A group of lesser-discussed greenhouse gasses is many times more powerful than CO2. Cracking down on them can provide immediate results.




The messy breakup of a liquid droplet that occurs when it hits a surface can be suppressed by giving the droplet an electrical charge.
Liquid droplets hit solid surfaces in a range of technological processes, such as spray coating and inkjet printing. Typically, the collision causes the droplet to break up into many tiny fragments, creating a splash. A research team has now shown that electrical charging of droplets can reduce or even entirely suppress the splashing, offering greater control over the impact process [1]. The findings could be useful in the design of more precise and efficient droplet-related technologies.
Electrical charging of droplets is very common both in nature and in technology, for example, in thundercloud electrification. The charging usually results from contact electrification, where friction, or even mere contact, between two surfaces results in electrons or ions passing between them. The effect can be exploited technologically: For example, mechanical engineer Zuankai Wang, now at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, and his colleagues have previously shown that the charge on falling water droplets can be harnessed for electricity generation [2].
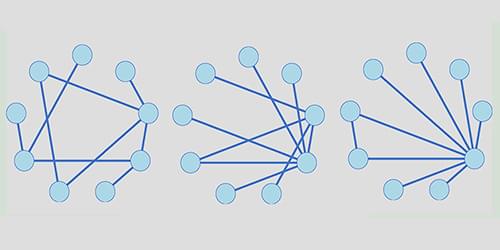
Network models provide a flexible way of representing objects and their multifaceted relationships. Deriving a network entails mapping hidden structures in inevitably noisy data—a critical task known as reconstruction. Now Gang Yan and Jia-Jie Qin of Tongji University in China have provided a mathematical proof showing what makes some networks easier to reconstruct than others [1].
