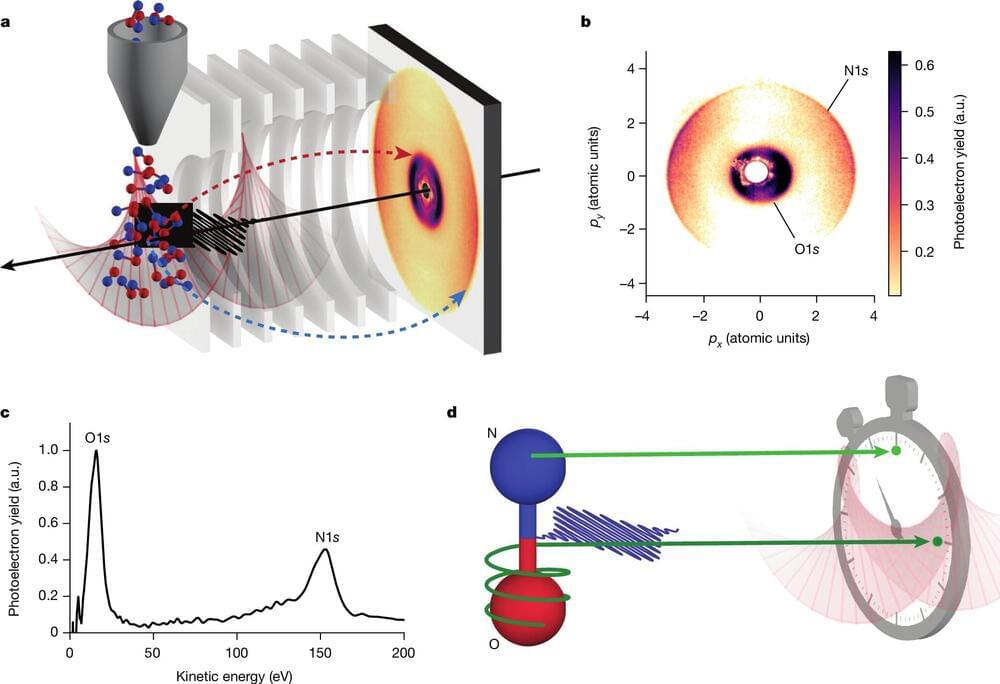
An international team of scientists is the first to report incredibly small time delays in a molecule’s electron activity when the particles are exposed to X-rays.

Mathematicians at Loughborough University have turned their attention to a fascinating observation that has intrigued scientists and cocktail enthusiasts alike: the mysterious way ouzo, a popular anise-flavored liquor, turns cloudy when water is added.

Just a few years ago, researchers discovered that changing the angle between two layers of graphene, an atom-thick sheet of carbon, also changed the material’s electronic and optical properties. They then learned that a “twist” of 1.1 degrees—dubbed the “magic” angle—could transform this metallic material into an insulator or a superconductor, a finding that ignited excitement about a possible pathway to new quantum technologies.
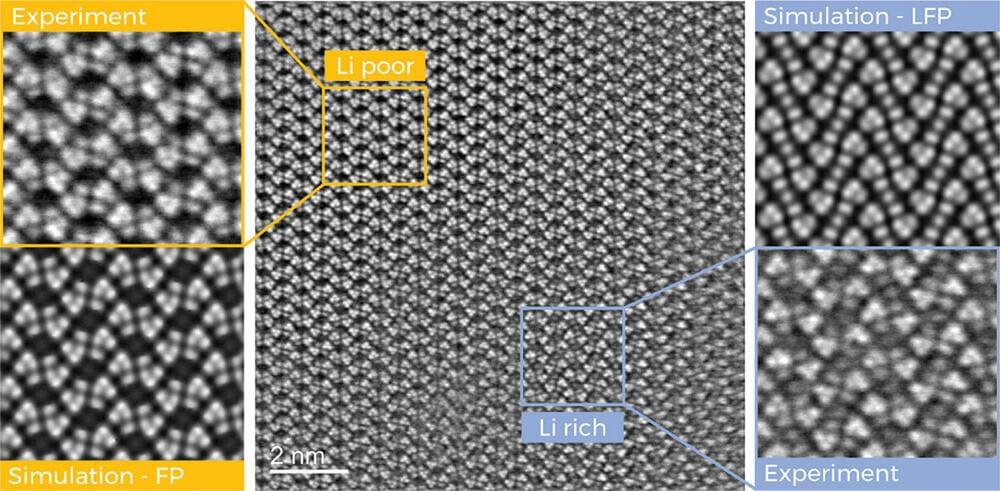
Lithium iron phosphate is one of the most important materials for batteries in electric cars, stationary energy storage systems and tools. It has a long service life, is comparatively inexpensive and does not tend to spontaneously combust. Energy density is also making progress. However, experts are still puzzled as to why lithium iron phosphate batteries undercut their theoretical electricity storage capacity by up to 25% in practice.
In order to utilize this dormant capacity reserve, it would be crucial to know exactly where and how lithium ions are stored in and released from the battery material during the charging and discharging cycles.
Researchers at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) have now taken a significant step in this direction. Using transmission electron microscopes, they were able to systematically track the lithium ions as they traveled through the battery material, map their arrangement in the crystal lattice of an iron phosphate cathode with unprecedented resolution and precisely quantify their distribution in the crystal.
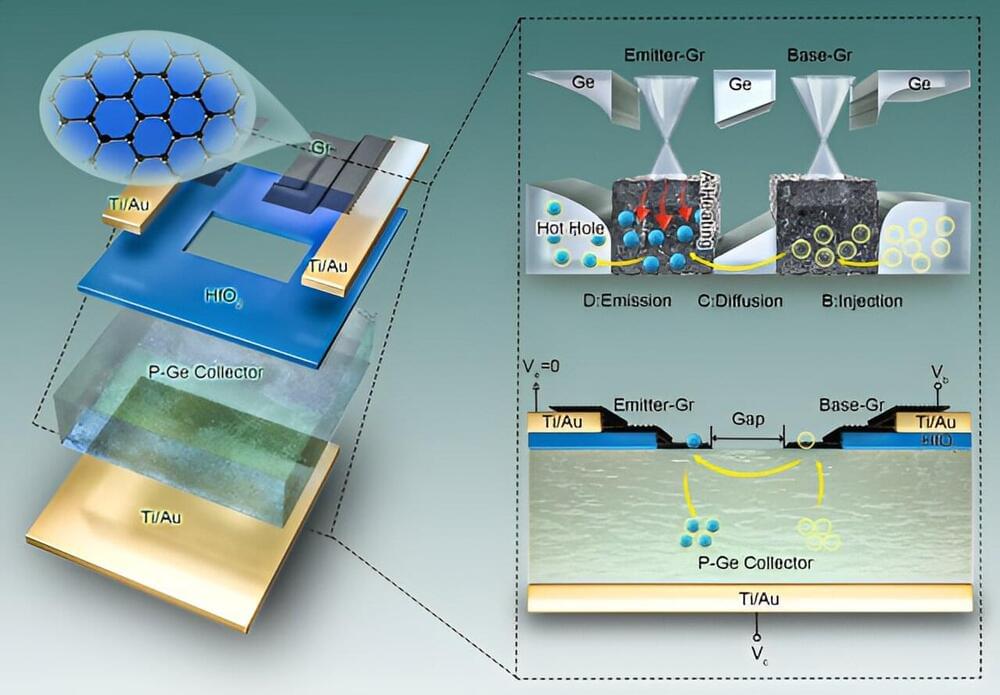
Transistors, the building blocks of integrated circuits, face growing challenges as their size decreases. Developing transistors that use novel operating principles has become crucial to enhancing circuit performance.
Hot carrier transistors, which utilize the excess kinetic energy of carriers, have the potential to improve the speed and functionality of transistors. However, their performance has been limited by how hot carriers have traditionally been generated.
A team of researchers led by Prof. Liu Chi, Prof. Sun Dongming, and Prof. CHeng Huiming from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a novel hot carrier generation mechanism called stimulated emission of heated carriers (SEHC).
University of Queensland researchers have discovered a mechanism in DNA that regulates how disease-causing mutations are inherited.
Dr Anne Hahn and Associate Professor Steven Zuryn from UQ’s Queensland Brain Institute said the findings could provide a promising therapeutic avenue to stop the onset of heritable and age-related diseases.
