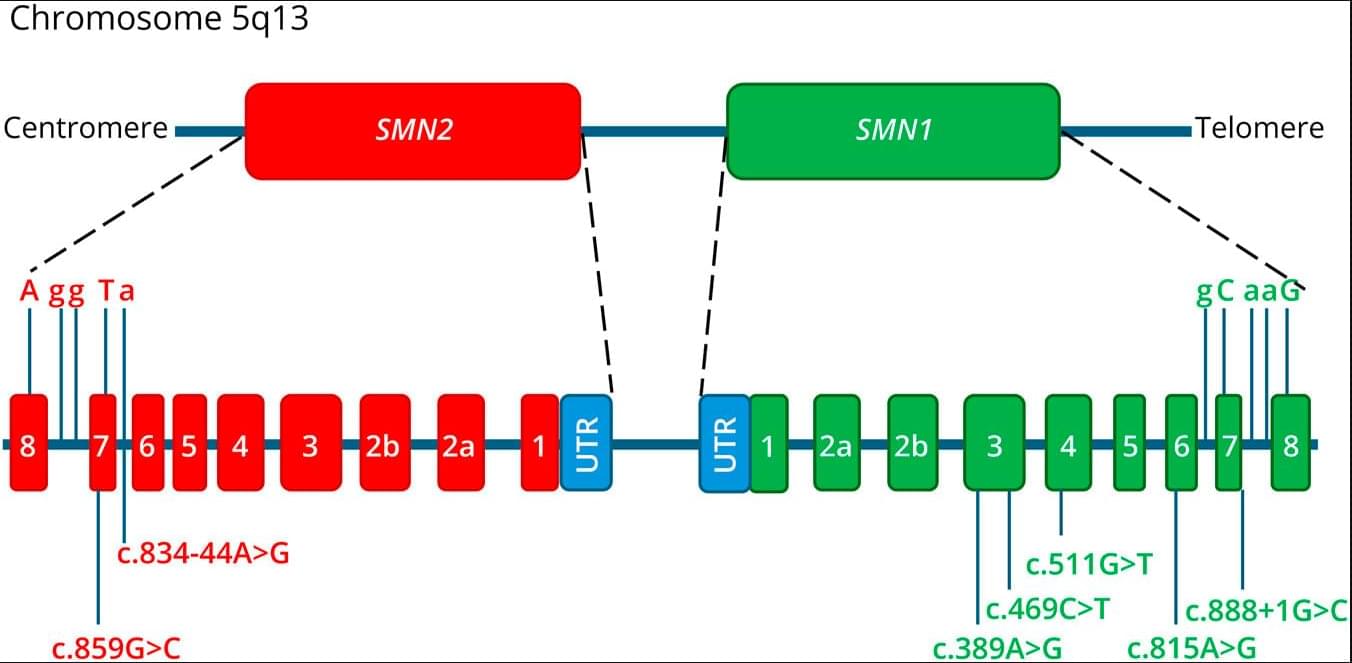
Background and ObjectivesSpinal muscular atrophy 5q (SMA) is a motor neuron disorder caused by recessive pathogenic variants in the SMN1 gene, which encodes the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. While the majority of patients with SMA exhibit…

Presented by Scans Factory.

The asteroid Bennu continues to provide new clues to scientists’ biggest questions about the formation of the early solar system and the origins of life. As part of the ongoing study of pristine samples delivered to Earth by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, and Security-Regolith Explorer) spacecraft, three new papers published Tuesday by the journals Nature Geosciences and Nature Astronomy present remarkable discoveries: sugars essential for biology, a gum-like substance not seen before in astromaterials, and an unexpectedly high abundance of dust produced by supernova explosions.
Scientists led by Yoshihiro Furukawa of Tohoku University in Japan found sugars essential for biology on Earth in the Bennu samples, detailing their findings in the journal Nature Geoscience. The five-carbon sugar ribose and, for the first time in an extraterrestrial sample, six-carbon glucose were found. Although these sugars are not evidence of life, their detection, along with previous detections of amino acids, nucleobases, and carboxylic acids in Bennu samples, show building blocks of biological molecules were widespread throughout the solar system.