Complex systems in biology, physics, and social sciences tend to involve a vast number of interacting entities. In a network model, these entities are represented by nodes, linked by connections weighted to describe the strength of each interaction. Yan and Qin took an empirical dataset and used a statistical inference method to calculate the likelihood that any pair of nodes is directly linked. Then, based on the true positive and false positive rates of these inferred connections, they analyzed the fidelity of the reconstructed networks. They found that the most faithful reconstructions are obtained with systems for which the number of connections per node varies most widely across the network. Yan and Qin saw the same tendency when they tested their model on synthetic and real networks, including metabolic networks, plant-pollinator webs, and power grids.
With the rapid increase in available data across research areas, network reconstruction has become an important tool for studying complex systems. Yan and Qin say their new result both solves the problem of what complex systems can be easily mapped into a network and provides a solid foundation for developing methods of doing so.
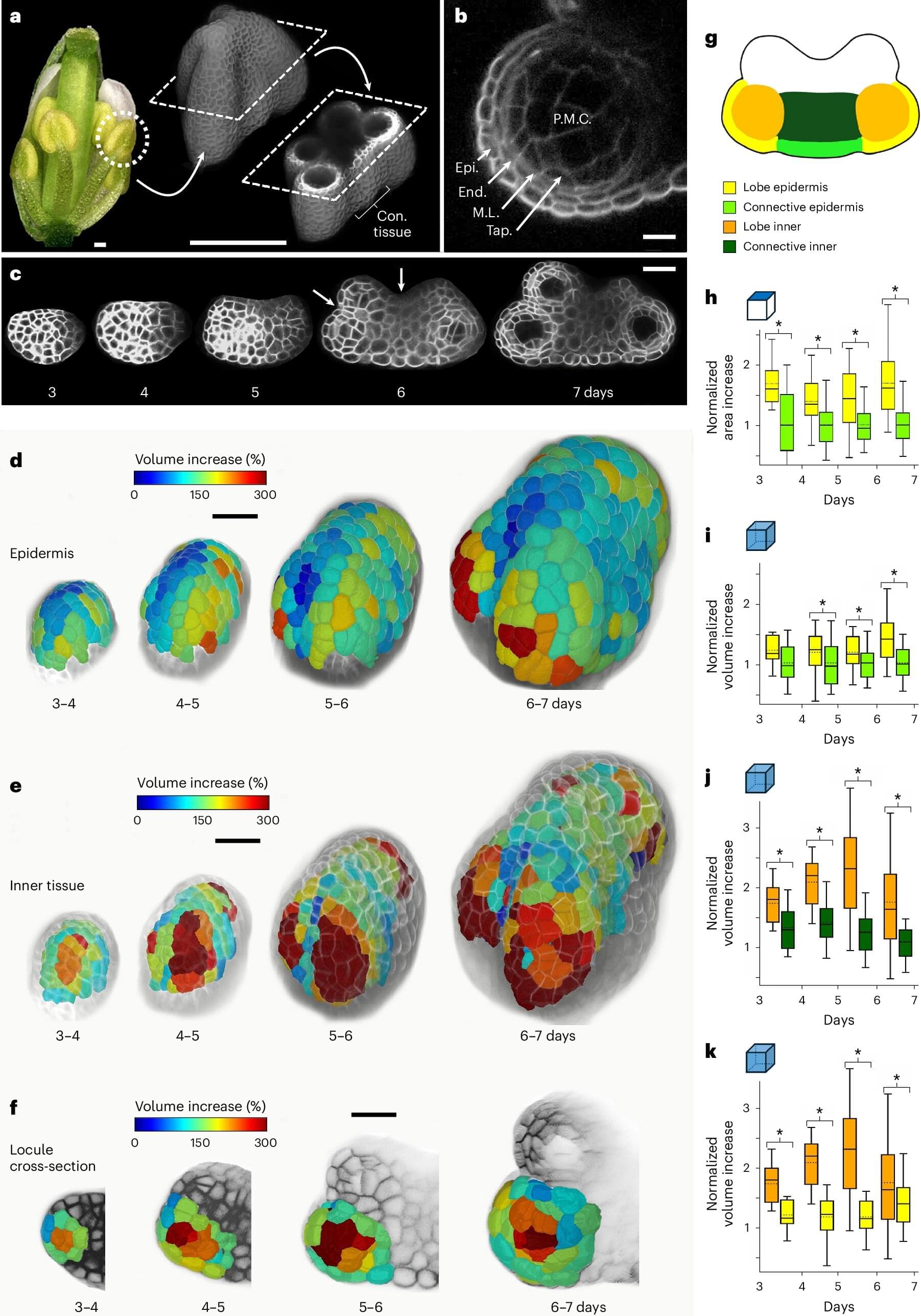
Plants don’t just grow, they build. From towering trees to delicate flowers, complex plant shapes are sculpted with remarkable precision. Now a study by biologists and biophysicists at Université de Montréal reveals how plants build their organs in three dimensions.
Anthers—the male reproductive organs of flowers—are crucial structures responsible for producing and releasing pollen and play a key role in fertilization, a process necessary for fruit and seed production, the scientists say in their paper, published last week in Nature Plants.
It’s the first time that scientists have successfully reverse-engineered the physical properties of cells located deep within a plant organ based on experimental data.
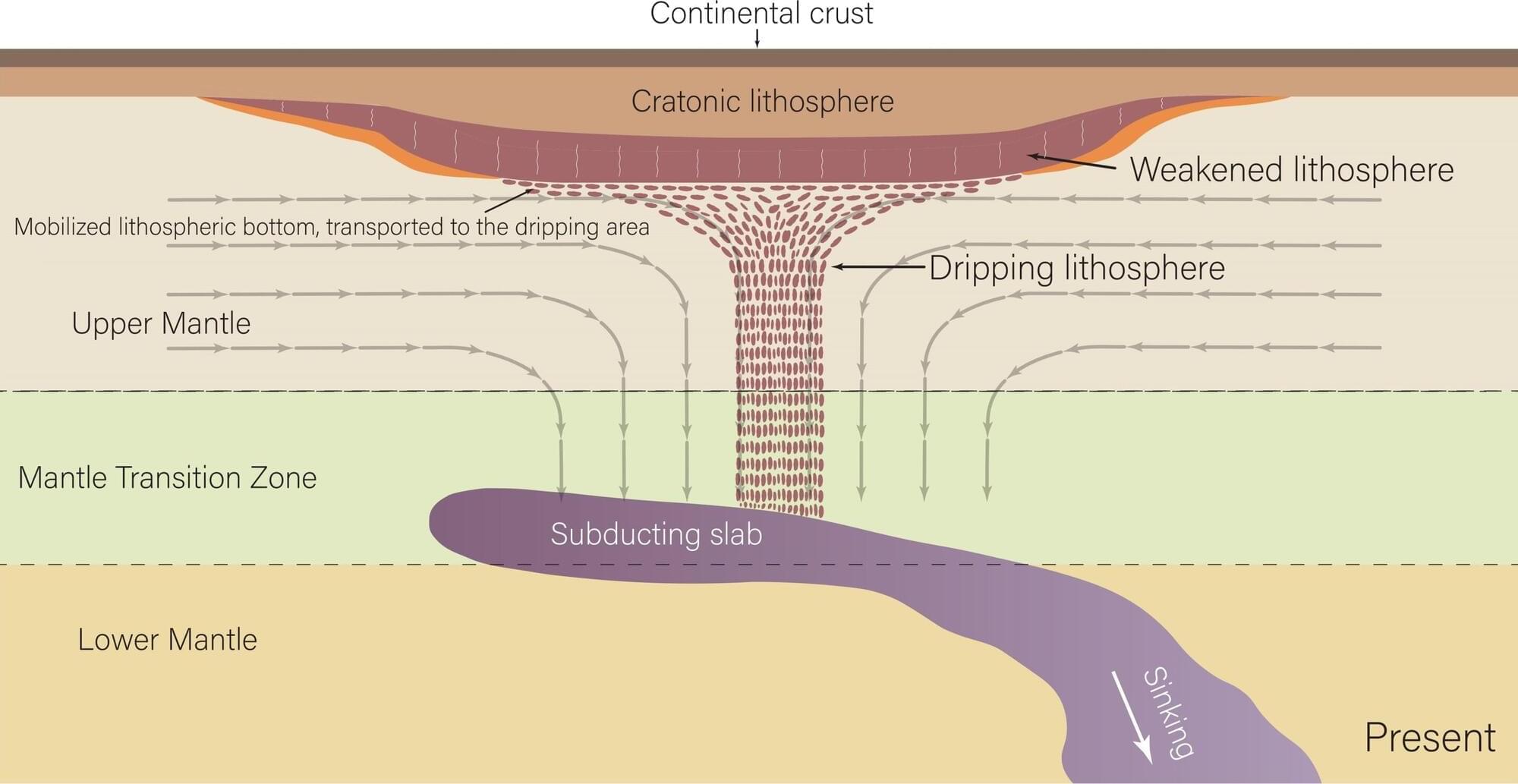
Researchers have discovered that the underside of the North American continent is dripping away in blobs of rock—and that the remnants of a tectonic plate sinking in Earth’s mantle may be the reason why.
