A large-scale analysis of more than 130,000 adults with chronic insomnia found that long-term melatonin use—defined as one year or more—was associated with a striking increase in heart failure, hospitalization, and mortality risk.


The study notes in its conclusions, “We have presented G-FLight printing as an effective tool for the rapid gravity-independent fabrication of aligned tissues, focusing on muscle tissue as an application.”
Can muscle tissue be 3D-printed in outer space to improve astronaut health? This is what a recent study published in Advanced Science hopes to address as a team of scientists investigated how human tissue can be manufactured in space. This study has the potential to help scientists, researchers, and the public better understand new methods for not only aiding in long-term space travel but also combating diseases on Earth.
For the study, the researchers used a series of parabolic flights to test G-FLight (Gravity-independent Filamented Light), which is a novel 3D printing biomanufacturing system capable of producing muscle cells and fibers in a matter of seconds. The purpose of the parabolic flights was to simulate microgravity, which is produced by the airplane sharply diving after gradually rising in altitude. The goal of the study was to ascertain if G-Flight could successfully 3D-print muscle fibers under microgravity conditions. In the end, the researchers found that G-FLight successfully produced muscle fibers under microgravity conditions during parabolic flights.

Pancreas development in pigs resembles humans much more closely than does the established mouse model. An international team headed by Helmholtz Munich and the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD) has now produced a comprehensive evolutionary comparison of single-cell atlases of pancreas development. The results open up new prospects for regenerative therapies.
For decades, the pancreas and its development have been a major focus of diabetes and cancer research. Until now, the science was almost exclusively based on mouse models. However, mice differ from humans in many respects—from developmental duration to metabolism and gene regulation.
“Particularly for complex diseases such as diabetes mellitus, we need models that truly resemble humans,” therefore emphasizes Prof. Heiko Lickert. The DZD researcher is the director of the Institute of Diabetes and Regeneration Research at Helmholtz Munich and professor at the Technical University of Munich (TUM).



How much do undergraduate computer science students trust chatbots powered by large language models like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT? And how should computer science educators modify their teaching based on these levels of trust?
These were the questions that a group of U.S. computer scientists set out to answer in a study that will be presented at the Koli Calling conference Nov. 11 to 16 in Finland. In the course of the study’s few weeks, researchers found that trust in generative AI tools increased in the short run for a majority of students.
But in the long run, students said they realized they needed to be competent programmers without the help of AI tools. This is because these tools often generate incorrect code or would not help students with code comprehension tasks.
A humanoid robot chef’s kitchen test went off the rails and the internet can’t stop watching.
A viral clip shows Unitree’s G1 humanoid attempting to cook — only to spill food, slip, and crash spectacularly.

Dopamine is often called the brain’s “motivation molecule,” but for me, it represents something deeper, a window into how fragile our neurons can be. The cells that produce dopamine, known as dopaminergic neurons, are among the first to die in Parkinson’s disease, leading to the motor symptoms that gradually rob patients of movement and independence.
To understand what makes these neurons so vulnerable, I used an in-vitro model where I exposed N27 dopaminergic cells to 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA), a toxin that triggers oxidative stress, like what occurs in the Parkinsonian brain. Then, I introduced Selenomethionine (SeMet), an organic form of selenium, to test whether this compound could counteract the damage and help the neurons survive.
Selenium has long intrigued scientists for its paradoxical nature. It is a trace element essential for antioxidant defense, yet in excess it can become toxic. I wanted to see whether a specific range of SeMet concentrations could offer meaningful protection without tipping that balance. My study, carried out at Charles University and the National Institute of Mental Health (NUDZ) in the Czech Republic, set out to define that “safe and effective window.” It is published in the journal In vitro models.

At Money20/20 I learned that Fintech has a new power couple, AI and Trust.
The combination of the two is the payment protocol of tomorrow. Come along with me as I share my findings from the world’s #1 fintech show.
There is bunch of interviews and images forthcoming from the event.
Thanks again to Tedd Huff of Fintech Confidential for inviting me to participate in the event. It allowed me to share My Instant AI with event attendees.
(https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/fintechs-new-power-couple-ai-…urke-eirte)
Tedd Huff asked me to be a confidential informant in Las Vegas recently. But, wait before you go down conspiracy theory rabbit hole, please let me explain.
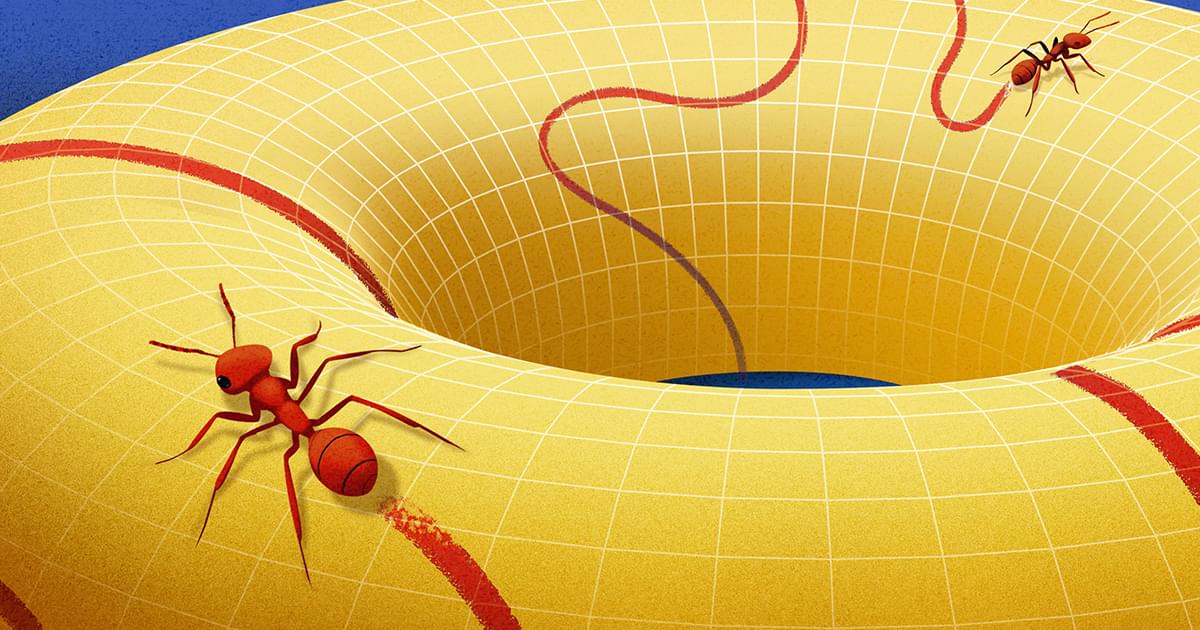
Standing in the middle of a field, we can easily forget that we live on a round planet. We’re so small in comparison to the Earth that from our point of view, it looks flat.
The world is full of such shapes — ones that look flat to an ant living on them, even though they might have a more complicated global structure. Mathematicians call these shapes manifolds. Introduced by Bernhard Riemann in the mid-19th century, manifolds transformed how mathematicians think about space. It was no longer just a physical setting for other mathematical objects, but rather an abstract, well-defined object worth studying in its own right.
This new perspective allowed mathematicians to rigorously explore higher-dimensional spaces — leading to the birth of modern topology, a field dedicated to the study of mathematical spaces like manifolds. Manifolds have also come to occupy a central role in fields such as geometry, dynamical systems, data analysis and physics.