What’s old is new again.
Driving at night might be a scary challenge for a new driver, but with hours of practice it soon becomes second nature. For self-driving cars, however, practice may not be enough because the lidar sensors that often act as these vehicles’ “eyes” have difficulty detecting dark-colored objects. Research published in ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces describes a highly reflective black paint that could help these cars see dark objects and make autonomous driving safer.
Lidar, short for light detection and ranging, is a system used in a variety of applications, including geologic mapping and self-driving vehicles. The system works like echolocation, but instead of emitting sound waves, lidar emits tiny pulses of near-infrared light. The light pulses bounce off objects and back to the sensor, allowing the system to map the 3D environment it’s in. But lidar falls short when objects absorb more of that near-infrared light than they reflect, which can occur on black-painted surfaces. Lidar can’t detect these dark objects on its own, so one common solution is to have the system rely on other sensors or software to fill in the information gaps. However, this solution could still lead to accidents in some situations. Rather than reinventing the lidar sensors, though, Chang-Min Yoon and colleagues wanted to make dark objects easier to detect with existing technology by developing a specially formulated, highly reflective black paint.
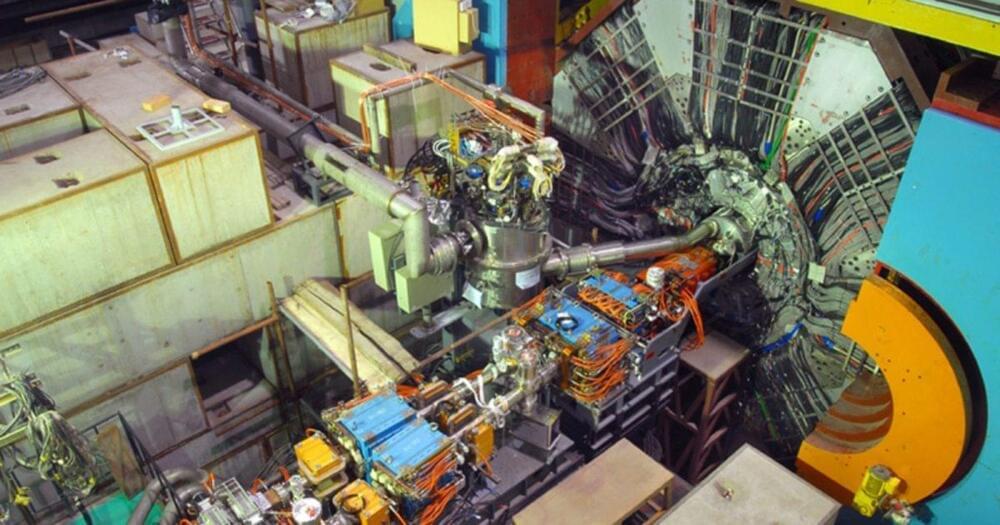
Glueballs are an unusual, unconfirmed Standard Model prediction, suggesting bound states of gluons alone exist. We just found our first one.
Microsoft is developing a new generative AI model that will take lots of data and energy to train, according to a new report from The Information published Monday.
Two Microsoft employees tell the outlet that the model has been dubbed MAI-1 internally and is being developed by a team led by Mustafa Suleyman. The ex-Google AI executive worked at AI firm Inflection before Microsoft bought Inflection’s IP and poached most of its staff, including Suleyman, who joined the tech giant in March. The employees say that MAI-1 is separate from Inflection’s Pi models.
Microsoft is reportedly reserving lots of servers with Nvidia graphics cards to train MAI-1, which is expected to be bigger than Microsoft’s previous open-source AI models. This means it will consume tons of electricity during its training phase—a broader issue researchers flag as harmful to the environment. Microsoft declined to comment on MAI-1, but linked to a Monday post from CTO Kevin Scott which states that Microsoft is and will continue to build AI models, some of which “have names like Turing, and MAI.”
String theory could provide a theory of everything for our universe—but it entails 10500 (more than a centillion) possible solutions. AI models could help to find the right one.
Tiny little threads whizzing through spacetime and vibrating incessantly: this is roughly how you can imagine the universe, according to string theory. The various vibrations of the threads generate the elementary particles, such as electrons and quarks, and the forces acting among them.
Researchers at the Universities of Melbourne and Manchester have invented a breakthrough technique for manufacturing highly purified silicon that brings powerful quantum computers a big step closer.
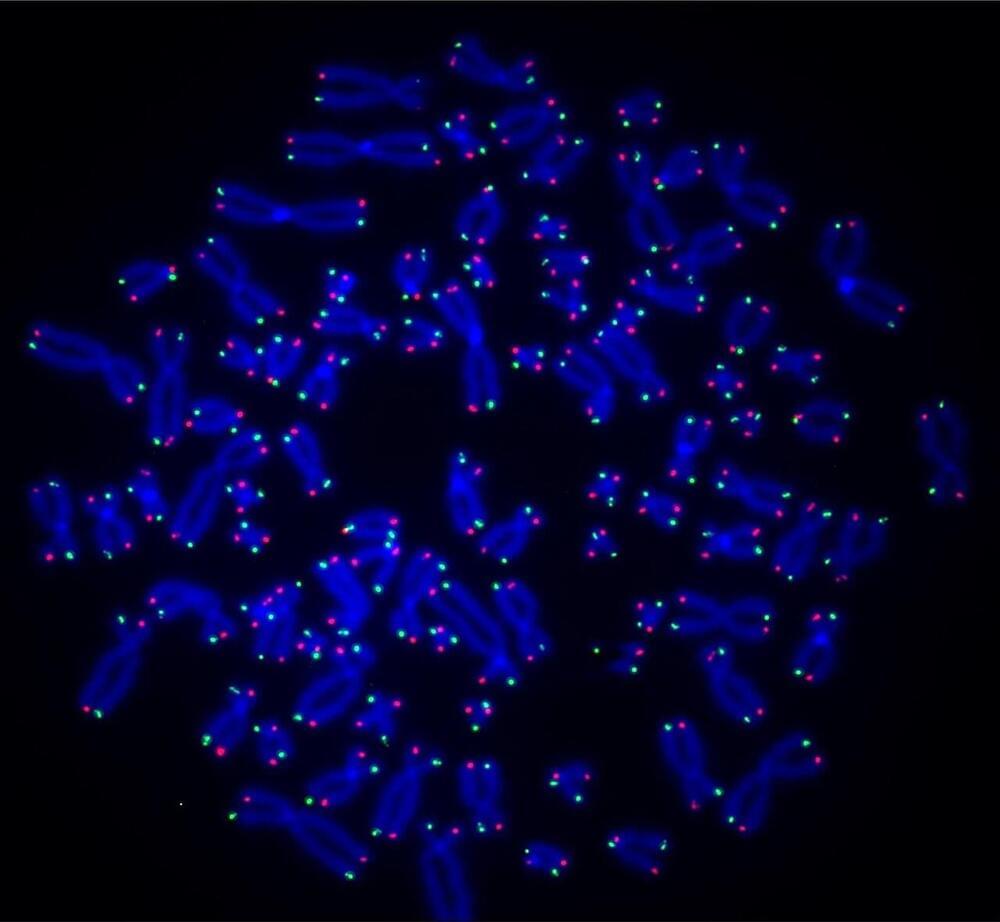
A new study led by University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Hillman Cancer Center researchers shows that an enzyme called PARP1 is involved in repair of telomeres, the lengths of DNA that protect the tips of chromosomes, and that impairing this process can lead to telomere shortening and genomic instability that can cause cancer.
It’s not every year that a major discovery is made in the basic natural sciences of Earth, but using painfully precise measurements, MIT has written a new chapter in something that most people probably thought they knew completely: evaporation.
The scientists say the discovery could explain “mysterious measurements” in the literature of clouds which may increase the precision of climate modeling, while also aiding in industrial applications.
In this study, the discovery that evaporation can occur just with light and without heat was so unexpected and surprising that it was subjected to 14 different tests and measurements to try and disprove what the scientists observed.
Researchers have discovered that individuals who live to be 100 years old and remain cognitively healthy possess genetic variations that may protect against Alzheimer’s disease. These “protective alleles” are significantly more prevalent among centenarians compared to Alzheimer’s patients and even middle-aged individuals without the disease. This finding could pave the way for new approaches in preventing and treating Alzheimer’s, particularly by focusing on enhancing these protective genetic mechanisms.
The new findings have been published in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that predominantly affects older adults, leading to a decline in cognitive functions such as memory and reasoning. Over time, this can result in a complete loss of independence and eventually death. The risk of developing Alzheimer’s increases significantly with age, and while it is not an inevitable part of aging, it is one of the most common causes of dementia among seniors.
Think of all the information we get based on how an object interacts with wavelengths of light — a.k.a. color. Color can tell us if food is safe to eat or if a piece of metal is hot. Color is an important diagnostic tool in medicine, helping practitioners diagnose diseased tissue, inflammation, or problems in blood flow.
Companies have invested heavily to improve color in digital imaging, but wavelength is just one property of light. Polarization — how the electric field oscillates as light propagates — is also rich with information, but polarization imaging remains mostly confined to table-top laboratory settings, relying on traditional optics such as waveplates and polarizers on bulky rotational mounts.