A massive genetic analysis of over one million people has revealed that APOE, long known for its role in Alzheimer’s disease, also independently increases a person’s risk of delirium.
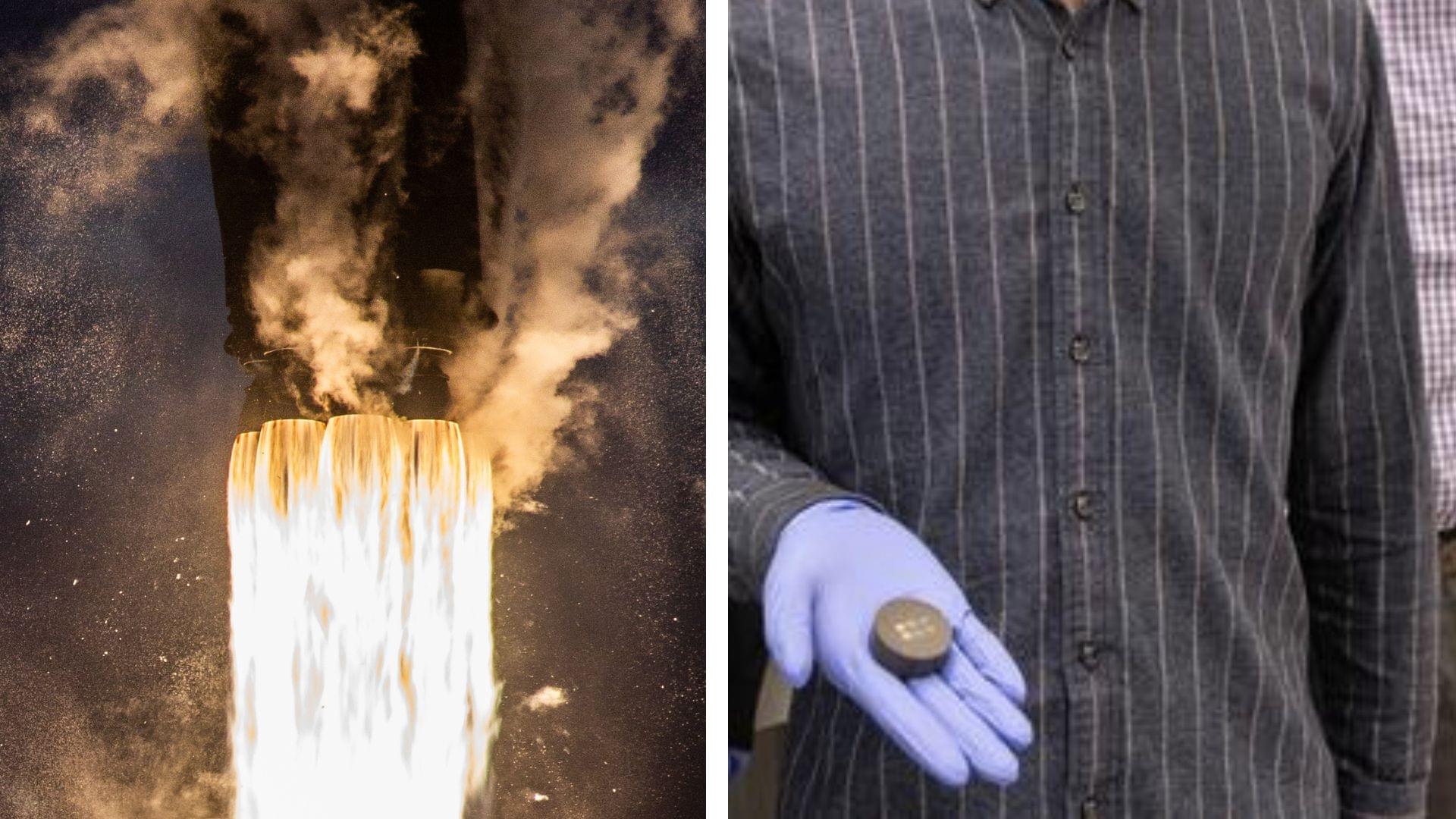



Researchers have developed very light and extremely strong material that can withstand extreme heat. The material could be useful for aerospace and other high-performance industries.
Developed by researchers from University of Toronto Engineering, the material can withstand temperatures up to 932°F (500° C).
The new composite material is made of various metallic alloys and nanoscale precipitates, and has a structure that mimics that of reinforced concrete, but on a microscopic scale.

