Long focused on antioxidants, researchers are now exploring a new route to combat prostate cancer: pro-oxidants.
In this episode of Bloomberg Primer, we explore the world of biocomputing–where scientists are laying the foundation for a field that may blur the lines between the biological and synthetic.
Bloomberg Primer cuts through the complex jargon to reveal the business behind technologies poised to transform global markets. This six-part, planet-spanning series offers a comprehensive look at the \.
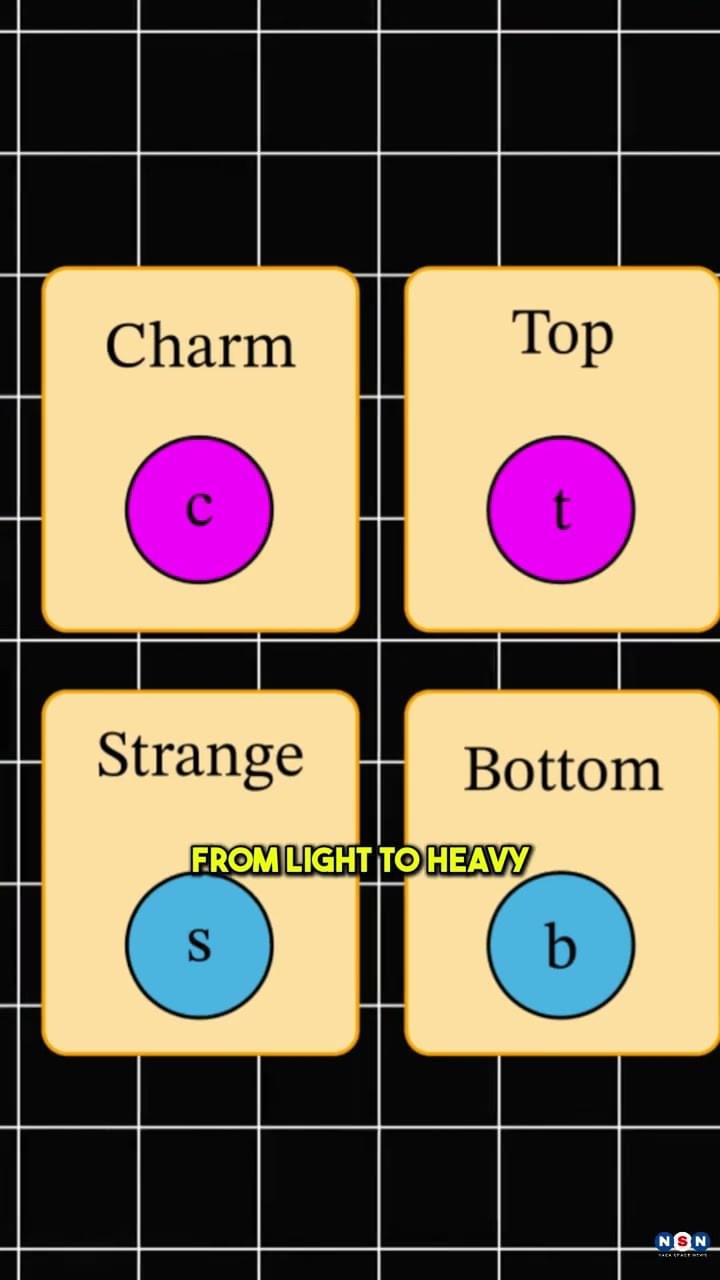
CERN scientists have detected top quark pairs in lead-lead collisions for the first time, confirming their presence in the early universe’s quark-gluon plasma. This groundbreaking discovery unlocks new insights into how matter formed just microseconds after the Big Bang. Join us as we explore the science, history, and future implications of this monumental finding.
Paper link : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.10186
paper link : https://arxiv.org/pdf/0810.5529
paper link : https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.
Visit our website for up-to-the-minute updates:
www.nasaspacenews.com.