For life on Earth, the sugars deoxyribose and ribose are key building blocks of DNA and RNA, respectively. DNA is the primary carrier of genetic information in cells. RNA performs numerous functions, and life as we know it could not exist without it. Ribose in RNA is used in the molecule’s sugar-phosphate “backbone” that connects a string of information-carrying nucleobases.

Cornell scientists have discovered a potentially transformative approach to manufacturing one of the world’s most widely used chemicals—hydrogen peroxide—using nothing more than sunlight, water and air. The research is published in the journal Nature Communications.
“Currently, hydrogen peroxide is made through the anthraquinone process, which relies on fossil fuels, produces chemical waste and requires transport of concentrated peroxide—all of which have safety and environmental concerns,” said Alireza Abbaspourrad, associate professor of Food Chemistry and Ingredient Technology in the Department of Food Science in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, and corresponding author of the research.
Hydrogen peroxide is ubiquitous in both industrial and consumer settings: It bleaches paper, treats wastewater, disinfects wounds and household surfaces, and plays a key role in electronics manufacturing. Global production runs into the millions of tons each year. Yet today’s process depends almost entirely on a complex method involving hazardous intermediates and large-scale central chemical plants.
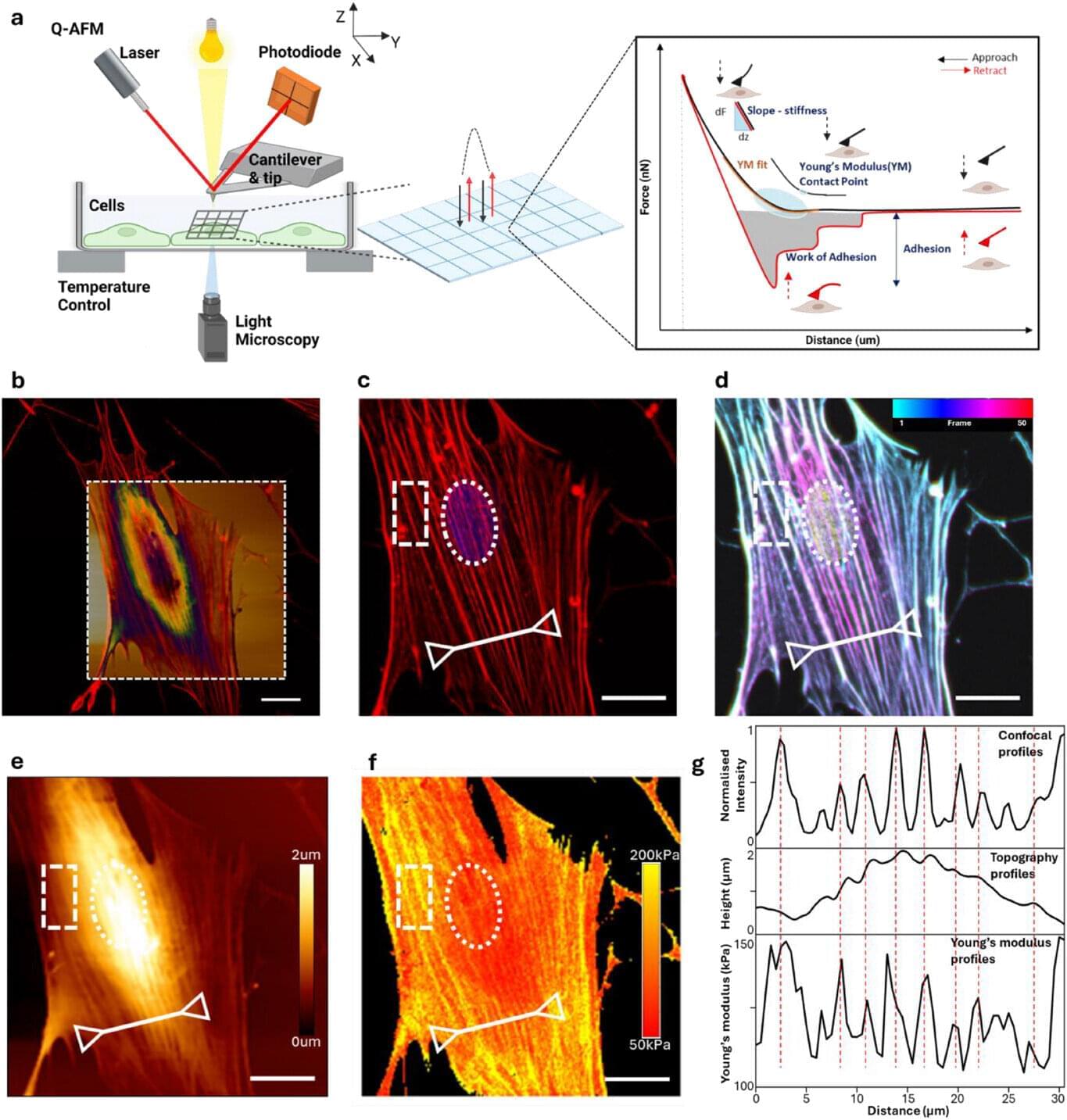
Scientists in Melbourne have discovered how tiny electrical pulses can steer stem cells as they grow, opening the door to new improved ways of creating new tissues, organs, nerves and bones.
Dr. Amy Gelmi, a senior lecturer at RMIT University’s School of Science, led the work using advanced atomic force microscopy to track how stem cells change their structure when exposed to electrical stimulation.