Amazon founder Jeff Bezos is stepping back into an active operating role in technology after four years, taking the co‑chief executive seat at a new artificial intelligence company called Project Prometheus. His move adds to the trend of tech billionaires emerging from semi‑retirement to participate directly in the AI boom reshaping Silicon Valley’s priorities.
Reportedly, Bezos will lead the startup alongside Vik Bajaj, a physicist‑chemist and former Google researcher who helped launch Verily, Alphabet’s life sciences unit. Project Prometheus has already raised about 6.2 billion dollars, including a substantial personal commitment from Bezos, placing it among the best‑funded early‑stage AI companies in the world.
Bezos has remained executive chair of Amazon and continued to back Blue Origin, his private space company, but Prometheus is his first formal operational role since he stepped down as Amazon’s CEO in 2021. The venture comes amid an intensifying global race to build advanced AI systems, as companies across the United States, Europe, and China pour money into research, data centres, and specialist talent.
From cyborgs to hive minds and civilizations of pure thought, we trace the possible futures of our species through the next trillion tomorrows.
Checkout Scav: https://go.nebula.tv/scav?ref=isaacar… Watch my exclusive video Autonomous Space Industry: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–… Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Grab one of our new SFIA mugs and make your morning coffee a little more futuristic — available now on our Fourthwall store! https://isaac-arthur-shop.fourthwall… Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a… Facebook Group:
/ 1,583,992,725,237,264 Reddit:
/ isaacarthur Twitter:
/ isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content. SFIA Discord Server:
/ discord Credits: The First Interstellar Colony Humanity’s Leap Beyond Sol Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur Editor: Keith Oxenrider Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images Music by Epidemic Sound: http://nebula.tv/epidemic & Stellardrone Chapters 0:00 Intro 0:15 The Road Ahead 2:24 What Do We Mean by “Human,” “Transhuman,” and “Posthuman”? 7:22 Life Extension – The Oldest Dream 10:33 Intelligence Beyond Biology – AI and Human Integration 14:19 Enhancing the Body and Mind 17:00 Civilizations of the Augmented 19:31 Scavenger Hunt 20:51 Strange Posthuman Pathways 23:11 Outward Migration – Stars and Timelines 25:00 Risks, Fears, and Pushback 26:27 Humanity on Cosmic Timescales 27:43 The Expanding Story.
Watch my exclusive video Autonomous Space Industry: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–…
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Grab one of our new SFIA mugs and make your morning coffee a little more futuristic — available now on our Fourthwall store! https://isaac-arthur-shop.fourthwall…
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
The First Interstellar Colony Humanity’s Leap Beyond Sol.
Written, Produced & Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Editor: Keith Oxenrider.
Select imagery/video supplied by Getty Images.
Music by Epidemic Sound: http://nebula.tv/epidemic & Stellardrone.
Chapters.
0:00 Intro.
0:15 The Road Ahead.
2:24 What Do We Mean by “Human,” “Transhuman,” and “Posthuman”?
7:22 Life Extension – The Oldest Dream.
10:33 Intelligence Beyond Biology – AI and Human Integration.
14:19 Enhancing the Body and Mind.
17:00 Civilizations of the Augmented.
19:31 Scavenger Hunt.
20:51 Strange Posthuman Pathways.
23:11 Outward Migration – Stars and Timelines.
25:00 Risks, Fears, and Pushback.
26:27 Humanity on Cosmic Timescales.