A paper published in Nature Geoscience describes the phenomenon, which was discovered at The University of Texas at Austin. It’s the first time that “cratonic thinning” may be captured in action.
“We made the observation that there could be something beneath the craton,” said the study’s lead author Junlin Hua, who conducted the research during a postdoctoral fellowship at UT’s Jackson School of Geosciences. “Luckily, we also got the new idea about what drives this thinning.”

A new study reveals that how your brain reacts to food purchasing decisions can be used to determine your political affiliation with almost 80% accuracy.
Researchers from Iowa State University, the University of Kansas Medical Center, Oklahoma State University, and the University of Exeter in England used brain imaging techniques to examine adults purchasing eggs and milk with various prices and produced in different ways.
Interestingly, the purchases did not significantly differ by the adults’ political party. What differed by political affiliation, were the areas of the brain that were active during the purchases. The study is published in the journal Politics and the Life Sciences.

Research led by Children’s Hospital of Fudan University in China has found that a gene called pancreatic progenitor cell differentiation and proliferation factor (PPDPF) helps protect kidney cells by supporting enzymes involved in maintaining cellular energy levels during chronic kidney disease.
Chronic kidney disease affects approximately 15% of the global population and is currently the ninth leading cause of death worldwide. Treatments that can slow the progression of this condition remain limited.
Genome-wide association studies have identified nearly 800 genetic loci associated with kidney function, yet more than 90% of these variants are located in noncoding regions. Specific genes and molecular mechanisms involved in early-stage chronic kidney disease remain incompletely understood.
