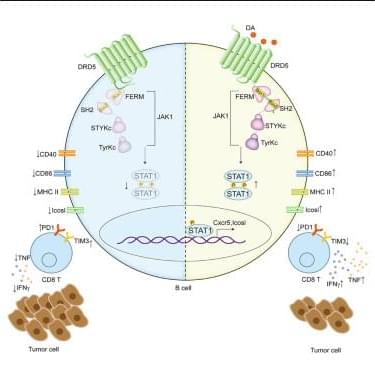
DA-DRD5 signaling reprograms B cells to promote CD8+ T cell-mediated antitumor immunity.

The landmark advance builds on a 2013 study by the team, published in Science, which described the construction of the first GRO. In that study, the researchers demonstrated new solutions for safeguarding genetically engineered organisms and for producing new classes of synthetic proteins and biomaterials with “unnatural,” or human-created, chemistries.
Ochre is a major step toward creating a non-redundant genetic code in E. coli, specifically, which is ideally suited to produce synthetic proteins containing multiple, different synthetic amino acids.
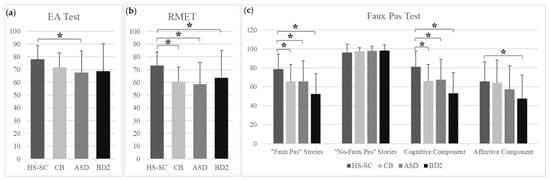
In the following paper, the authors aimed to compare the social cognition profiles of individuals with cerebellar neurodegenerative disorders, autism, bipolar disorder type 2, or healthy subjects using a battery of social tests requiring different degrees of prediction processing.
📝 — Olivito, et al.
Full text is available 👇
Social prediction is a key feature of social cognition (SC), a function in which the modulating role of the cerebellum is recognized. Accordingly, cerebellar alterations are reported in cerebellar pathologies, neurodevelopmental disorders, and psychiatric conditions that show SC deficits. Nevertheless, to date, no study has directly compared populations representative of these three conditions with respect to SC and cerebellar alterations. Therefore, the present exploratory study aimed to compare the SC profiles of individuals with cerebellar neurodegenerative disorders (CB), autism (ASD), bipolar disorder type 2 (BD2), or healthy subjects (HS) using a battery of social tests requiring different degrees of prediction processing. The patterns of cerebellar gray matter (GM) alterations were compared among the groups using voxel-based morphometry.
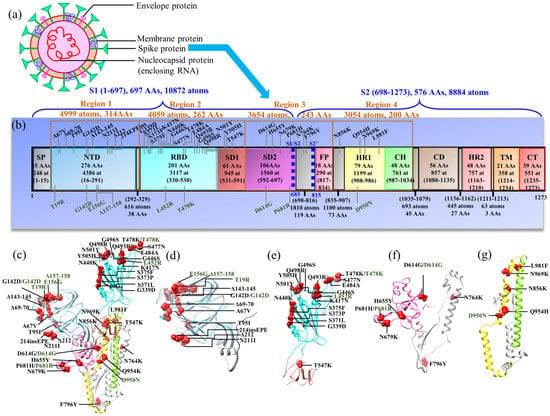
📝 — Ching, et al.
Full text is available 👇
The spike protein (S-protein) is a crucial part of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), with its many domains responsible for binding, fusion, and host cell entry. In this review we use the density functional theory (DFT) calculations to analyze the atomic-scale interactions and investigate the consequences of mutations in S-protein domains. We specifically describe the key amino acids and functions of each domain, which are essential for structural stability as well as recognition and fusion processes with the host cell; in addition, we speculate on how mutations affect these properties.
Common Side Effects airs Sundays at 11:30pm on Adult Swim — next day on Max.
Watch Adult Swim on Max: http://bit.ly/3Gy0aXA
SUBSCRIBE: https://youtube.com/adultswim1?sub_confirmation=1
About Adult Swim:
Watch Adult Swim on Max, www.adultswim.com or by downloading the Adult Swim app. Binge marathons or watch selected episodes of many of your favorite shows including Rick and Morty, SMILING FRIENDS, The Boondocks, Aqua Teen Hunger Force, and many more.