27:43 The Expanding Story
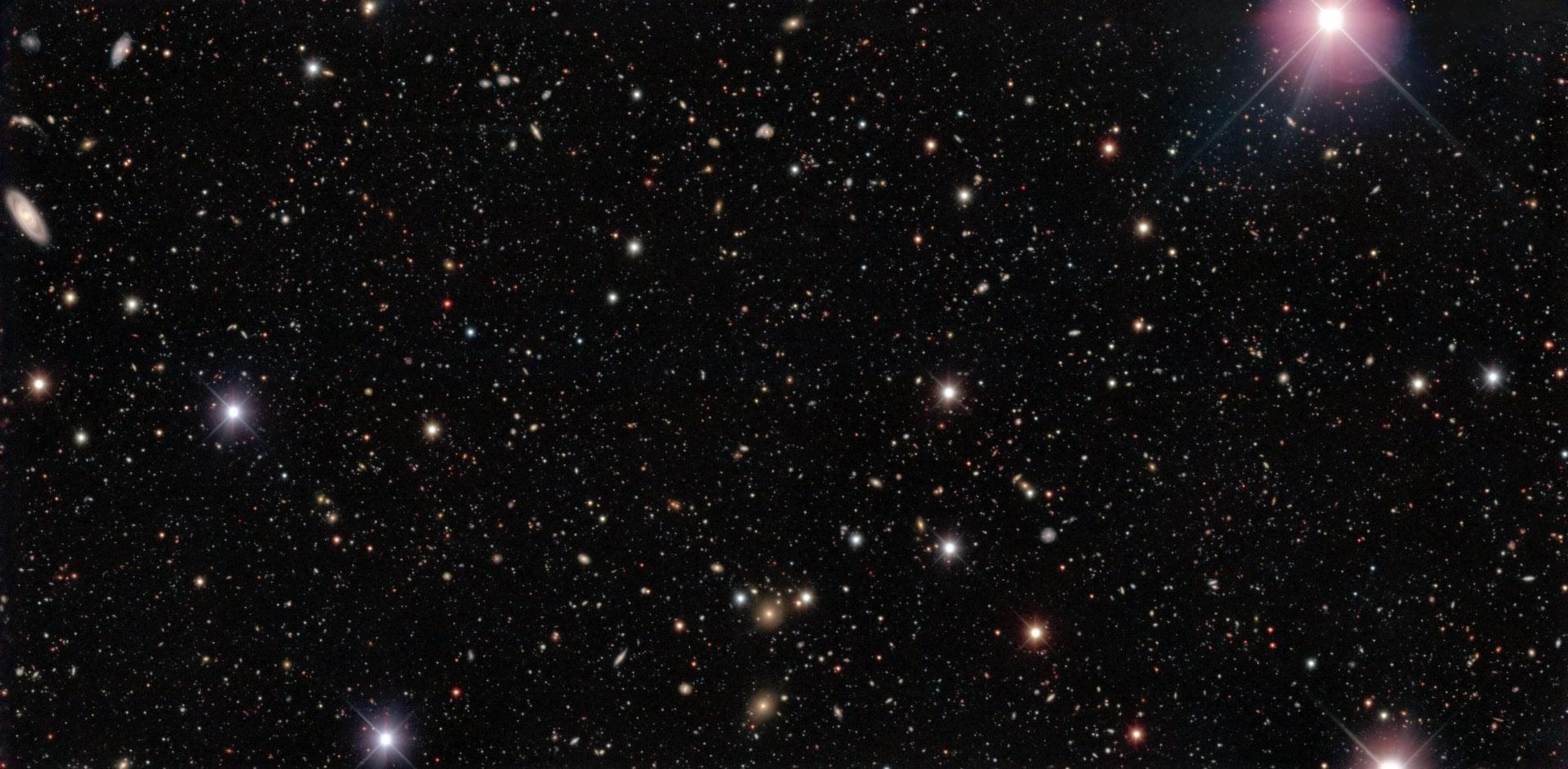

An expanding universe complicates this picture just a little bit, because the universe absolutely refuses to be straightforward. Objects are still emitting light, and that light takes time to travel from them over to here, but in that intervening time the universe grows larger, with the average distance between galaxies getting bigger (yes, I know that sometimes galaxies can collide, but we’re talking on average, at big scales here).
So when we see an image of a distant galaxy, and that light has traveled for billions of years to finally end in our telescopes, we don’t know how far away that galaxy is right now, at the moment that we get the light. We have to turn to a cosmological model that incorporates the expansion history of the universe, so we know how much the universe has grown in a given amount of time.
Our current best model of the universe is called LCDM, which involved both dark matter (different episode) and dark energy (different episode). We can discuss the relative merits and weaknesses of LCDM (different episode), but for now let’s just take it as a given, as deviations from LCDM don’t really change the picture much.