The study reveals, for the first time, how living stem cells physically respond to external signals in real time—reshaping themselves within minutes and setting off changes that influence what type of cell they eventually become. The paper is published in the journal Advanced Materials Interfaces.

California State University, Sacramento, researchers traced how disordered childhood social worlds in women connected to faster life history traits and greater mating effort, with those traits explaining 22.2% of the association between childhood microsystems and adult sexual behavior.
Life History theory treats childhood ecology as a starting point for strategies that govern survival, mating effort, and parental effort. Mating effort involves behavior that increases access to sexual opportunities, while parental effort involves investing time and resources so children survive to reproduce.
Faster strategies align with earlier sexual debut, more short-term mating, more lifetime partners, and more offspring at younger ages. Slower strategies align with later sexual debut, safer reproductive behavior such as monogamy and contraceptive use, fewer lifetime partners, and greater parental investment.

Americans who grow up in historically violent states may move to a safer state, but they remain far more likely to die violently, according to new research co-authored at the University of California, Berkeley.
In effect, the research finds, people who migrate from states with a strong “culture of honor” bring with them a don’t-back-down defensiveness learned in their home communities. That makes them more likely to die by violence wherever they are, says the study led by UC Berkeley political scientist Gabriel Lenz, a specialist in crime and criminal justice.
The study, “Migration and the Persistence of Violence,” was published today in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Lenz’s co-authors were Martin Vinæs Larsen, an associate professor of political science at Aarhus University in Denmark, and Anna Mikkelborg, a Berkeley Ph.D. graduate and now an assistant professor of political science at Colorado State University.
