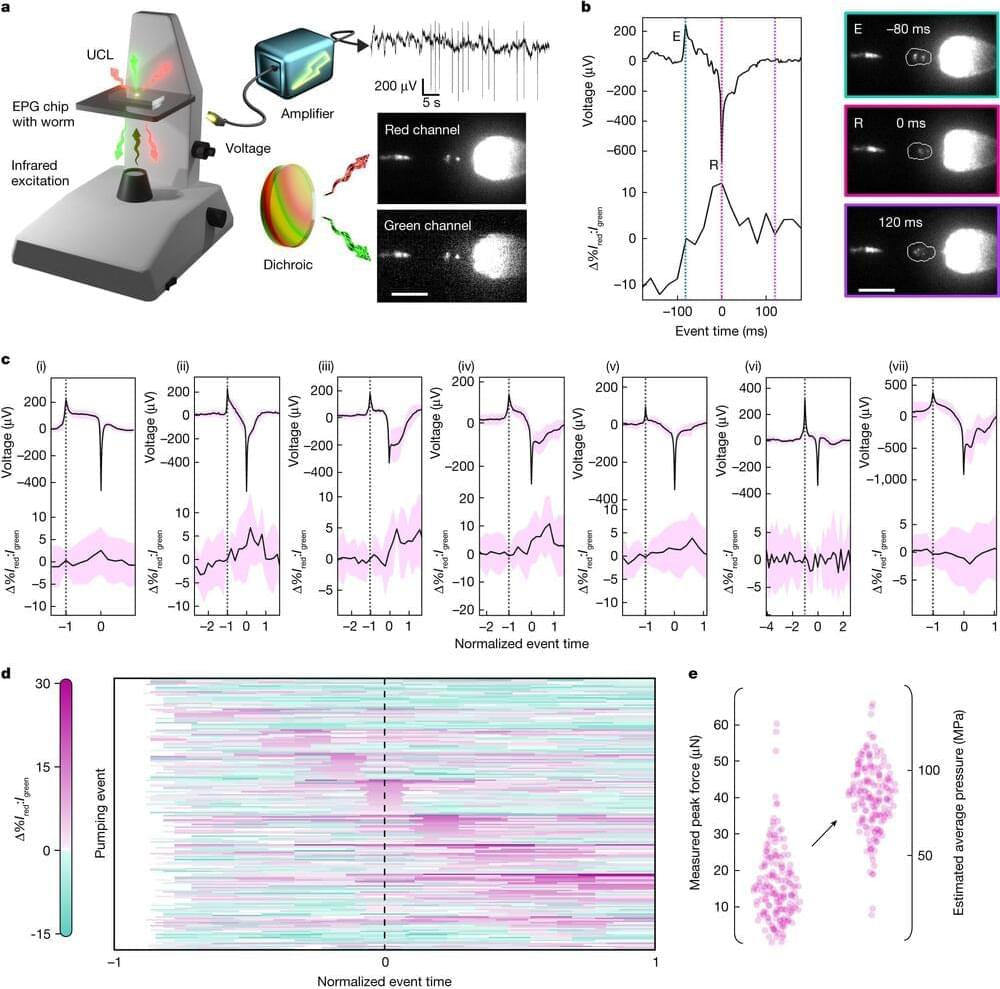
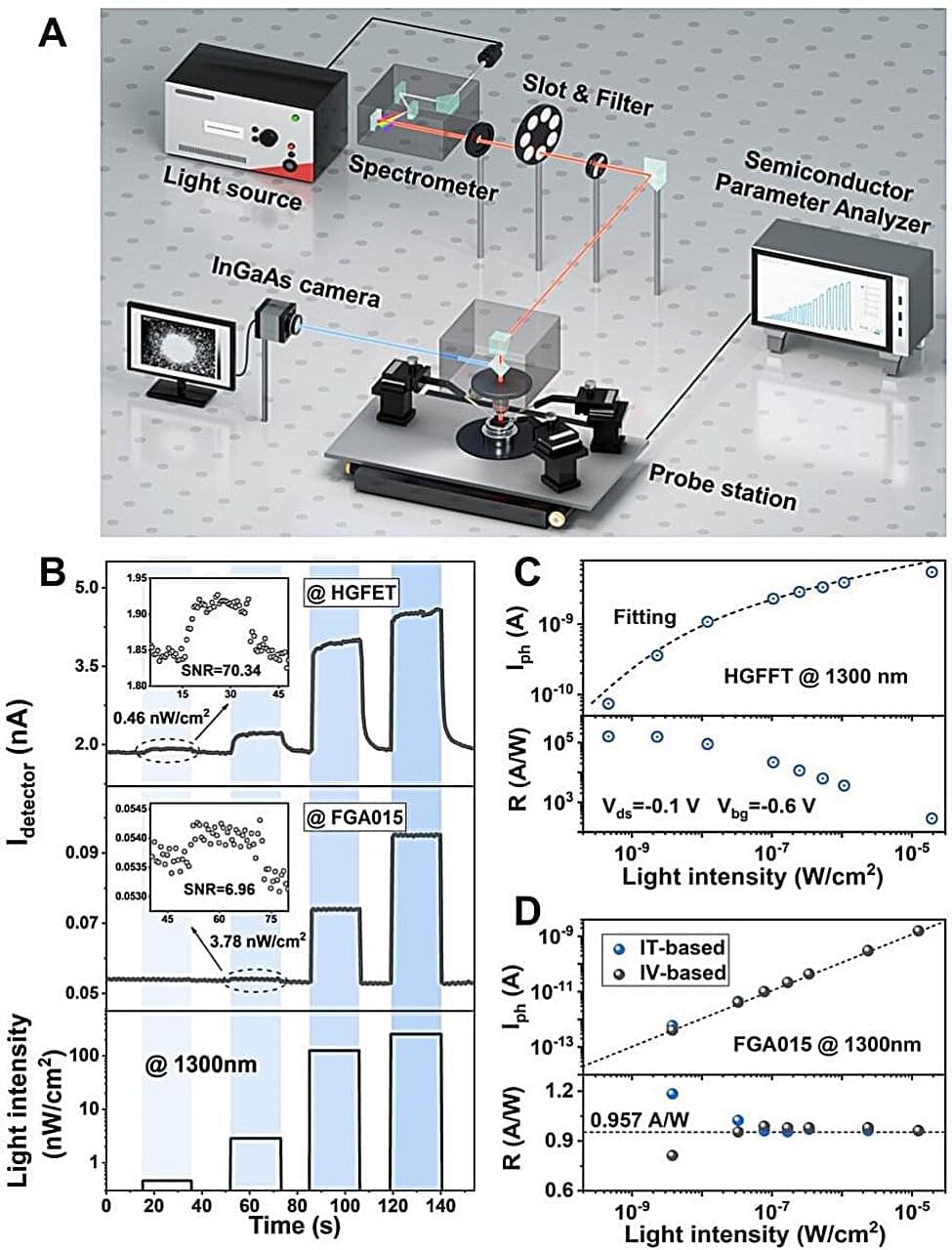
A team of materials scientists, physicists, mechanical engineers, and molecular physiologists at Stanford University have developed a nanoparticle technique that can be used to measure force dynamics inside a living creature, such as Caenorhabditis elegans worms biting their food.
In their paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how they used infrared radiation to excite luminescent nanocrystals in a way that allowed the energy levels of cells inside a C. elegans worm to be measured.
Andries Meijerink, with Utrecht University, has published a News & Views piece in the same journal issue, outlining the work done by the team in California.