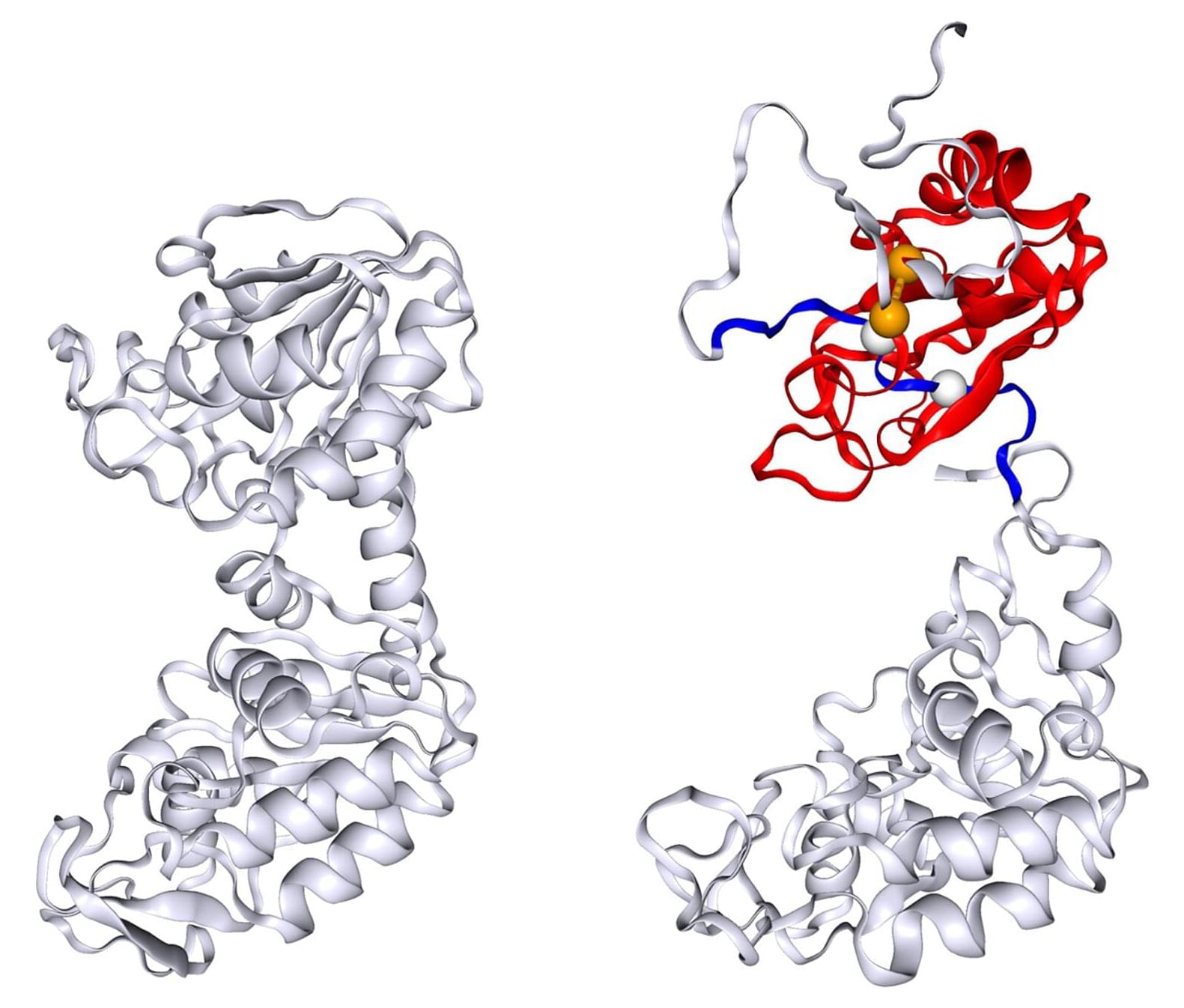
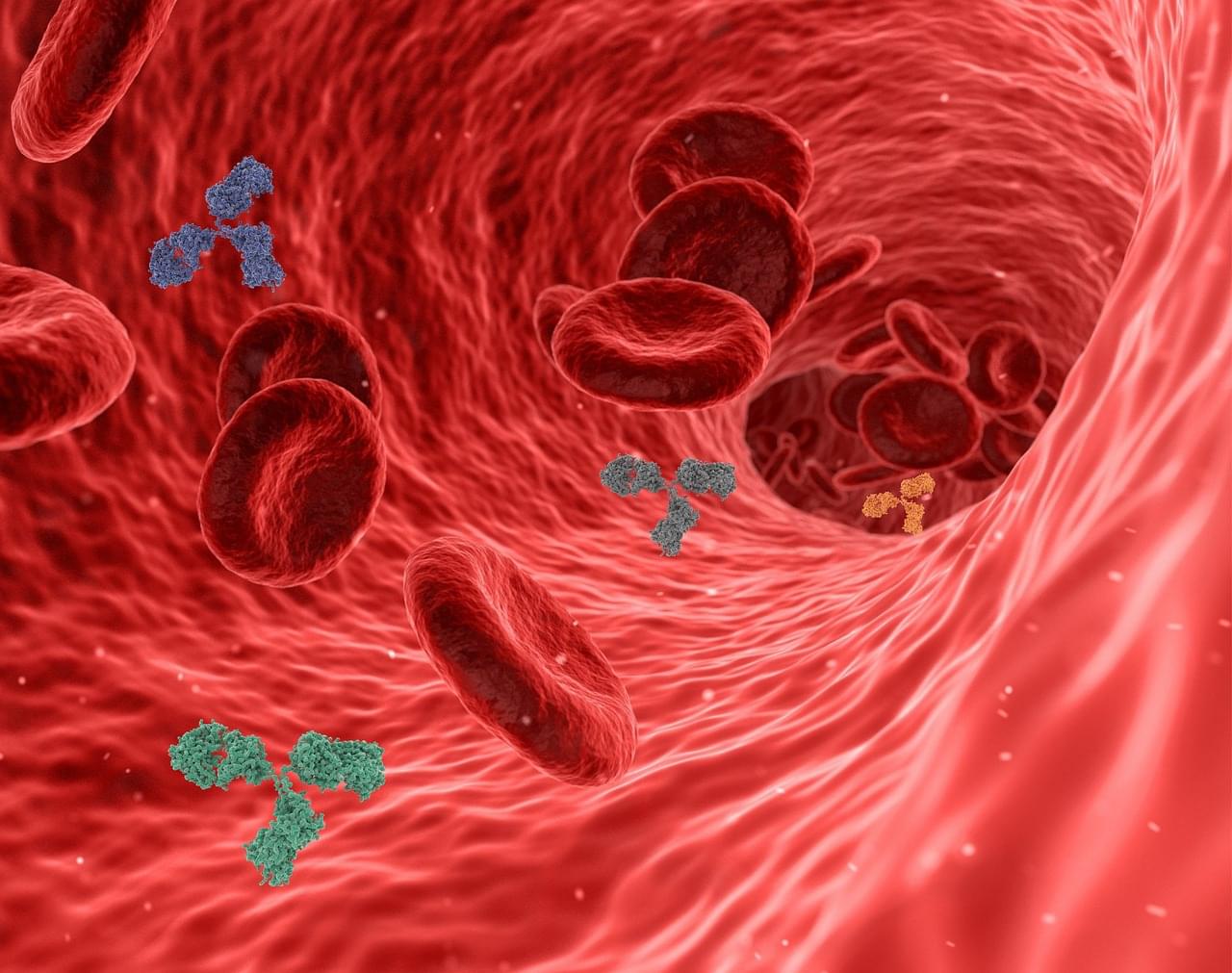
A Brazilian study published in Nutrients suggests that fish oil may help reduce insulin resistance and improve glucose tolerance by influencing the body’s inflammatory response.
Funded by FAPESP, the study was conducted on rats that, while not obese, exhibited a condition resembling type 2 diabetes—a disorder marked by high blood sugar levels due to diminished insulin effectiveness.
As the authors explain, supplementation with omega-3 fatty acids such as those present in fish oil has been prescribed for individuals with cardiovascular problems and type 2 diabetes, but the effects of these nutrients on insulin resistance without obesity are poorly understood.
Fish oil supplementation modified the profile of defense cells, shifting them from a pro-inflammatory to an anti-inflammatory state, effectively reversing a condition resembling type 2 diabetes.
A Brazilian study published in Nutrients suggests that fish oil may help reduce insulin.
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. It helps cells in the body absorb glucose from the bloodstream and convert it into energy or store it for future use. Insulin production and action are essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels. In people with diabetes, the body either does not produce enough insulin (Type 1 diabetes) or cannot effectively use the insulin it does produce (Type 2 diabetes), leading to elevated levels of glucose in the blood. This can cause various health complications over time, including heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve dysfunction. Insulin therapy, where insulin is administered through injections or an insulin pump, is a common treatment for managing diabetes, particularly Type 1. The discovery of insulin in 1921 by Frederick Banting and Charles Best was a landmark in medical science, transforming diabetes from a fatal disease to a manageable condition.


 https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51MOSiURIHL._AC_SX425_.jpg’:[425,425],’
https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51MOSiURIHL._AC_SX425_.jpg’:[425,425],’