Connect with Adult Swim Online:
Download the APPS: http://www.adultswim.com/apps/
Visit Adult Swim WEBSITE: http://www.adultswim.com.
Like Adult Swim on FACEBOOK: https://facebook.com/adultswim.
Follow Adult Swim on TWITTER: https://twitter.com/adultswim.
Follow Adult Swim on INSTAGRAM: http://instagram.com/adultswim.
Watch Adult Swim in your country:
United Kingdom: https://bit.ly/AS_GB
Republic of Ireland: https://bit.ly/AS_GB
USA: https://bit.ly/AS_US
France: https://bit.ly/AS_FRA
Germany: https://bit.ly/AS_GERMAN
Italy: https://bit.ly/AS_IT
Central and Eastern Europe: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Denmark: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Finland: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Hungary: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Netherlands: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Norway: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Poland: https://bit.ly/AS_HBOMAX
Australia: https://bit.ly/AS_AU
New Zealand: https://bit.ly/AS_NZL
Sponsored by World of Warships! Follow this link https://wo.ws/40Q4JZz and use the code IMPACTFORCE to get a cool starter pack! For new players only.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
DELTA-V Calculators: https://www.overvieweffekt.com/tools/brachistochrone-rocket-calculator.
Thanks to for the Mass Effect music. Check it out and his channel here:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=57-xIuu4Vvw.
REFERENCES
https://www.projectrho.com/public_html/rocket/enginelist3.ph…ein_Drive_)
https://www.projectrho.com/public_html/rocket/torchships.php#brachistochrone.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
ATTRIBUTION
“SpaceX Starship Ship 24 & Booster 7 V4” (https://skfb.ly/oD9TL) by Clarence365 is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
“MCRN Tachi \[Expanse TV Show]” (https://skfb.ly/o6JGy) by Jakub. Vildomec is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Saturn” (https://skfb.ly/orVqA) by NestaEric is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
“MCRN Donnager (The Expanse)” (https://skfb.ly/6XU7L) by Chris Kun.
“Epstein’s Yacht (The Expanse)” (https://skfb.ly/6XTu7) by Chris Kun.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀

Coal ash in the U.S. holds substantial rare earth elements, potentially reducing dependence on imports, with ongoing research and pilot projects working to make extraction economically viable.
Coal ash, the powdery residue left after burning coal for fuel, has accumulated across the United States for decades. New research from the University of Texas at Austin reveals that this vast supply contains enough rare earth elements to significantly strengthen the nation’s reserves without the need for additional mining.
“This really exemplifies the ‘trash to treasure’ mantra,” said co-lead author Bridget Scanlon, a research professor at UT’s Bureau of Economic Geology at the Jackson School of Geosciences. “We’re basically trying to close the cycle and use waste and recover resources in the waste, while at the same time reducing environmental impacts.”
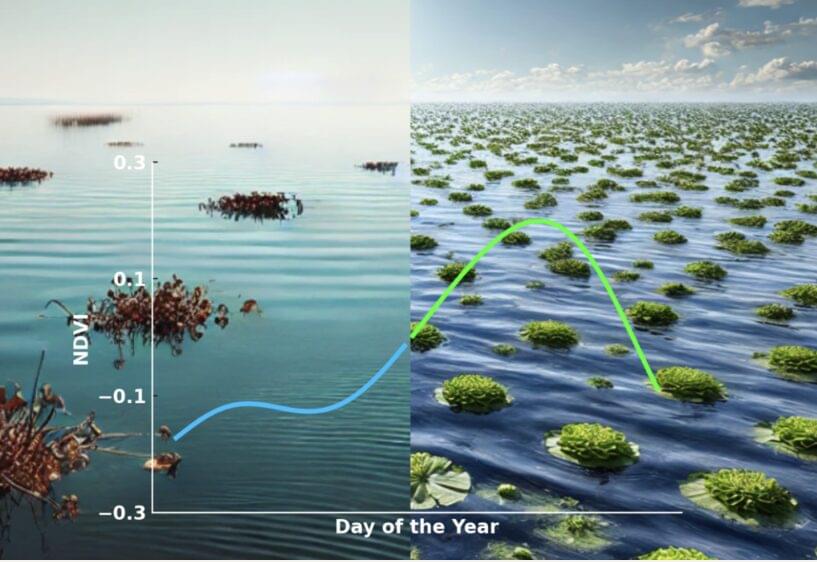

Recent advances in astronomical observations have found a significant number of extrasolar planets that can sustain surface water, and the search for extraterrestrial life on such planets is gaining momentum. A team of astrobiologists has proposed a novel approach for detecting life on ocean planets. By conducting laboratory measurements and satellite remote sensing analyses, they have demonstrated that the reflectance spectrum of floating vegetation could serve as a promising biosignature. Seasonal variations in floating vegetation may provide a particularly effective means for remote detection.
