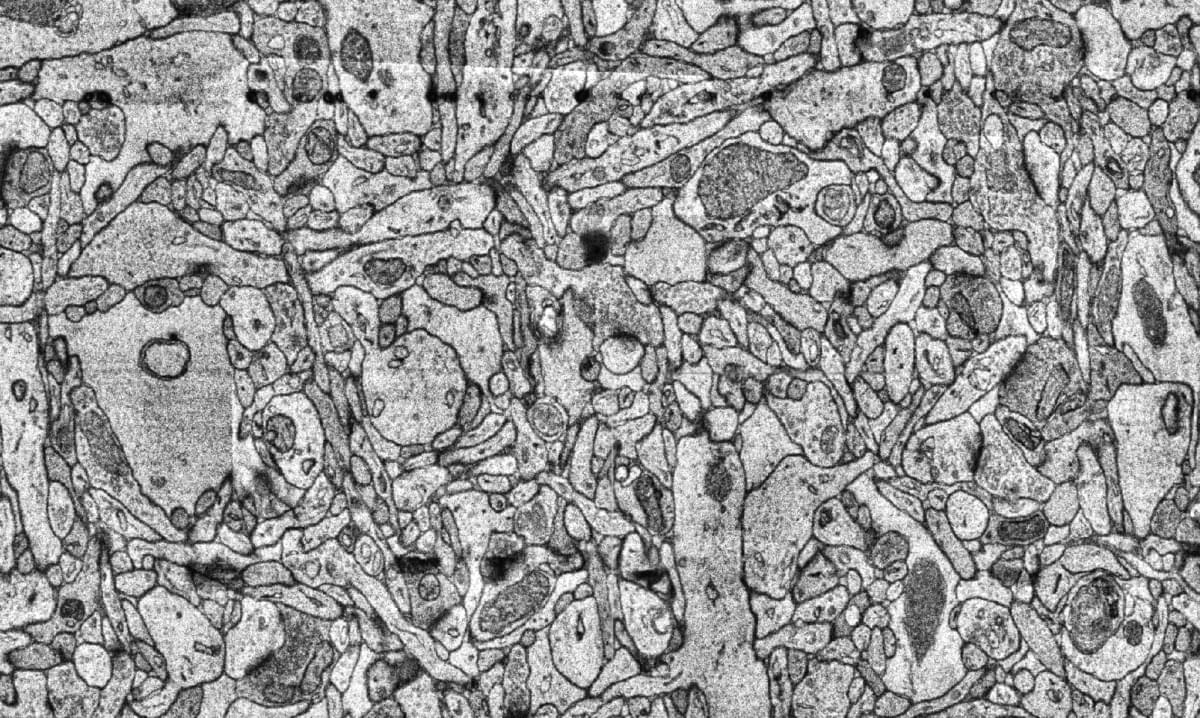
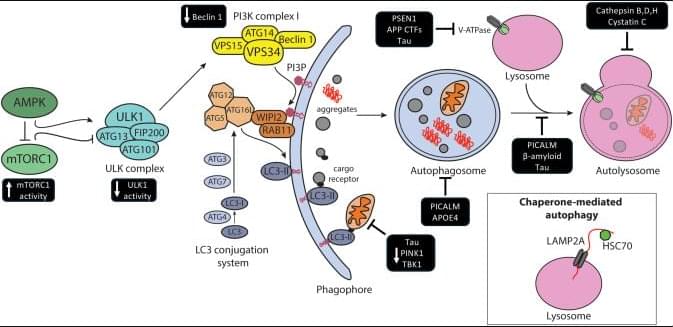
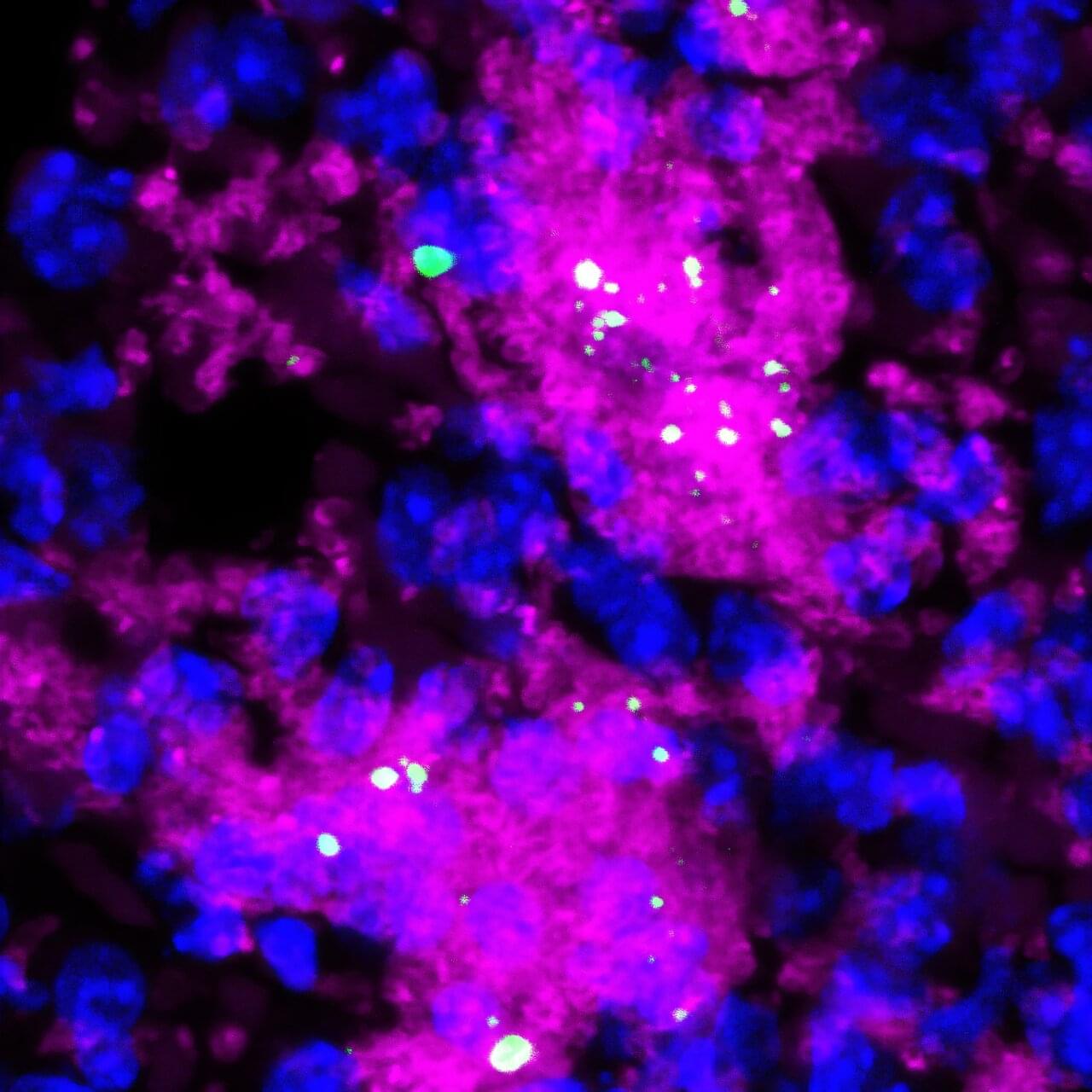
While the trial is limited to members of families with genetic mutations that all but guarantee they will develop Alzheimer’s at a young age, typically in their 30s, 40s or 50s, the researchers expect that the study’s results will inform prevention and treatment efforts for all forms of Alzheimer’s disease.
Called the Primary Prevention Trial, the new study investigates whether remternetug — an investigational antibody being developed by Eli Lilly and Company — can remove plaques of a key Alzheimer’s protein called amyloid beta from the brain or block them from accumulating in the first place. Both genetic and nongenetic forms of Alzheimer’s disease start with amyloid slowly collecting in the brain two decades before memory and thinking problems arise. By clearing out low levels of amyloid beta plaques or preventing them from accumulating during the early, asymptomatic phase of the disease, or both, the researchers hope to interrupt the disease process at the earliest stage and spare people from ever developing symptoms.
“We have seen tremendous progress in the treatment of Alzheimer disease in the past few years,” said Eric McDade, DO, a professor of neurology and the trial’s principal investigator. “Two amyloid-targeting drugs were shown to slow symptoms of the disease and have now been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as treatments for people with mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. This provides strong support for our hypothesis that intervening when amyloid beta plaques are at the very earliest stage, long before symptoms arise, could prevent symptoms from emerging in the first place.”
The trial is part of the Knight Family Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network-Trials Unit (Knight Family DIAN-TU), a clinical trials platform designed to find medicines to prevent or treat Alzheimer’s disease. It is closely associated with DIAN, a National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded international research network led by WashU Medicine that involves research institutes in North America, Australia, Europe, Asia and South America. DIAN follows families with mutations in any of three genes that cause Alzheimer’s at a young age. A child born into such a family has a 50% chance of inheriting such a mutation, and those who do so typically develop signs of dementia near the same age his or her parent did. All the participants in the Primary Prevention Trial come from such families.
“My grandfather passed away from Alzheimer’s, and so did his mother and all but one of his brothers,” said Hannah Richardson, 24, a participant in the Primary Prevention Trial. “My mom and my uncle have been participating in DIAN trials since I was about 10 years old. My mom was always very open about her diagnosis and how it spurred her advocacy for Alzheimer’s research, and I’ve always known I wanted to follow in her footsteps. I am happy to be involved in the Primary Prevention Trial and be involved in research because I know how important it is.”