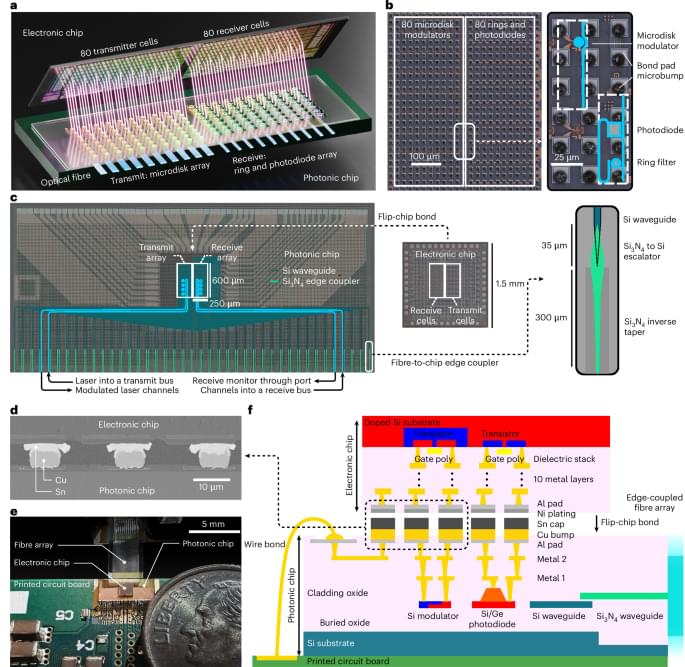
This compares some of the ringworlds, centrifuges, space stations, and ships that use spin to make gravity. It also try’s to show how the variables of artificial gravity are used to make centripetal acceleration into spin gravity.
Calculator used: https://www.artificial-gravity.com/sw/SpinCalc/
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
REFERENCES
1. Hill, Paul R.; Schnitzer, Emanuel (1962 September). “Rotating Manned Space Stations.” In, Astronautics (vol. 7, no. 9, p. 14
18). Reston, Virginia, USA: American Rocket Society / American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics.
2. Gilruth, Robert R. (1969). “Manned Space Stations – Gateway to our Future in Space.” In S. F. Singer (Ed.), Manned.
Laboratories in Space (p. 1–10). Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag.
3. Gordon, Theodore J.; Gervais, Robert L. (1969). “Critical Engineering Problems of Space Stations.” In S. F. Singer (Ed.).
Manned Laboratories in Space (p. 11–32). Berlin, Germany: Springer-Verlag.
4. Stone, Ralph W. (1973). “An Overview of Artificial Gravity.” In A. Graybiel (Ed.), Fifth Symposium on the Role of the.
Vestibular Organs in Space Exploration (NASA SP-314, p. 23–33). Pensacola, Florida, USA, 19–21 August 1970.
Washington, DC, USA: NASA
5. Cramer, D. Bryant (1985). “Physiological Considerations of Artificial Gravity.” In A. C. Cron (Ed.), Applications of Tethers in.
Space (NASA CP-2364, vol. 1, p. 3·95–3·107). Williamsburg, Virginia, USA, 15–17 June 1983. Washington, DC, USA:
NASA.
6. Graybiel, Ashton (1977). “Some Physiological Effects of Alternation Between Zero Gravity and One Gravity.” In J. Grey (Ed.).
Space Manufacturing Facilities (Space Colonies): Proceedings of the Princeton / AIAA / NASA Conference, May 7–9, 1975
7. Hall, Theodore W. “Artificial Gravity in Theory and Practice.” International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2016, www.artificial-gravity.com/ICES-2016–194.pdf.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
SOCIAL
Twitter: https://twitter.com/OverviewEfect.
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/overviewefects/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/profile.php?id=61552024642764
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀
ATTRIBUTION
Mass Effect music from @MrHulthen Check it out and his channel here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=57-xIuu4Vv.
“Citadel (Mass Effect)” (https://skfb.ly/6CLEX) by Yanez Designs is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Babylon 5 Station (Babylon 5)” (https://skfb.ly/6pFJp) by uperesito is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Halo Ring” (https://skfb.ly/orU8C) by Inditrion Dradnon is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Empire State Building” (https://skfb.ly/BGwU) by Microsoft is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
“MCRN Tachi [Expanse TV Show]” (https://skfb.ly/o6JGy) by Jakub. Vildomec is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“endurance spaceship” (https://skfb.ly/6TnFK) by devanshujha is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Discovery 1″ (https://skfb.ly/6oRCD) by uperesito is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Soviet Nuclear Computer Terminal” (https://skfb.ly/prtFw) by PIPO is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution.
“Hail Mary Ship” by MallocArray https://www.printables.com/model/232479-hail-mary-ship/files.
“Death Star — Star Wars” (https://skfb.ly/oqGZX) by Quiznos323.
▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀▀