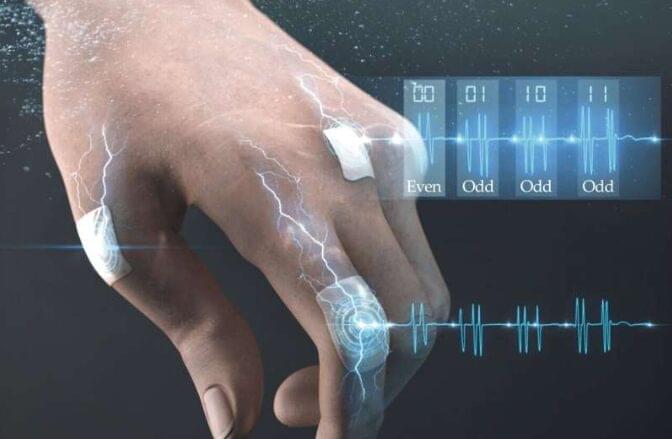
Visit Microsoft Azure Quantum here to learn about quantum computing for free https://quantum.microsoft.com/?ocid=2… https://quantum.microsoft.com/en-us/e… Topological quantum computing is a brand new form of quantum computing being developed by Microsoft as they enter the race to build the world’s first useful quantum computer. In this video I visited Microsoft’s quantum labs to see how they are making their topological quantum computers and learn how topology helps their quantum devices avoid noise by harnessing the power of Majorana quasiparticles which are made from an exotic form of superconductivity where the electrons behave like there is a Majorana particle there which has the special properties of topology.
Get My Posters Here.
For North America visit my DFTBA Store: https://store.dftba.com/collections/d… the rest of the world go to my RedBubble Store: https://www.redbubble.com/people/Domi… I have also made posters available for personal or educational use which you can find here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/9586967… Some Awesome People And many thanks to my $10 supporters and above on Patreon, you are awesome! Join the gang and help support me produce free and high quality science content: / domainofscience Tut Arom Anja Jason Evans machinator rimor Mirik Gogri Eric Epstein Sebastian Theodore Chu My Science Books I also write science books for kids called Professor Astro Cat. You can see them all here: https://flyingeyebooks.com/book/profe… http://profastrocat.com Follow me around the internet http://dominicwalliman.com
/ dominicwalliman
/ dominicwalliman Credits Writer, art, animation and edited by Dominic Walliman I use Adobe Illustrator and After Effects for the graphics (for the many people who ask smile References “InAs-Al hybrid devices passing the topological gap protocol” https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract… “A cryogenic CMOS chip for generating control signals for multiple qubits” https://www.nature.com/articles/s4192… Topological qubit noise levels — “Assessing requirements to scale to practical quantum advantage” chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/ https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.07629 Chapters 00:00 Topological Quantum Computing 02:01 Topology Explained 04:47 Resilience to Noise 05:51 Anatomy of a Quantum Computer 07:05 Chip Fabrication and Lab Tour 09:41 How to Build a Quantum Computer 11:21 Topological Quantum Computing Lego Explainer 15:40 Microsoft’s Results 17:50 Majorana Particle Explained 21:31 Sponsor Message 23:03 Thanks Patrons!
For the rest of the world go to my RedBubble Store: https://www.redbubble.com/people/Domi…
I have also made posters available for personal or educational use which you can find here: https://www.flickr.com/photos/9586967…
Some Awesome People.
And many thanks to my $10 supporters and above on Patreon, you are awesome!
Join the gang and help support me produce free and high quality science content:
/ domainofscience.
Tut Arom.