“Mitochondrial DNA is essential for cell function,” Dr Hahn said.

Researchers from North Carolina State University and Johns Hopkins University have demonstrated a technology capable of a suite of data storage and computing functions—repeatedly storing, retrieving, computing, erasing or rewriting data—that uses DNA rather than conventional electronics. Previous DNA data storage and computing technologies could complete some but not all of these tasks.
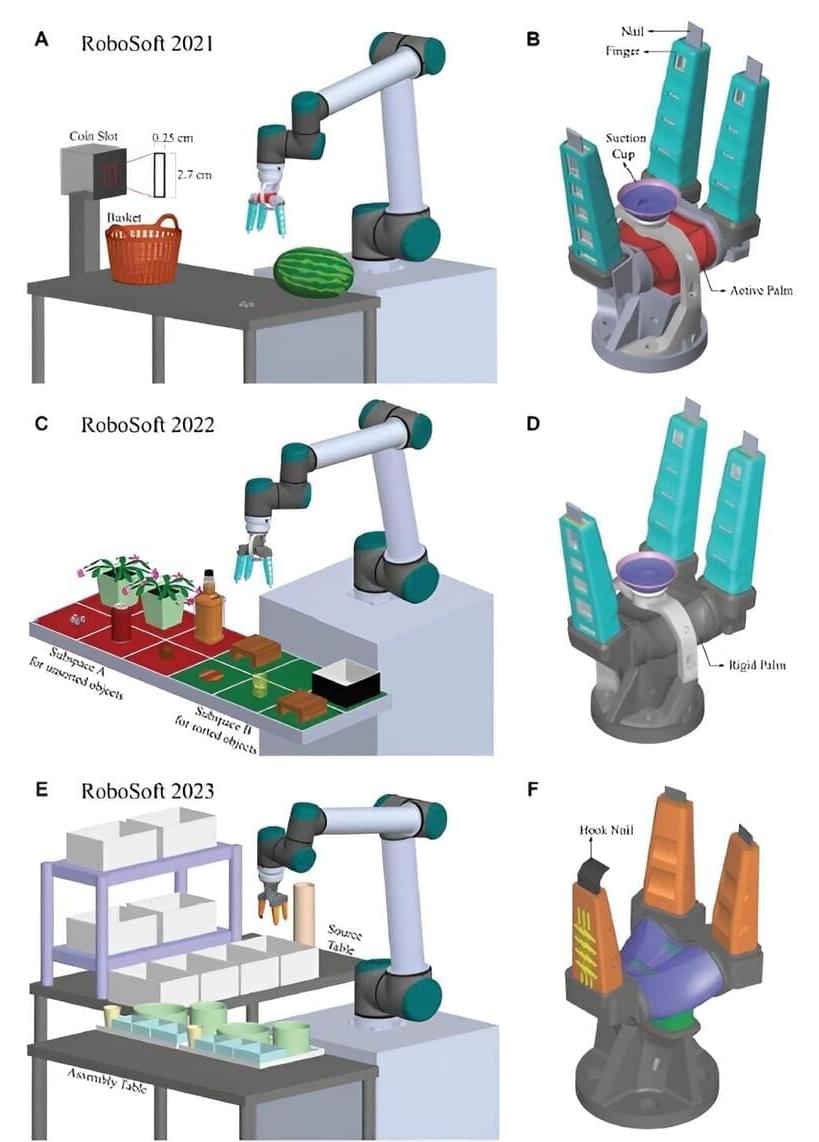
Robotic automation has become a game-changer in addressing labor shortages. While traditional rigid grippers have effectively automated various routine tasks, boosting efficiency and productivity in industries that deal with objects of well-defined specifications, they fall short in sectors like the food industry, where delicate objects of varying sizes and shapes need to be handled. In these cases, a more specialized type of gripper is required.
“Bioinspired soft robotics seeks to develop technologies that draw inspiration from nature and leverage advanced materials and fabrication processes,” said Dr. Pablo Valdivia y Alvarado, Associate Professor at the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD).
Soft grippers inspired by the natural dexterity and control of human hands are particularly well-suited to the food industry. They can adapt to objects of varying sizes and shapes while distributing forces more evenly, making them ideal for handling delicate items.