Traditional large language model (LLM) agent systems face significant challenges when deployed in real-world scenarios due to their limited flexibility and adaptability. Existing LLM agents typically select actions from a predefined set of possibilities at each decision point, a strategy that works well in closed environments with narrowly scoped tasks but falls short in more complex and dynamic settings. This static approach not only restricts the agent’s capabilities but also requires considerable human effort to anticipate and implement every potential action beforehand, which becomes impractical for complex or evolving environments. Consequently, these agents are unable to adapt effectively to new, unforeseen tasks or solve long-horizon problems, highlighting the need for more robust, self-evolving capabilities in LLM agents.
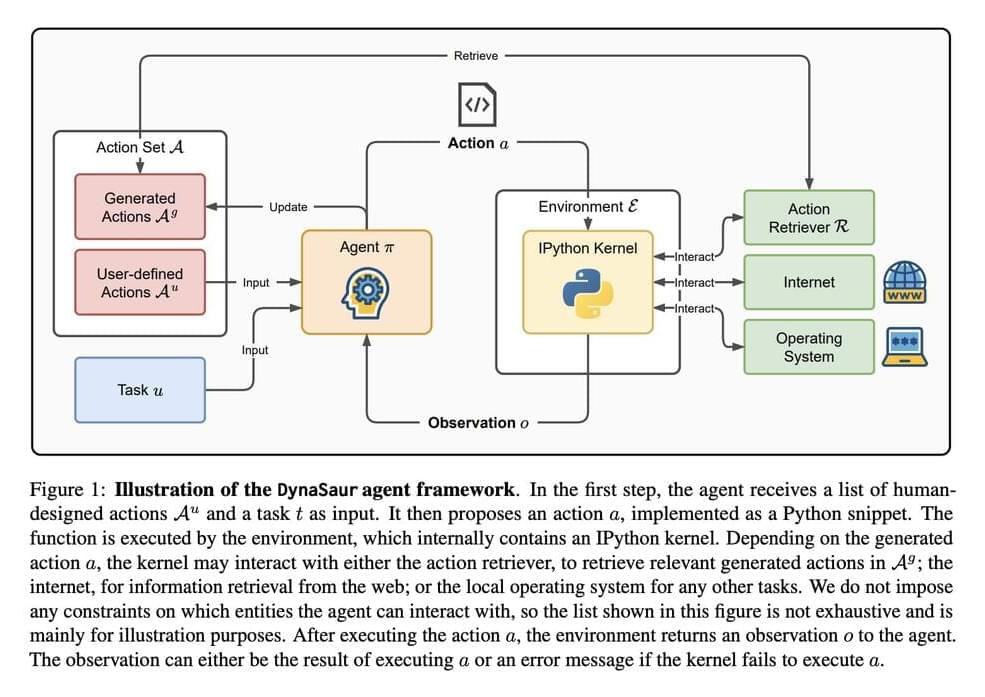
Researchers from the University of Maryland and Adobe introduce DynaSaur: an LLM agent framework that enables the dynamic creation and composition of actions online. Unlike traditional systems that rely on a fixed set of predefined actions, DynaSaur allows agents to generate, execute, and refine new Python functions in real-time whenever existing functions prove insufficient. The agent maintains a growing library of reusable functions, enhancing its ability to respond to diverse scenarios. This dynamic ability to create, execute, and store new tools makes AI agents more adaptable to real-world challenges.
The technical backbone of DynaSaur revolves around the use of Python functions as representations of actions. Each action is modeled as a Python snippet, which the agent generates, executes, and assesses in its environment. If existing functions do not suffice, the agent dynamically creates new ones and adds them to its library for future reuse. This system leverages Python’s generality and composability, allowing for a flexible approach to action representation. Furthermore, a retrieval mechanism allows the agent to fetch relevant actions from its accumulated library using embedding-based similarity search, addressing context length limitations and improving efficiency.