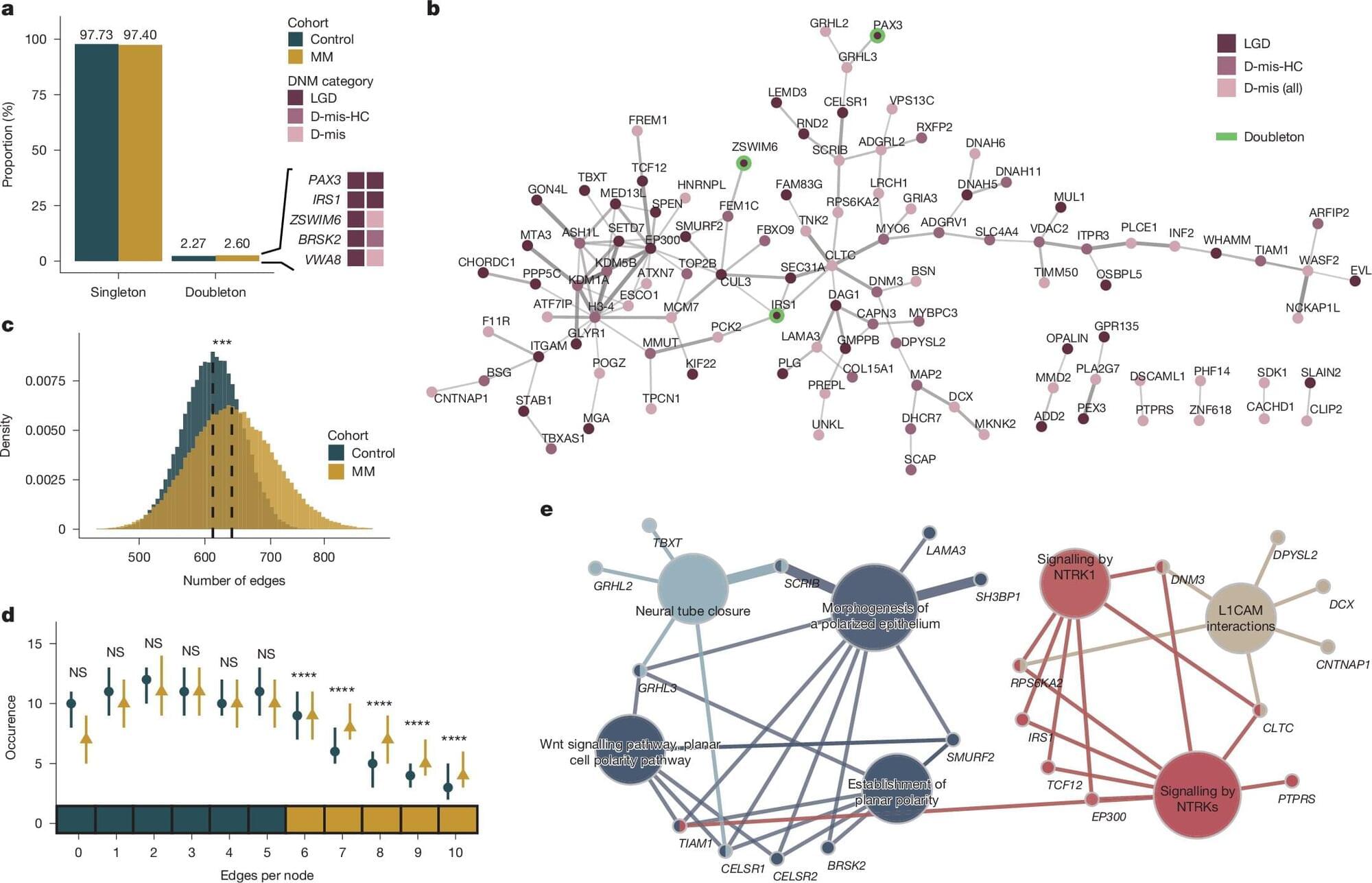
Scientists at Rady Children’s Institute for Genomic Medicine, and the Department of Neurosciences and Pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego, have made a significant breakthrough in understanding the causes of spina bifida, a serious birth defect affecting thousands of newborns each year.
The new study, published in Nature, reveals critical insights into how this condition develops and opens the door for potential future treatments.
Spina bifida, or meningomyelocele, occurs when the spine and spinal cord do not form properly during early pregnancy. Most often identified during prenatal ultrasound, the condition can lead to lifelong disabilities of the lower limbs and bladder. Newborn sequencing is not routinely used in this condition because causes remain unknown. While researchers have long understood certain environmental risk factors, the new study provides a deeper look into the molecular mechanisms underlying the condition.