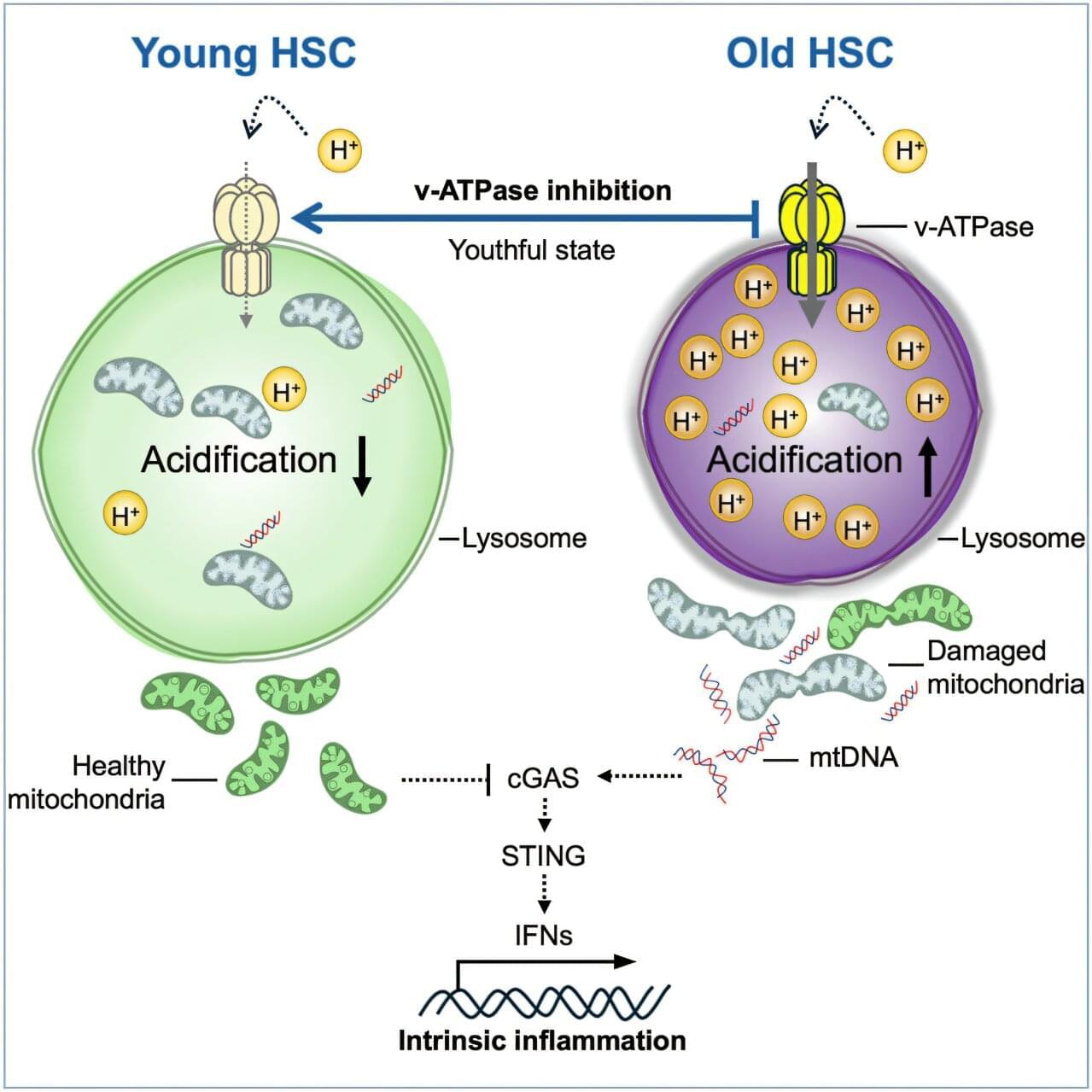
Researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have discovered how to reverse aging in blood-forming stem cells in mice by correcting defects in the stem cell’s lysosomes. The breakthrough, published in Cell Stem Cell, identifies lysosomal hyperactivation and dysfunction as key drivers of stem cell aging and shows that restoring lysosomal slow degradation can revitalize aged stem cells and enhance their regenerative capacity.
Lysosomes are specialized structures that act as the cell’s recycling system, breaking down proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids. Lysosomes accumulate and degrade waste, and eventually recycle it to be reused in biosynthetic processes. Lysosomes can also store nutrients to be released when needed. Lysosomes are recognized as pivotal for regulating metabolism in the cell, both catabolism (breaking down complex molecules to simple ones) and anabolism (building complex molecules from simpler ones).
The study, led by corresponding author Saghi Ghaffari, MD, Ph.D., Professor of Cell, Developmental, and Regenerative Biology at the Icahn School of Medicine and a member of the Black Family Stem Cell Institute, focuses on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). These are the rare long-lived cells in the bone marrow responsible for generating all blood and immune cells.
Researchers have suspected for some time that the link between our gut and brain plays a role in the onset of Parkinson’s disease.
A recent study identified gut microbes likely to be involved and linked them with decreased riboflavin (vitamin B2) and biotin (vitamin B7), suggesting an unexpectedly simple treatment that may help: B vitamins.
“Supplementation therapy targeting riboflavin and biotin holds promise as a potential therapeutic avenue for alleviating Parkinson’s symptoms and slowing disease progression,” said medical researcher Hiroshi Nishiwaki from Nagoya University in Japan, when the paper was published in May 2024.