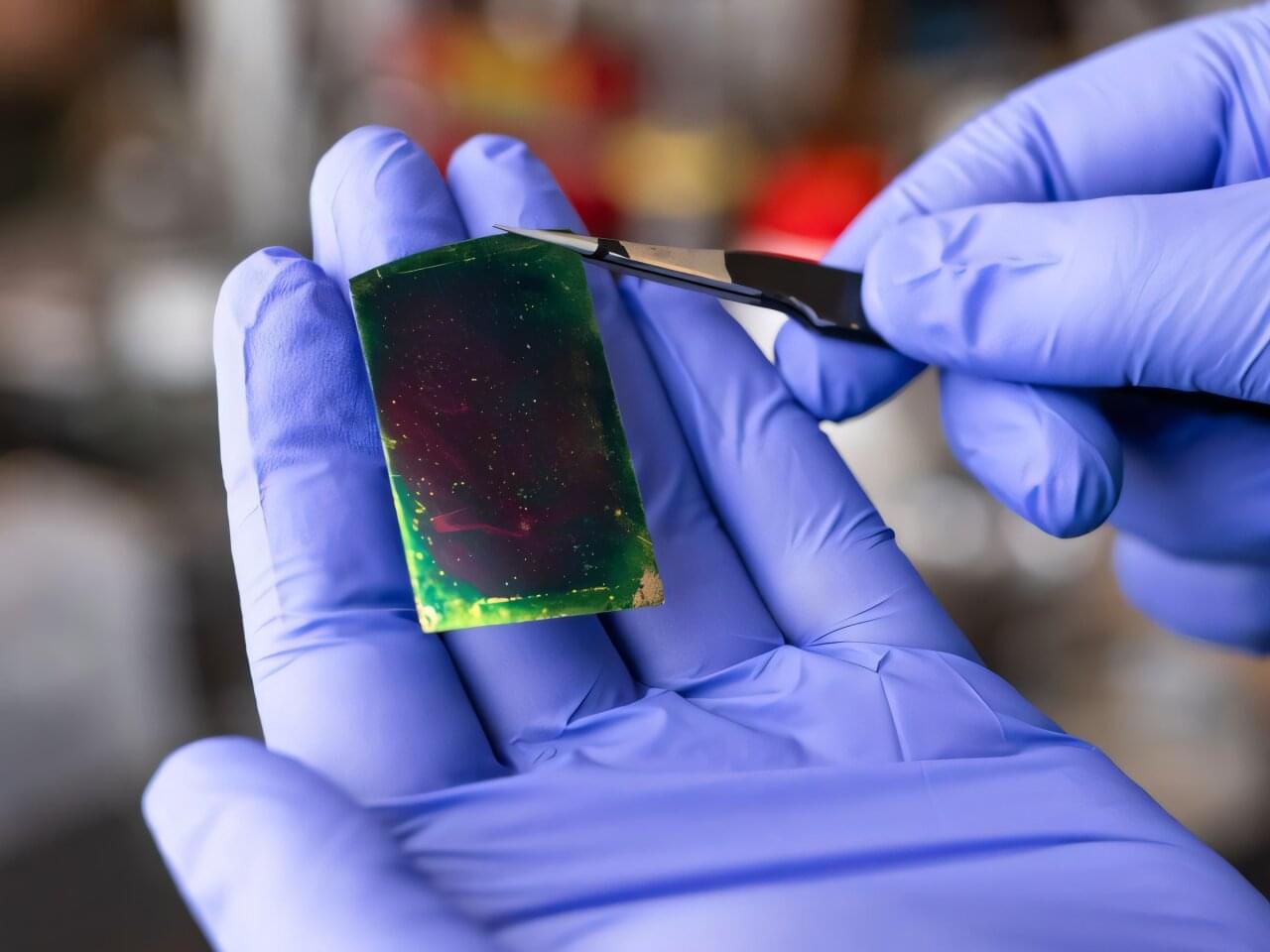
Addressing the staggering power and energy demands of artificial intelligence, engineers at the University of Houston have developed a revolutionary new thin-film material that promises to make AI devices significantly faster while dramatically cutting energy consumption.
The breakthrough, detailed in the journal ACS Nano, introduces a specialized two-dimensional (2D) thin film dielectric —or an electric insulator—designed to replace traditional, heat generating components in integrated circuit chips. This new thin film material, which does not store electricity, will help reduce the significant energy cost and heat produced by the high-performance computing necessary for AI.
“AI has made our energy needs explode,” said Alamgir Karim, Dow Chair and Welch Foundation Professor at the William A. Brookshire Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at UH.