Follow us.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/nasaspacenews.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/SpacenewsNasa.
Join this channel to get access to these perks:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCEuhsgmcQRbtfiz8KMfYwIQ/join.
#NSN #NASA #Astronomy#TopQuark.
Meditation has been linked to a slowdown in aging and reduction in stress. Biohacker Dave Asprey speaks with Fox News Digital about the health benefits of
Studies show psychological strain can accelerate tumors — could beta blockers slow them down?
Niamh Peren | From Neurons to Networks: Whole Brain Emulation @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
Posted in bioengineering, cryonics, encryption, nanotechnology, nuclear energy, robotics/AI, satellites, security | Leave a Comment on Niamh Peren | From Neurons to Networks: Whole Brain Emulation @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
*This video was recorded at Foresight’s Vision Weekend 2025 in Puerto Rico*
https://foresight.org/vw2025pr/
Our Vision Weekends are the annual festivals of Foresight Institute. Held in two countries, over two weekends, you are invited to burst your tech silos and plan for flourishing long-term futures. This playlist captures the magic of our Puerto Rico edition, held February 21–23, 2025, in the heart of Old San Juan. Come for the ideas: join the conference, unconference, mentorship hours, curated 1-1s, tech demos, biohacking sessions, prize awards, and much more. Stay for fun with new friends: join the satellite gatherings, solarpunk future salsa night, beach picnic, and surprise island adventures. This year’s main conference track is dedicated to “Paths to Progress”; meaning you will hear 20+ invited presentations from Foresight’s core community highlighting paths to progress in the following areas: Existential Hope Futures, Longevity, Rejuvenation, Cryonics, Neurotech, BCIs & WBEs, Cryptography, Security & AI, Fusion, Energy, Space, and Funding, Innovation, Progress.
══════════════════════════════════════
*About The Foresight Institute*
The Foresight Institute is a research organization and non-profit that supports the beneficial development of high-impact technologies. Since our founding in 1986 on a vision of guiding powerful technologies, we have continued to evolve into a many-armed organization that focuses on several fields of science and technology that are too ambitious for legacy institutions to support. From molecular nanotechnology, to brain-computer interfaces, space exploration, cryptocommerce, and AI, Foresight gathers leading minds to advance research and accelerate progress toward flourishing futures.
*We are entirely funded by your donations. If you enjoy what we do please consider donating through our donation page:* https://foresight.org/donate/
*Visit* https://foresight.org, *subscribe to our channel for more videos or join us here:*
Yuri Deigin | Brain Rejuvenation by Partial Reprogramming @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
Posted in bioengineering, cryonics, encryption, nanotechnology, nuclear energy, robotics/AI, satellites, security | Leave a Comment on Yuri Deigin | Brain Rejuvenation by Partial Reprogramming @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
*This video was recorded at Foresight’s Vision Weekend 2025 in Puerto Rico*
https://foresight.org/vw2025pr/
Our Vision Weekends are the annual festivals of Foresight Institute. Held in two countries, over two weekends, you are invited to burst your tech silos and plan for flourishing long-term futures. This playlist captures the magic of our Puerto Rico edition, held February 21–23, 2025, in the heart of Old San Juan. Come for the ideas: join the conference, unconference, mentorship hours, curated 1-1s, tech demos, biohacking sessions, prize awards, and much more. Stay for fun with new friends: join the satellite gatherings, solarpunk future salsa night, beach picnic, and surprise island adventures. This year’s main conference track is dedicated to “Paths to Progress”; meaning you will hear 20+ invited presentations from Foresight’s core community highlighting paths to progress in the following areas: Existential Hope Futures, Longevity, Rejuvenation, Cryonics, Neurotech, BCIs & WBEs, Cryptography, Security & AI, Fusion, Energy, Space, and Funding, Innovation, Progress.
══════════════════════════════════════
*About The Foresight Institute*
The Foresight Institute is a research organization and non-profit that supports the beneficial development of high-impact technologies. Since our founding in 1986 on a vision of guiding powerful technologies, we have continued to evolve into a many-armed organization that focuses on several fields of science and technology that are too ambitious for legacy institutions to support. From molecular nanotechnology, to brain-computer interfaces, space exploration, cryptocommerce, and AI, Foresight gathers leading minds to advance research and accelerate progress toward flourishing futures.
*We are entirely funded by your donations. If you enjoy what we do please consider donating through our donation page:* https://foresight.org/donate/
*Visit* https://foresight.org, *subscribe to our channel for more videos or join us here:*
Niccolo Zanichelli | The State of Brain Emulation in 2025 @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
Posted in bioengineering, cryonics, encryption, nanotechnology, nuclear energy, robotics/AI, satellites, security | Leave a Comment on Niccolo Zanichelli | The State of Brain Emulation in 2025 @ Vision Weekend 2025, Puerto Rico
*This video was recorded at Foresight’s Vision Weekend 2025 in Puerto Rico*
https://foresight.org/vw2025pr/
Our Vision Weekends are the annual festivals of Foresight Institute. Held in two countries, over two weekends, you are invited to burst your tech silos and plan for flourishing long-term futures. This playlist captures the magic of our Puerto Rico edition, held February 21–23, 2025, in the heart of Old San Juan. Come for the ideas: join the conference, unconference, mentorship hours, curated 1-1s, tech demos, biohacking sessions, prize awards, and much more. Stay for fun with new friends: join the satellite gatherings, solarpunk future salsa night, beach picnic, and surprise island adventures. This year’s main conference track is dedicated to “Paths to Progress”; meaning you will hear 20+ invited presentations from Foresight’s core community highlighting paths to progress in the following areas: Existential Hope Futures, Longevity, Rejuvenation, Cryonics, Neurotech, BCIs & WBEs, Cryptography, Security & AI, Fusion, Energy, Space, and Funding, Innovation, Progress.
══════════════════════════════════════
*About The Foresight Institute*
The Foresight Institute is a research organization and non-profit that supports the beneficial development of high-impact technologies. Since our founding in 1986 on a vision of guiding powerful technologies, we have continued to evolve into a many-armed organization that focuses on several fields of science and technology that are too ambitious for legacy institutions to support. From molecular nanotechnology, to brain-computer interfaces, space exploration, cryptocommerce, and AI, Foresight gathers leading minds to advance research and accelerate progress toward flourishing futures.
*We are entirely funded by your donations. If you enjoy what we do please consider donating through our donation page:* https://foresight.org/donate/
*Visit* https://foresight.org, *subscribe to our channel for more videos or join us here:*
*This video was recorded at Foresight’s Vision Weekend 2025 in Puerto Rico*https://foresight.org/vw2025pr/Our Vision Weekends are the annual festivals of For…
We’re closer than ever to being able to upload our minds and become “digitally immortal.” But should we?
❍ Subscribe to The Well on YouTube: https://bit.ly/welcometothewell.
❍ Up next: Michio Kaku: 3 mind-blowing predictions about the future • Michio Kaku: 3 mind-blowing predictio…
What if our minds could live after our bodies have died? What if mortality became obsolete? Steven Kotler, award-winning journalist and executive director of the Flow Research Collective, has studied these seemingly sci-fi ideas, and it turns out that they’re not so fictional, after all. In fact, mind-uploading technology is expected to be available as early as 2045.
“Digital immortality” would have its upsides; we could preserve the minds of modern geniuses and have their guidance through future conflicts. Or, alternatively, things could get dark, as we have never before interfered with such complex evolutionary processes. Kotler explains that the ability to store human personalities and consciousness on computers poses profound ethical and societal questions.
By developing and using this mind-uploading technology, we are simultaneously redefining what it means to be a human being, pushing the boundary between life, death, and whatever is in between. It seems, whether we’re ready or not, that it is going to happen soon.