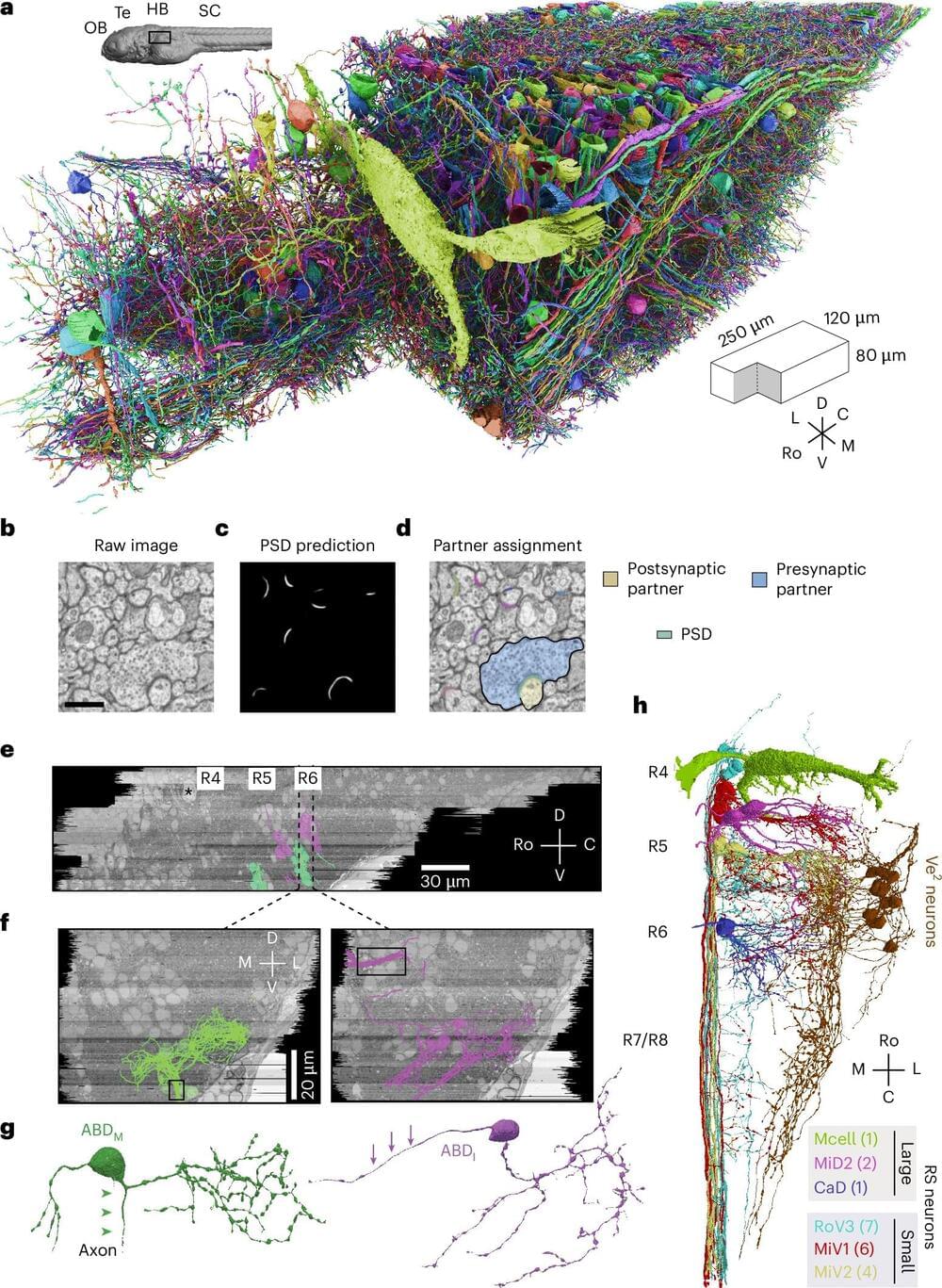
Working with week-old zebrafish larva, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues decoded how the connections formed by a network of neurons in the brainstem guide the fishes’ gaze.
The study, published Nov. 22 in Nature Neuroscience, found that a simplified artificial circuit, based on the architecture of this neuronal system, can predict activity in the network. In addition to shedding light on how the brain handles short-term memory, the findings could lead to novel approaches for treating eye movement disorders.
Organisms are constantly taking in an array of sensory information about the environment that is changing from one moment to the next. To accurately assess a situation, the brain must retain these informational nuggets long enough to use them to form a complete picture—for instance, linking together the words in a sentence or allowing an animal to keep its eyes directed to an area of interest.