Data from NISAR will improve our understanding of such phenomena as earthquakes, volcanoes, and landslides, as well as damage to infrastructure.
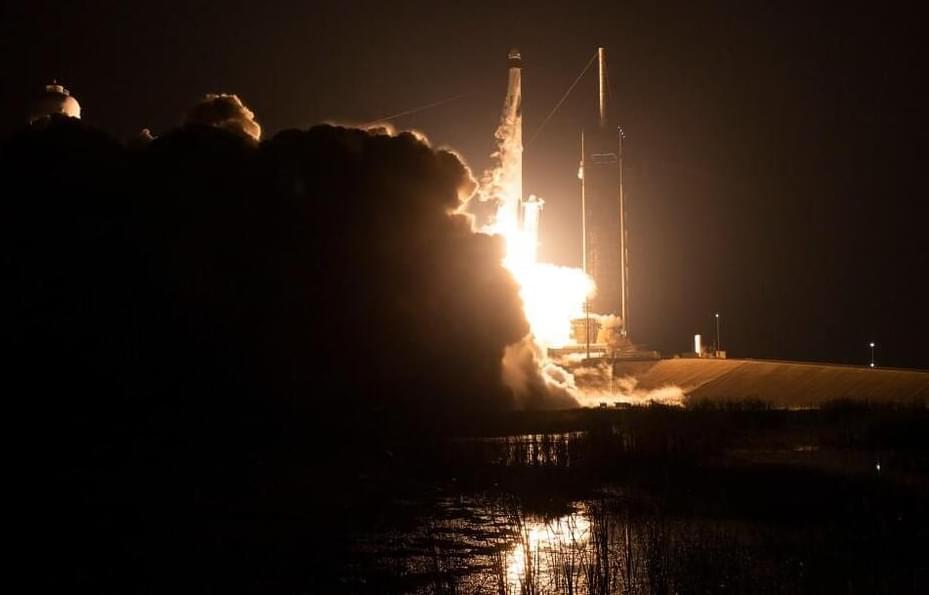
We don’t always notice it, but much of Earth’s surface is in constant motion. Scientists have used satellites and ground-based instruments to track land movement associated with volcanoes, earthquakes, landslides, and other phenomena. But a new satellite from NASA and the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) aims to improve what we know and, potentially, help us prepare for and recover from natural and human-caused disasters.
The NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) mission will measure the motion of nearly all of the planet’s land and ice-covered surfaces twice every 12 days. The pace of NISAR’s data collection will give researchers a fuller picture of how Earth’s surface changes over time. “This kind of regular observation allows us to look at how Earth’s surface moves across nearly the entire planet,” said Cathleen Jones, NISAR applications lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California.