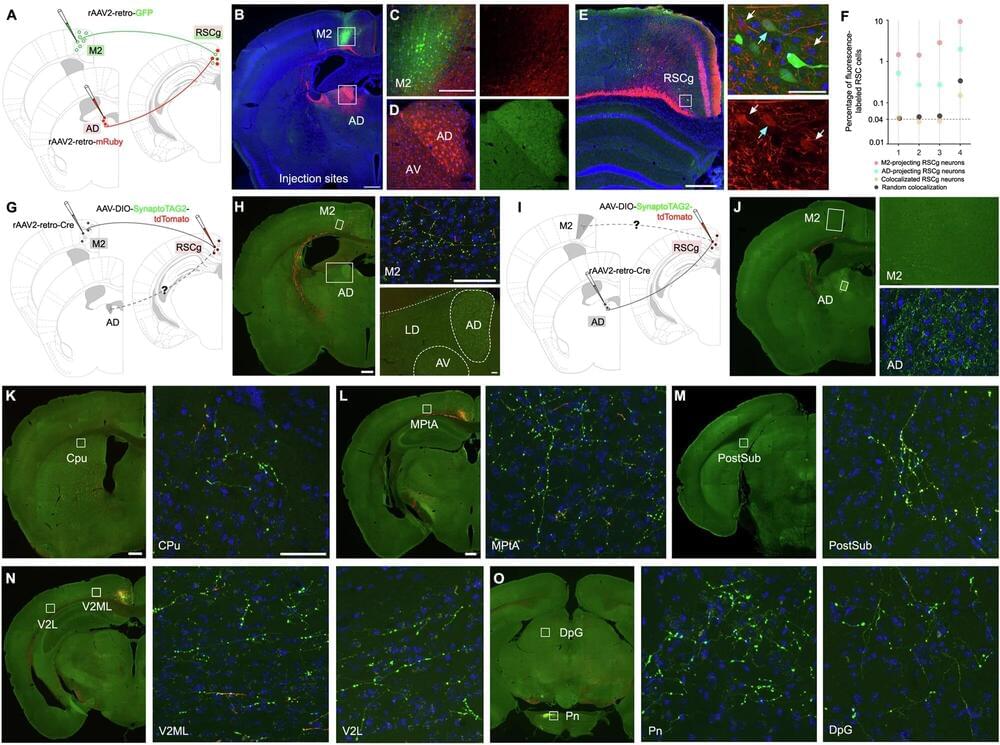
Researchers led by the University of California, Irvine are the first to reveal how two neural circuits located in the brain’s retrosplenial cortex are directly linked to spatial navigation and memory storage. This discovery could lead to more precise medical treatments for Alzheimer’s disease and other cognitive disorders by allowing them to target pathway-specific neural circuits.
The study, published in Molecular Psychiatry, identified two types of RSC pathways, connected to different parts of the brain, each with its own pattern of inputs and functions.
“By demonstrating how specific circuits in the RSC contribute to different aspects of cognition, our findings provide an anatomical foundation for future studies and offer new insights into how we learn and remember the space around us,” said lead and co-corresponding author Xiangmin Xu, UC Irvine Chancellor’s Professor of anatomy and neurobiology and director of the campus’s Center for Neural Circuit Mapping.