The mystery of collapsing bubbles, impossible temperatures, and what might be hiding in the space between


Preface and Index.
Imagine if meaning — the elusive essence of language and thought — could be broken down into mathematical building blocks as fundamental as prime numbers. What if computers could “reason” by synchronizing oscillators, much like neurons firing in harmony in our brains?
That’s the bold idea behind TinyAleph, a new framework and library I’ve developed for semantic computing. Unlike today’s AI models that gobble up massive datasets to mimic understanding, TinyAleph grounds meaning in pure math: primes, hypercomplex algebra, and dynamic oscillators.
In this article, I’ll walk you through the core ideas of TinyAleph, stripping away the academic jargon to show why this could be a game-changer for AI, cryptography, and even quantum-inspired simulations. No PhD required — just an open mind.

This isn’t a high-security government facility. It’s Beverly Hills High School.
District superintendent Alex Cherniss says the striking array of surveillance tools is a necessity, and one that ensures the safety of his students. “We are in the hub of an urban setting of Los Angeles, in one of the most recognizable cities on the planet. So we are always a target and that means our kids are a target and our staff are a target,” he said. In the 2024–2025 fiscal year, the district spent $4.8 million on security, including staff. The surveillance system spots multiple threats per day, the district said.
Beverly Hills’ apparatus might seem extreme, but it’s not an outlier. Across the U.S., schools are rolling out similar surveillance systems they hope will keep them free of the horrific and unceasing tide of mass shootings. There have been 49 deaths from gunfire on school property this year. In 2024, there were 59, and in 2023 there were 45, per Everytown for Gun Safety. Between 2000 and 2,022,131 people were killed and 197 wounded at schools in the U.S., most of them children. Given those appalling metrics, allocating a portion of your budget to state of the art AI-powered safety and surveillance tools is a relatively easy decision.

In Current Biology, the Miller Lab at MIT provides new evidence that the brain recruits and controls ad hoc groups of neurons for cognitive tasks by applying brain waves to patches of the cortex.
News: Study:
#neuroscience #cognition #brain
In a new study, MIT researchers tested their theory of Spatial Computing, which holds that the brain recruits and controls ad hoc groups of neurons for cognitive tasks by applying brain waves to patches of the cortex.
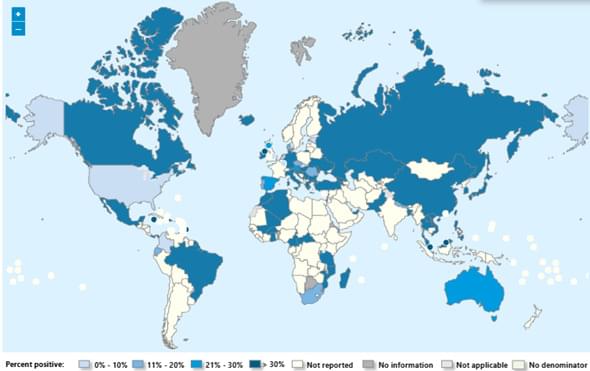
Seasonal influenza activity has increased globally in recent months, and influenza A(H3N2) viruses are predominant. This rise coincides with the onset of winter in the northern hemisphere. Epidemics and outbreaks of seasonal influenza and other circulating respiratory viruses can place significant pressure on healthcare systems. Although global activity remains within expected seasonal ranges, early increases and higher activity than typical at this time of year have been observed in some regions. Seasonal influenza could place significant pressure on healthcare systems even in non-temperate countries. Genetically drifted influenza A(H3N2) viruses, known as subclade K viruses, have been detected in many countries. While data on how well the vaccine works against clinical disease this season are still limited, vaccination is still expected to protect against severe illness and remains one of the most effective public health measures.
Surveillance
Due to the constantly evolving nature of influenza viruses, WHO continues to stress the importance of year-round global surveillance to detect and monitor virological, epidemiological and clinical changes associated with emerging or circulating influenza viruses that may affect human health and timely virus sharing for risk assessment. Countries are encouraged to remain vigilant to the threat of influenza viruses and review any unusual epidemiological patterns.

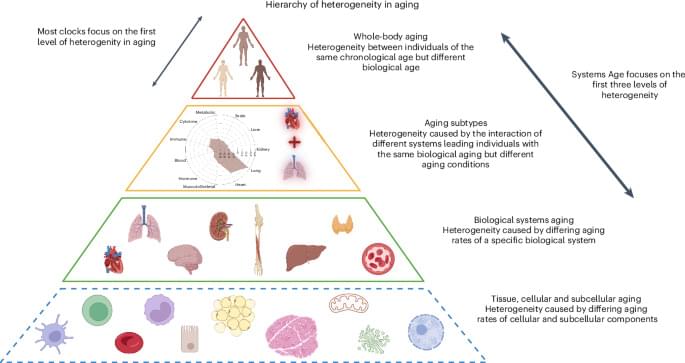
We developed a single blood-based methylation test that estimates biological aging across 11 physiological systems. This multisystem measure predicts mortality and health outcomes more precisely than existing epigenetic clocks, and reveals distinct aging patterns that could guide personalized gerotherapeutic and geroprotective interventions.
Fluid flows mimicking biological flows can be controlled in the lab using a feedback system, which could be useful in robotics and other technologies.
Ordinary fluids can flow when driven by pressure or gravity, but biological fluids, such as those inside cells, generate complex flows through internal sources of chemical energy. Flows of such “active fluids” could be extremely useful in robotics and other areas of engineering, but controlling them remains difficult. Now researchers have demonstrated a method of control that maintains a constant fluid speed despite changing conditions [1]. They hope that the approach can be used to stabilize active-matter flows in future technologies.
Life depends on biochemical processes that respond to many situations while maintaining fixed chemical conditions despite external and internal disruptions. Inspired by this impressive stability, researchers have been developing analogous artificial systems by assembling active fluids from key biochemical components akin to those inside cells. For example, they have created fluids that can generate their own bulk contractions or undergo spontaneous flows. Although these rudimentary designs mimic some features of living matter, researchers have so far failed to demonstrate techniques that keep properties such as fluid flow speeds stable over time.