Astronomical surveys have discovered nearly 6,000 exoplanets, including many habitable planets, which may harbor liquid water on their surfaces. The search for life on such planets is one of the most significant scientific endeavors of this century, with direct imaging observation projects currently under development.
On Earth-like planets, the characteristic reflectance spectrum of terrestrial vegetation, known as “vegetation red edge,” is considered as a key biosignature.
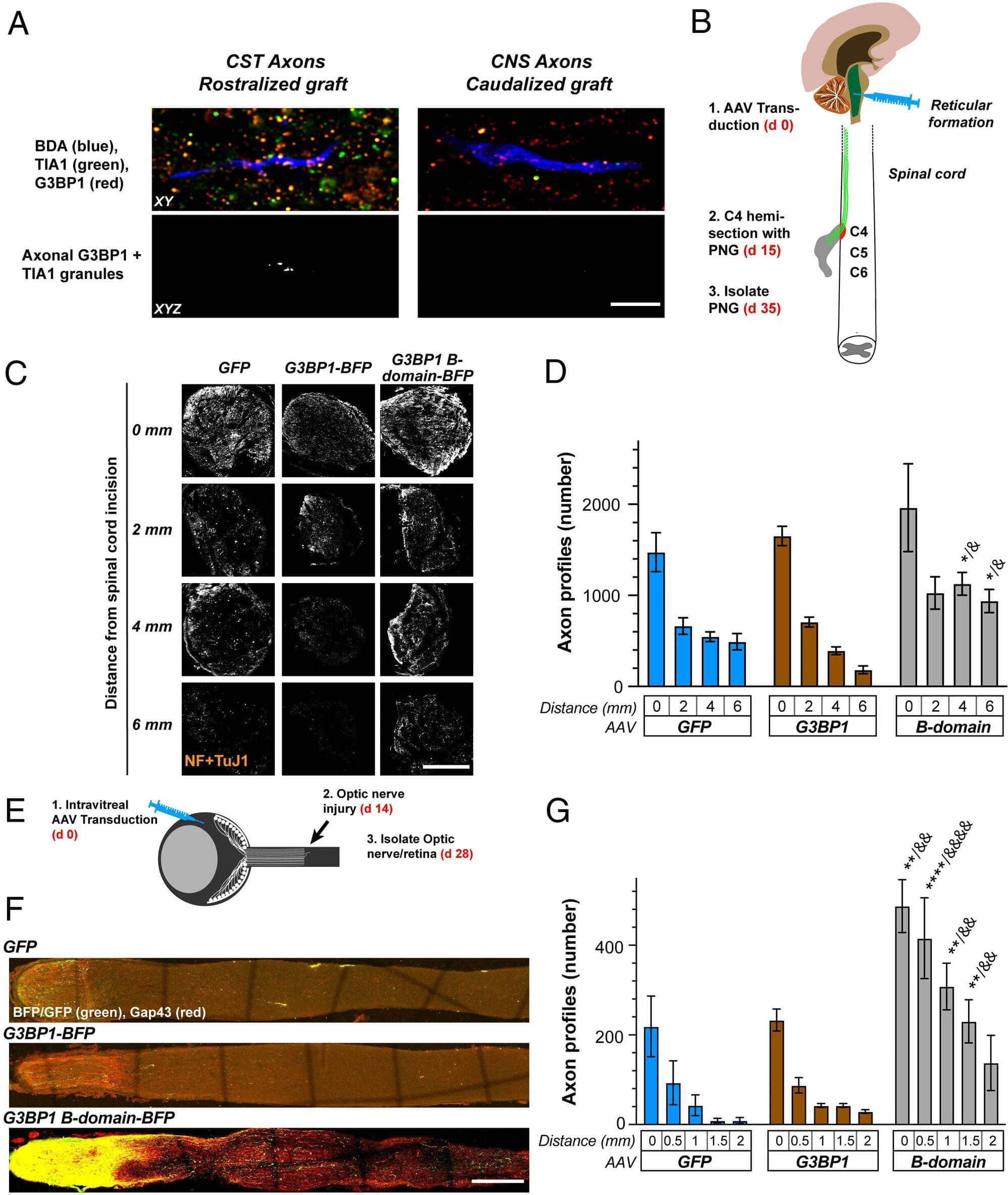
Each year, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH), millions of people in the U.S. are affected by spinal cord and traumatic brain injuries, along with neuro-developmental and degenerative diseases such as ADHD, autism, cerebral palsy, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, epilepsy and Parkinson’s disease.
Assistant Professor Pabitra Sahoo, of Rutgers University-Newark’s Department of Biological Sciences, has made it his life’s work to understand how our neurological system becomes damaged by these injuries and conditions, and when and how neurons in our central and peripheral nervous systems regenerate and heal.
Recently, Sahoo and his RU-N research team made a breakthrough, using a peptide to help nerve cells in both the peripheral and central nervous systems regenerate. They published their findings in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
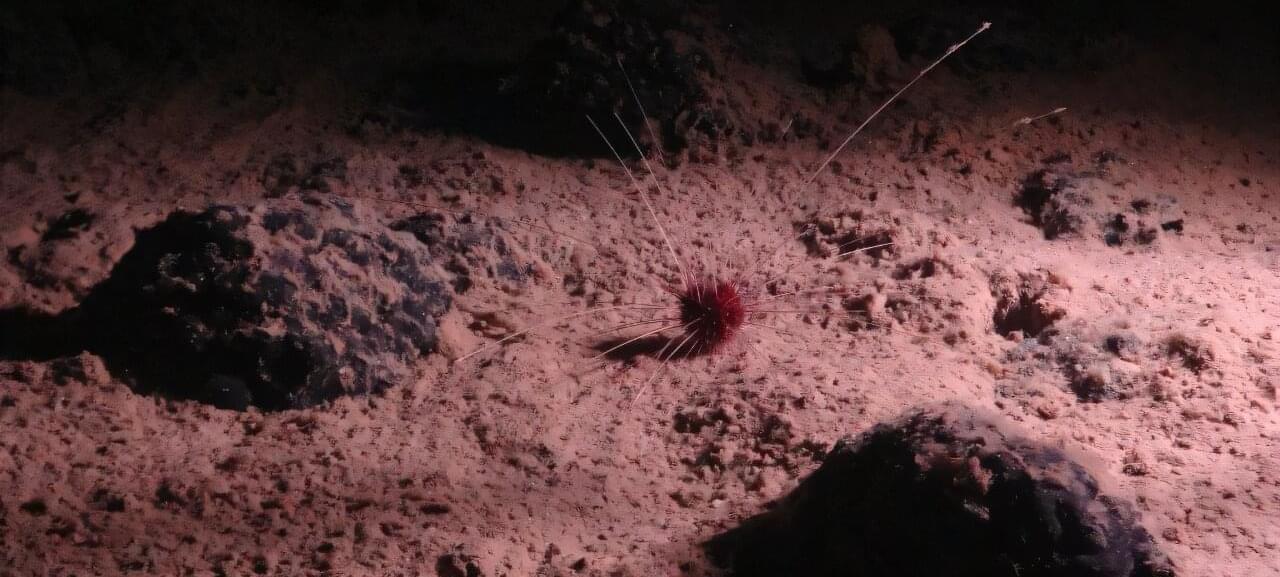

Could lumpy metallic rocks in the deepest, darkest reaches of the ocean be making oxygen in the absence of sunlight?
Some scientists think so, but others have challenged the claim that so-called “dark oxygen” is being produced in the lightless abyss of the seabed.
The discovery—detailed last July in the journal Nature Geoscience —called into question long-held assumptions about the origins of life on Earth, and sparked intense scientific debate.