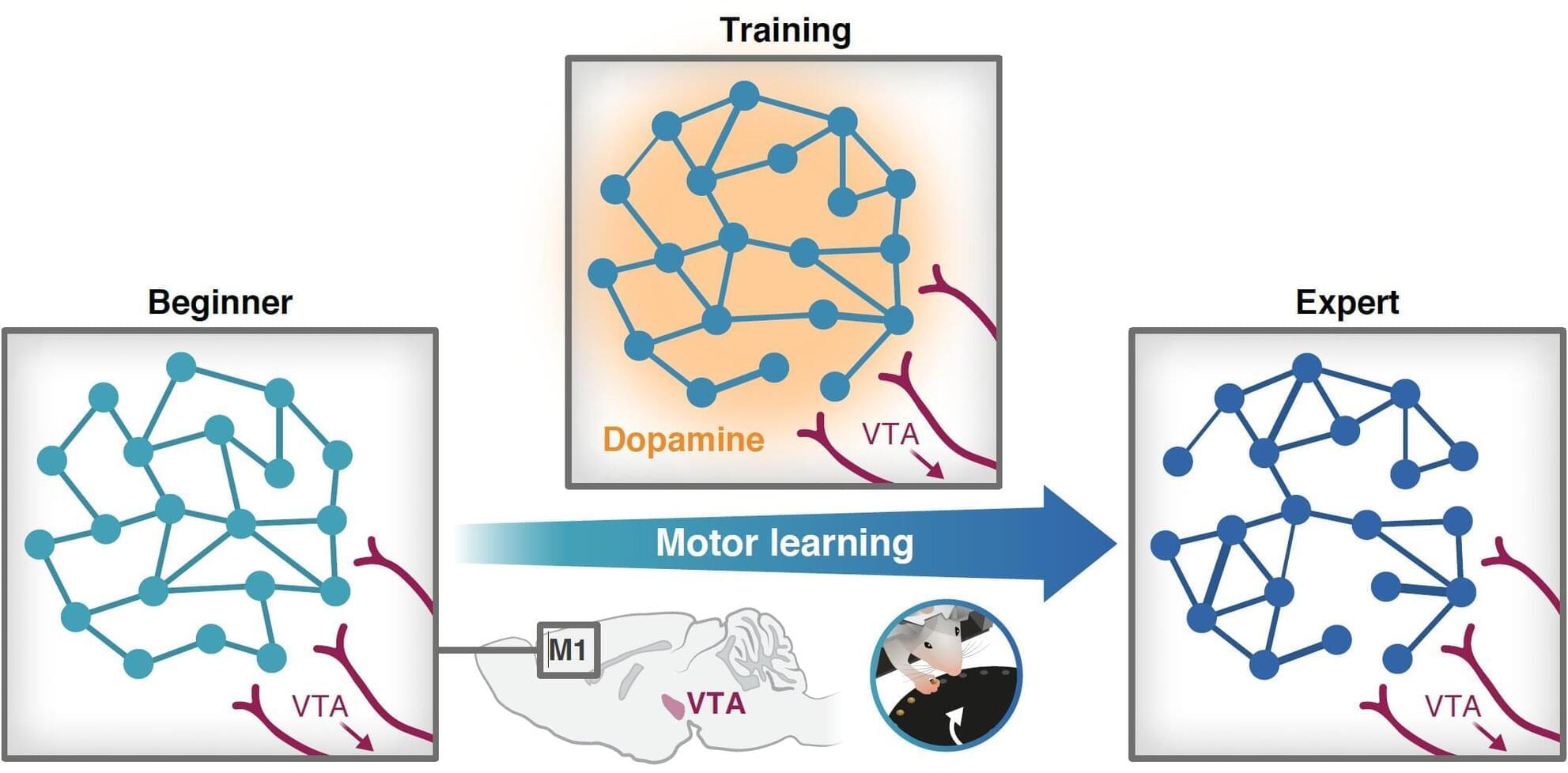
A new interdisciplinary study by researchers from the Ruth and Bruce Rappaport Faculty of Medicine and the Andrew and Erna Viterbi Faculty of Electrical and Computer Engineering at the Technion reveals a surprising insight: local release of dopamine—a molecule best known for its role in the brain’s reward system—is a key factor in acquiring new motor skills