Hackers exploit CSS in emails to bypass spam filters and track user actions, raising privacy concerns.


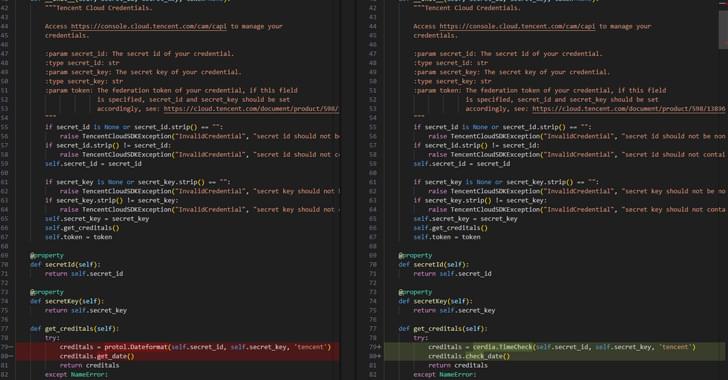


The Black Basta ransomware operation created an automated brute-forcing framework dubbed ‘BRUTED’ to breach edge networking devices like firewalls and VPNs.
The framework has enabled BlackBasta to streamline initial network access and scale ransomware attacks on vulnerable internet-exposed endpoints.
The discovery of BRUTED comes from EclecticIQ researcher Arda Büyükkaya following an in-depth examination of the ransomware gang’s leaked internal chat logs.

Cybercriminals are promoting malicious Microsoft OAuth apps that masquerade as Adobe and DocuSign apps to deliver malware and steal Microsoft 365 accounts credentials.
The campaigns were discovered by Proofpoint researchers, who characterized them as “highly targeted” in a thread on X.
The malicious OAuth apps in this campaign are impersonating Adobe Drive, Adobe Drive X, Adobe Acrobat, and DocuSign.

One of the most enduring questions humans have is how long we’re going to live. With this comes the question of how much of our lifespan is shaped by our environment and choices, and how much is predetermined by our genes.
A study recently published in the prestigious journal Nature Medicine has attempted for the first time to quantify the relative contributions of our environment and lifestyle versus our genetics in how we age and how long we live.
The findings were striking, suggesting our environment and lifestyle play a much greater role than our genes in determining our longevity.

An interesting article where Lee et al. develop a new chemical label for studying the dynamics of select glycolipids found in tuberculosis bacteria. They target specific types of glycolipids that are involved in pathogenesis, opening the door to new insights on tuberculosis. As tuberculosis kills more than a million people every year, tools for studying the disease are sorely needed. #chemicalbiology #chemistry #microbiology

Central sensitization: analysis by physio meets science.
Neurophysiological Mechanism of Central Sensitization in the Spinal Cord following Surgery:
▶️ Central sensitization was first described by Woolf in 1983 (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/6656869/) as a form of long-term adaptive neuroplasticity that amplifies the transmission of nociceptive information by affecting spinal cord neurons and is believed to be a principal neurophysiological mechanism with regard to pain persistence.
▶️ Peripheral nociception can trigger a prolonged increase in the excitability of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons, which transmit nociceptive signals to the spinal cord, resulting in central sensitization.
▶️ This condition involves heightened responsiveness of spinal neurons, driven by signaling molecules like adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and neurotransmitters such as glutamate (Glu) and substance P (SP).
▶️ These molecules activate specific receptors on spinal neurons, including purinergic receptor 2 (P2-R), N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR), α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR), and neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R).
▶️ The activation of these receptors sets off a cascade of intracellular pathways involving enzymes like calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII), protein kinase C (PKC), protein kinase A (PKA), mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR), phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2), all of which amplify the transmission of nociceptive signals to the brain.

I’ve long been fascinated by the fundamental mystery of our universe’s origin. In my work, I explore an alternative to the traditional singularity-based models of cosmology. Instead of a universe emerging from an infinitely dense point, I propose that a flat universe and its time-reversed partner—an anti-universe—can emerge together from nothing through a smooth, quantum process.
This model, described in a manuscript accepted for publication in Europhysics Letters, addresses some of the key challenges in earlier proposals, such as the Hartle–Hawking no-boundary and Vilenkin’s tunneling approaches.