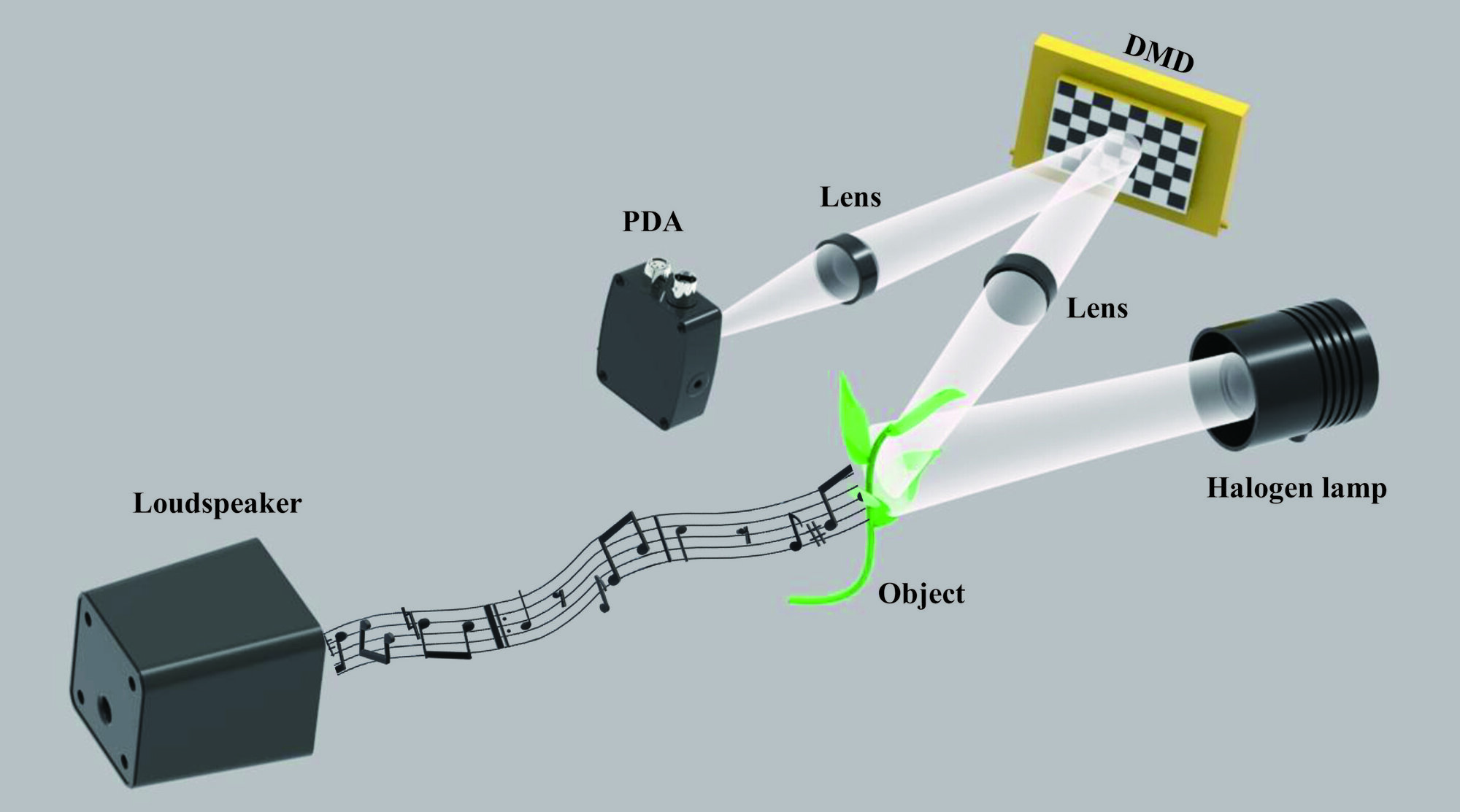
Researchers have created a microphone that listens with light instead of sound. Unlike traditional microphones, this visual microphone captures tiny vibrations on the surfaces of objects caused by sound waves and turns them into audible signals.
“Our method simplifies and reduces the cost of using light to capture sound while also enabling applications in scenarios where traditional microphones are ineffective, such as conversing through a glass window,” said research team leader Xu-Ri Yao from Beijing Institute of Technology in China. “As long as there is a way for light to pass through, sound transmission isn’t necessary.”
In the journal Optics Express, the researchers describe the new approach, which applies single-pixel imaging to sound detection for the first time. Using an optical setup without any expensive components, they demonstrate that the technique can recover sound by using the vibrations on the surfaces of everyday objects such as leaves and pieces of paper.