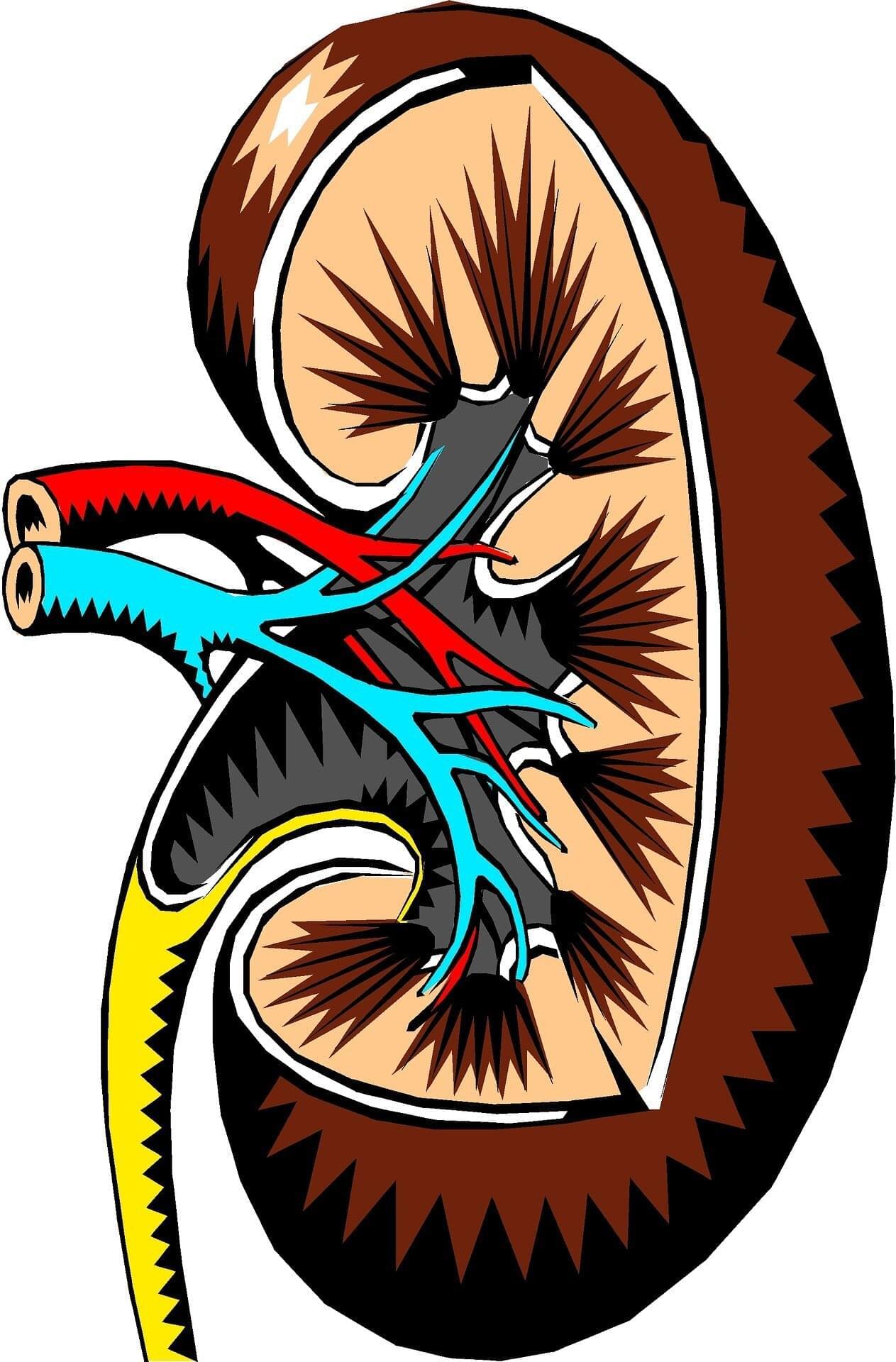
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute researchers report that all nine patients in a clinical trial being treated for stage III or IV clear cell renal cell carcinoma (a form of kidney cancer), generated a successful anti-cancer immune response after initiation of a personalized cancer vaccine.
The vaccines were administered after surgery to remove the tumor and are designed to train the body’s immune system to recognize and eliminate any remaining tumor cells. At the time of data cut-off (median of 34.7 months), all patients remained cancer-free.
The results of this Phase I trial were reported in Nature.