Theoretical physicists have long been trying to devise a complete theory of gravity that would also account for quantum mechanics phenomena, as existing models do not. Such a theory could collectively explain the many intricate physical and cosmological phenomena observed over the past decades.
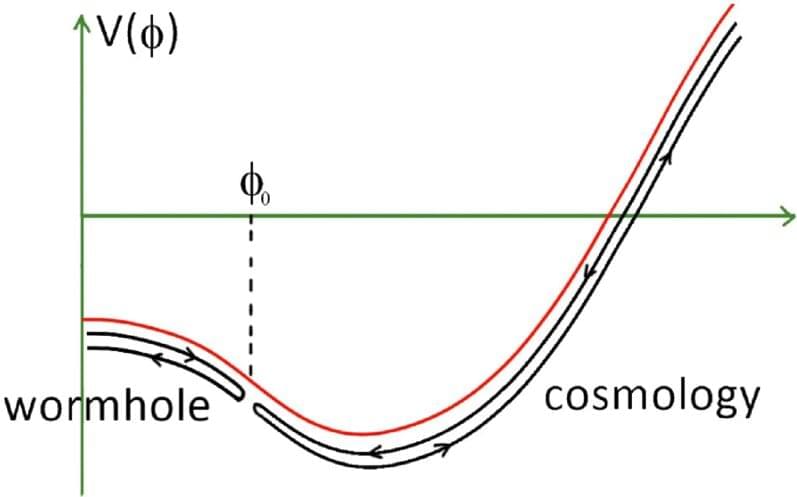
Researchers at University of Maryland and University of British Columbia recently carried out a theoretical study exploring the possibility that holography, an approach to quantum gravity that includes some features of conventional holograms, could be used to describe quantum mechanical phenomena. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, introduces a theoretical argument that could suggests a link between observable cosmological phenomena and the physics that would underpin wormhole spacetimes.
“Coming up with a theory of gravity that includes the physics of quantum mechanics has been a major forefront area in theoretical physics for decades,” Mark Van Raamsdonk, one of the researchers who carried out the study, told Phys.org. “This is necessary to really understand the physics of black holes and the Big Bang, and to make progress towards a fully unified theory of physics.